
A convex lens (of focal length 20 cm) and a concave mirror, having their principal axes along the same line, are kept 80 cm apart from each other. The concave mirror is to the right of the convex lens. When an object is kept at a distance of 30 cm to the left of the lens, it’s image remains at the same position even if the concave mirror is removed. The maximum distance for which this concave mirror, by itself would produce a virtual image would be:
A. 20cm
B. 10cm
C. 25cm
D. 30cm
Answer
523.5k+ views
Hint: We need to know the basic lens formula and the condition for formation of virtual image by a concave mirror. We will first calculate the radius of curvature of the concave mirror. And then we can find the focal length of the concave mirror which will be the answer.
Formula used: $$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$$
Complete step-by-step solution:
The image distance of the lens is given to be u=-30cm. And the focal length f=30 cm. Putting these values in the lens formula,
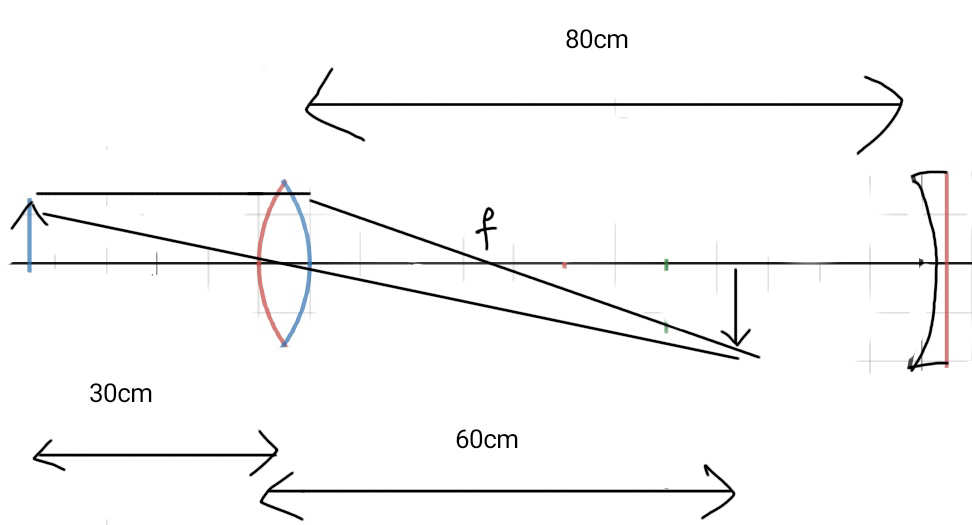
$$v=\dfrac{uf}{f-u}=60 cm $$
Distance of this image from the concave mirror is
$(80-60)=20cm$
Now we know, when an object is kept at a distance of $2f_m$ from a concave mirror, the image is formed at the same position. Here, $f_m$ is the focal length of the mirror. So, we got….
$$2f_m=20cm$$
$\Rightarrow f_m=10cm$
Now, to get a virtual image by the concave mirror, the object distance must be less than focal length. Hence, the required maximum object distance is 10 cm.
Option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The virtual image can be formed by a convex lens or concave mirror only when, object distance is less than focal length. Concave lens and convex mirror can form nothing but virtual images.
Note: Take care of the sign convention of object and mirror distances. The sign will be positive in the direction of light and negative in the opposite direction. Never confuse the radius of curvature of a mirror with its focal length. Their relation is $R=2f_m$. Also know that virtual image is formed by the concave mirror when the object distance is less than the focal length but not equal to the focal length.
Formula used: $$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$$
Complete step-by-step solution:
The image distance of the lens is given to be u=-30cm. And the focal length f=30 cm. Putting these values in the lens formula,

$$v=\dfrac{uf}{f-u}=60 cm $$
Distance of this image from the concave mirror is
$(80-60)=20cm$
Now we know, when an object is kept at a distance of $2f_m$ from a concave mirror, the image is formed at the same position. Here, $f_m$ is the focal length of the mirror. So, we got….
$$2f_m=20cm$$
$\Rightarrow f_m=10cm$
Now, to get a virtual image by the concave mirror, the object distance must be less than focal length. Hence, the required maximum object distance is 10 cm.
Option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The virtual image can be formed by a convex lens or concave mirror only when, object distance is less than focal length. Concave lens and convex mirror can form nothing but virtual images.
Note: Take care of the sign convention of object and mirror distances. The sign will be positive in the direction of light and negative in the opposite direction. Never confuse the radius of curvature of a mirror with its focal length. Their relation is $R=2f_m$. Also know that virtual image is formed by the concave mirror when the object distance is less than the focal length but not equal to the focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




