
A convex lens made of material of refractive index ${\eta _1}$ is kept in a medium of refractive index ${\eta _2}$. A parallel beam of light is incident on the lens. Compare the path of rays of light refracted from the lens when
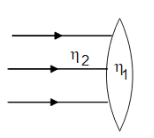
(i) ${\eta _2} > {\eta _1}$
(ii) ${\eta _2} = {\eta _1}$
(iii) ${\eta _2} < {\eta _1}$

Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Light bends whenever it travels into another medium with a different refractive index. This change of direction is caused by a change in speed. Using this concept of different media with different refractive index, we will answer the three given cases.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the ray diagrams for each of the cases separately. Let us first start with the case when
Case 1: ${\eta _2} > {\eta _1}$
This means that the rays are going from denser to rarer medium. Therefore, the rays passing through the lens will diverge which is shown in the diagram below.
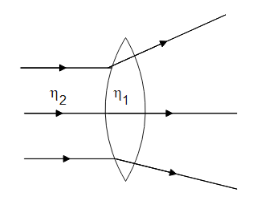
Case 2: ${\eta _2} = {\eta _1}$
There is no change in the medium and therefore no bending of light will occur and the rays will pass straight through the medium.
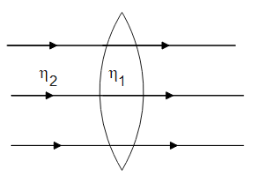
Case 3: ${\eta _2} < {\eta _1}$
This means the rays are going from a rarer medium to a denser medium and thus the rays passing through the rays will converge as shown in the figure.
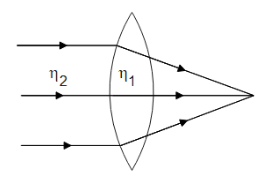
Note:
We have studied the characteristic of the rays passing from one medium to another when the refractive indexes are equal, the refractive index of the lens is more than the refractive index of the medium, and the refractive index of the lens is less than the refractive index of the material.
Real time example: When light travels from air into water, it slows down, causing it to continue to travel at a different angle or direction from its original path. This bending of light is called Refraction. We should confuse refraction with reflection. The refractive index is the measure of how fast light travels through a material. It tells us about the optical density of the medium.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the ray diagrams for each of the cases separately. Let us first start with the case when
Case 1: ${\eta _2} > {\eta _1}$
This means that the rays are going from denser to rarer medium. Therefore, the rays passing through the lens will diverge which is shown in the diagram below.

Case 2: ${\eta _2} = {\eta _1}$
There is no change in the medium and therefore no bending of light will occur and the rays will pass straight through the medium.

Case 3: ${\eta _2} < {\eta _1}$
This means the rays are going from a rarer medium to a denser medium and thus the rays passing through the rays will converge as shown in the figure.

Note:
We have studied the characteristic of the rays passing from one medium to another when the refractive indexes are equal, the refractive index of the lens is more than the refractive index of the medium, and the refractive index of the lens is less than the refractive index of the material.
Real time example: When light travels from air into water, it slows down, causing it to continue to travel at a different angle or direction from its original path. This bending of light is called Refraction. We should confuse refraction with reflection. The refractive index is the measure of how fast light travels through a material. It tells us about the optical density of the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




