
What is a converging lens?
A.lens which directs light to a point at the optical centre or axis of the lens
B.lens which directs light away from point at the optical centre or axis of the lens
C.lens which directs light to a point at the focal point or axis of the lens
D.lens which directs light away from the focal point at the optical centre or axis of the lens
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Converging lenses are those lenses which converge the light rays coming towards them, whereas diverging lenses are lenses which diverge the rays coming towards them. Converging lenses form a real image, whereas diverging lenses form a virtual image
Complete answer:
A convex lens is thicker at the centre than at the edges. A convex lens is basically a converging lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens, the refracted rays converge at one point, which is called the principal focus. The distance between the principal focus and the centre of the lens is called the focal length.
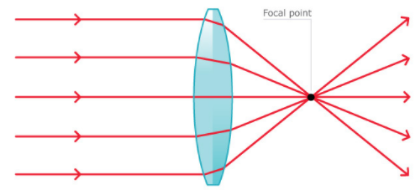
The properties of the converging lens:
- Any incident ray travelling parallel to the principal axis of a converging lens will refract through the lens and travel through the focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
- Any incident ray travelling through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and travel parallel to the principal axis.
- An incident ray that passes through the centre of the lens will, in effect, continue in the same direction that it had when it entered the lens.
The correct answer is A.
Note:
The diverging lenses always produce the virtual images, and converging lenses are capable of producing both real and virtual images. The real images are produced when the object is located at a distance greater than one focal length from the lens. When refracted rays diverge, a virtual image is formed.
Complete answer:
A convex lens is thicker at the centre than at the edges. A convex lens is basically a converging lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens, the refracted rays converge at one point, which is called the principal focus. The distance between the principal focus and the centre of the lens is called the focal length.

The properties of the converging lens:
- Any incident ray travelling parallel to the principal axis of a converging lens will refract through the lens and travel through the focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
- Any incident ray travelling through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and travel parallel to the principal axis.
- An incident ray that passes through the centre of the lens will, in effect, continue in the same direction that it had when it entered the lens.
The correct answer is A.
Note:
The diverging lenses always produce the virtual images, and converging lenses are capable of producing both real and virtual images. The real images are produced when the object is located at a distance greater than one focal length from the lens. When refracted rays diverge, a virtual image is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




