
A constant voltage is applied between two ends of a metallic wire. If the length is halved and the radius of the wire is doubled, the rate of heat developed in the wire will be:
A. Increased 8 times
B. Doubled
C. Halved
D. Unchanged
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Heat developed in a wire is inversely proportional to length of the wire and directly proportional to its radius. This relationship will help us determine the ratio of the heat developed in the two conditions.
Formula used:
Power/Heat developed: $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Where $P$ is the power developed in the wire (in this case heat energy) and is expressed in Joules \[(J)\], $V$ Is the voltage applied across the ends of the wire and is expressed Volts \[(V)\] and $R$ is the resistance applied in the wire and is expressed in Ohms $(\Omega )$.
Resistance applied to the wire: $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}$
Where $l$ is the length of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$, $A$ is the area of the wire and is expressed in meter squares $({m^2})$ and $r$ is the radius of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine the rate of heat developed in the metallic wire, we need to compare the two conditions in which it is given in the question: constant length and radius and halved length and doubled radius. Taking a ratio of the two will provide us with the change in heat energy and no real time values are not given.
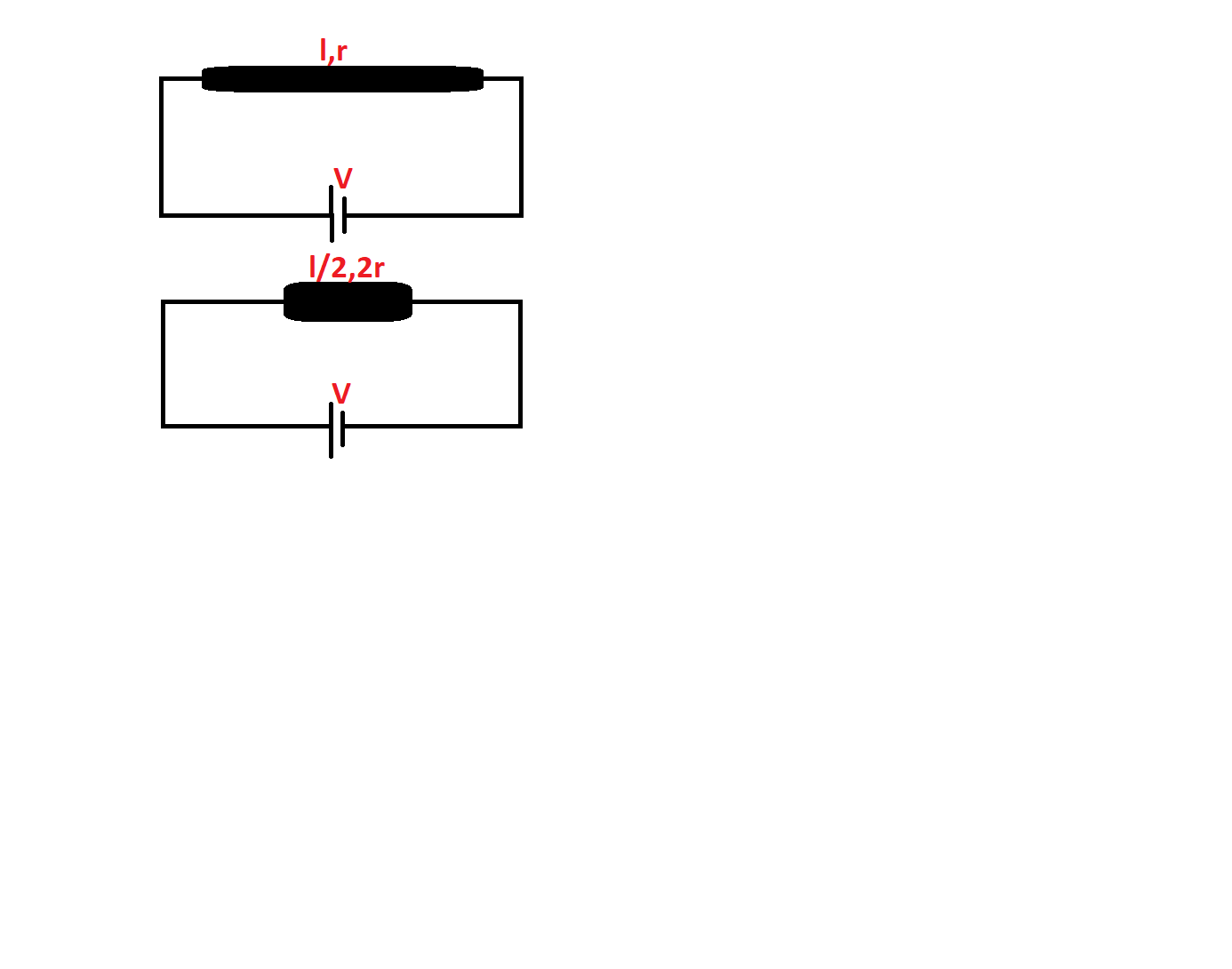
We know the formula for the calculation of resistance of a wire. It is $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}$.
We also know the formula for power developed in a wire. This can be equated to heat energy developed. It is given as $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$.
Substituting the value of resistance in the power equation we get the following relation:
$
P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} \\
\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} \\
$
This is the value of power in the original state of the wire.
Now, it is given that length is halved and radius is doubled. That is, $\dfrac{l}{2}$ is the new length and $2r$ is the new radius.
Substituting these new values of $l$ and $r$ in the power equation we get,
$
P = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {{(2r)}^2}}}{{\rho (l/2)}} \\
\Rightarrow P = 8(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}}) \\
$
On dividing the original heat value to the new heat value we will get the rate of heat generation.
Therefore,
$
P = 8(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}})/(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}}) \\
\Rightarrow P = 8 \\
$
Therefore, we determined the heat generation on halving the length and doubling the radius to be eight times than the original value. That means, the rate of heat developed in the wire increased eight times.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
It is of utmost importance that doubling the radius is not taken in the sense of doubling the power. Also, noticing the variations in wire dimensions given in the question is essential to prevent errors while calculation.
Formula used:
Power/Heat developed: $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Where $P$ is the power developed in the wire (in this case heat energy) and is expressed in Joules \[(J)\], $V$ Is the voltage applied across the ends of the wire and is expressed Volts \[(V)\] and $R$ is the resistance applied in the wire and is expressed in Ohms $(\Omega )$.
Resistance applied to the wire: $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}$
Where $l$ is the length of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$, $A$ is the area of the wire and is expressed in meter squares $({m^2})$ and $r$ is the radius of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine the rate of heat developed in the metallic wire, we need to compare the two conditions in which it is given in the question: constant length and radius and halved length and doubled radius. Taking a ratio of the two will provide us with the change in heat energy and no real time values are not given.

We know the formula for the calculation of resistance of a wire. It is $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A} = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{{\pi {r^2}}}$.
We also know the formula for power developed in a wire. This can be equated to heat energy developed. It is given as $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$.
Substituting the value of resistance in the power equation we get the following relation:
$
P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} \\
\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} \\
$
This is the value of power in the original state of the wire.
Now, it is given that length is halved and radius is doubled. That is, $\dfrac{l}{2}$ is the new length and $2r$ is the new radius.
Substituting these new values of $l$ and $r$ in the power equation we get,
$
P = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}} = \dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {{(2r)}^2}}}{{\rho (l/2)}} \\
\Rightarrow P = 8(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}}) \\
$
On dividing the original heat value to the new heat value we will get the rate of heat generation.
Therefore,
$
P = 8(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}})/(\dfrac{{{V^2} \times \pi {r^2}}}{{\rho l}}) \\
\Rightarrow P = 8 \\
$
Therefore, we determined the heat generation on halving the length and doubling the radius to be eight times than the original value. That means, the rate of heat developed in the wire increased eight times.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
It is of utmost importance that doubling the radius is not taken in the sense of doubling the power. Also, noticing the variations in wire dimensions given in the question is essential to prevent errors while calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




