
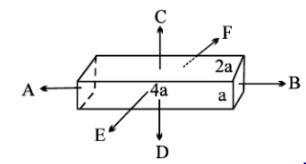
A conductor with rectangular cross section has dimensions $\left( {4a \times 2a \times a} \right)$ as shown in figure. Resistance across $AB$ is $x$, across $CD$ is $y$ and across $EF$ is $Z$.
(A) $x = y = z$
(B) $x > y > z$
(C) $y > x > z$
(D) $x > z > y$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:Useful formula: Use the relation between the resistance and resistivity to calculate the value of resistance at the point $x,\,y$ and $z$. Substitute the values of length and cross sectional area given in the formula. Compare the values of obtained resistance of $x,\,y$ and $z$to find the answer for this question.
Formulae Used:
Resistance formula is
$R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
Where $R$ is the resistance of the conductor, $\rho $ is the resistivity of the conductor, $l$ is the length of the conductor and $A$ is the cross sectional area of the conductor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given data from the question are
Resistance across $AB$ is $x$
Resistance across $CD$ is $y$
Resistance across $EF$ is $z$
By using the resistance formula,
The resistance across $x$ is $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$. Cross sectional area at $x$ is $4a \times a$.
Substituting the values at the above equation
$x = \dfrac{{\rho \left( {4a} \right)}}{{2a \times a}}$
$x = \dfrac{{\rho \left( {2a} \right)}}{{{a^2}}}$
By simplifying the above equation,
$x = \dfrac{{2\rho }}{a}$
Cross sectional area at $y$ is $4a \times 2a$.
Similarly, finding the values of resistance at $y$.
$y = \dfrac{\rho }{{8a}}$
Cross sectional area at $z$ is $4a \times a$.
In the same way, finding the values of resistance at $z$.
$z = \dfrac{\rho }{{2a}}$
From the obtained values of $x,\,y$ and $z$, it is known that $x > z > y$.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note:- Remember that the cross sectional area at a particular point is calculated by the sectional area which is obtained by a sliced section of the considered object. For example: the cross sectional area at $x$ is calculated as the area of the cross section of AB which is $2a \times a$.
Formulae Used:
Resistance formula is
$R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$
Where $R$ is the resistance of the conductor, $\rho $ is the resistivity of the conductor, $l$ is the length of the conductor and $A$ is the cross sectional area of the conductor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given data from the question are
Resistance across $AB$ is $x$
Resistance across $CD$ is $y$
Resistance across $EF$ is $z$
By using the resistance formula,
The resistance across $x$ is $R = \dfrac{{\rho l}}{A}$. Cross sectional area at $x$ is $4a \times a$.
Substituting the values at the above equation
$x = \dfrac{{\rho \left( {4a} \right)}}{{2a \times a}}$
$x = \dfrac{{\rho \left( {2a} \right)}}{{{a^2}}}$
By simplifying the above equation,
$x = \dfrac{{2\rho }}{a}$
Cross sectional area at $y$ is $4a \times 2a$.
Similarly, finding the values of resistance at $y$.
$y = \dfrac{\rho }{{8a}}$
Cross sectional area at $z$ is $4a \times a$.
In the same way, finding the values of resistance at $z$.
$z = \dfrac{\rho }{{2a}}$
From the obtained values of $x,\,y$ and $z$, it is known that $x > z > y$.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note:- Remember that the cross sectional area at a particular point is calculated by the sectional area which is obtained by a sliced section of the considered object. For example: the cross sectional area at $x$ is calculated as the area of the cross section of AB which is $2a \times a$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




