
A conductor ab of arbitrary shape carries current \[I\]flowing from b to a. The length vector \[\overrightarrow {ab} \]is oriented from a to b. The force \[\overrightarrow F \] experienced by the conductor in a uniform magnetic field \[\overrightarrow B \] is.
(A) \[\overrightarrow F = - I(\overrightarrow {ab} \times B)\]
(B) \[\overrightarrow F = I(B \times \overrightarrow {ab} )\]
(C) \[\overrightarrow F = - I(\overrightarrow {ba} \times B)\]
(D) All of these
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:We should know the formula for force on a current-carrying wire.
We should know the identity of\[(A \times B) = - (B \times A)\].We should know the reversal of a vector \[\overrightarrow {ab} = - \overrightarrow {ba} \].
Complete step by step answer:
A magnetic field is a vector quantity that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetized materials. A charge that is moving in a magnetic field experiences a force normal to its velocity and the magnetic field. Lorentzforce, the force exerted on a charged particle q moving with velocity v through an electric field E and magnetic field B. The entire electromagnetic force F on the charged particle is called the Lorentz force (after the Dutch physicist Hendrik A. Lorentz) and is given by
\[F\; = \;qE\; + \;\left( {qv\; \times \;B} \right)\]
Let us consider a wire of length ab, and a current is passing from b to a.
Then force experienced on the wire is,
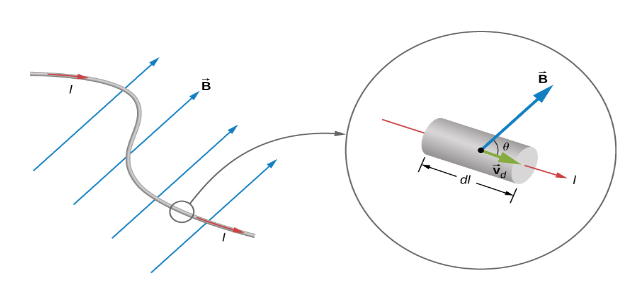
We know that,
\[dF = I(dl \times B)\]
By integrating this we can find the value of F.
\[\int {dF} = \int\limits_b^a {I(dl \times B)} \]
\[\int {dF} = I\int\limits_b^a {(dl \times B)} \]
\[F = I(ba \times B)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (1)
So Option (C) is correct.
We know that \[\overrightarrow {ab} = - \overrightarrow {ba} \] . - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (2)
By rearranging (1) using (2)
We get,
\[F = I(ba \times B) = - I(ab \times B)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (3)
Hence Option (A) is correct.
Again we know that \[(A \times B) = - (B \times A)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (4)
By rearranging (3) using (4),
we get,
So,
\[\begin{gathered}
F = - I(ab \times B) \\
= - I( - B \times ab) \\
= I(B \times ab) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Since options (A), (B), (C) are correct, hence the correct Option is (D)
Note: You should be aware of vector identities.If any two options are correct, then no need to find the other one since there is an option of all are correct. ( you can save time)
You should also be aware and careful about sign conversion.
We should know the identity of\[(A \times B) = - (B \times A)\].We should know the reversal of a vector \[\overrightarrow {ab} = - \overrightarrow {ba} \].
Complete step by step answer:
A magnetic field is a vector quantity that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetized materials. A charge that is moving in a magnetic field experiences a force normal to its velocity and the magnetic field. Lorentzforce, the force exerted on a charged particle q moving with velocity v through an electric field E and magnetic field B. The entire electromagnetic force F on the charged particle is called the Lorentz force (after the Dutch physicist Hendrik A. Lorentz) and is given by
\[F\; = \;qE\; + \;\left( {qv\; \times \;B} \right)\]
Let us consider a wire of length ab, and a current is passing from b to a.
Then force experienced on the wire is,

We know that,
\[dF = I(dl \times B)\]
By integrating this we can find the value of F.
\[\int {dF} = \int\limits_b^a {I(dl \times B)} \]
\[\int {dF} = I\int\limits_b^a {(dl \times B)} \]
\[F = I(ba \times B)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (1)
So Option (C) is correct.
We know that \[\overrightarrow {ab} = - \overrightarrow {ba} \] . - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (2)
By rearranging (1) using (2)
We get,
\[F = I(ba \times B) = - I(ab \times B)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (3)
Hence Option (A) is correct.
Again we know that \[(A \times B) = - (B \times A)\]- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (4)
By rearranging (3) using (4),
we get,
So,
\[\begin{gathered}
F = - I(ab \times B) \\
= - I( - B \times ab) \\
= I(B \times ab) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Since options (A), (B), (C) are correct, hence the correct Option is (D)
Note: You should be aware of vector identities.If any two options are correct, then no need to find the other one since there is an option of all are correct. ( you can save time)
You should also be aware and careful about sign conversion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




