
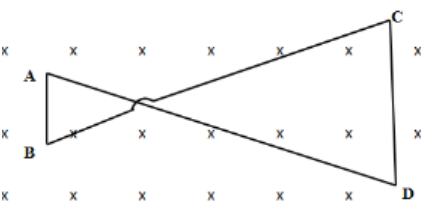
A conducting wire frame is placed in a magnetic field, which is directed into paper. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. The directions of induced current in wires AB and CD are?
A. B to A and D to C
B. A to B and C to D
C. A to B and D to C
D. B to A and C to D

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: In the problem, it is given that the magnetic field is directed into paper and is increasing at a constant rate. Therefore, the magnetic flux will also increase at a constant rate and there will be an induced emf to oppose increasing magnetic flux. Due to this an induced current will be generated in the loop. The induced current will oppose the magnetic flux and magnetic field. If this magnetic field needs to be decreased, then another magnetic field needs to be applied that is directed outwards the paper.
Formula Used:
The magnetic flux is given by: \[d\phi = \overrightarrow B .d\overrightarrow A \]
where, \[\overrightarrow B \] is the magnetic field, \[d\overrightarrow A \] is the area element and \[\phi \] is the magnetic flux.
The Lenz’s law is given by: \[E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\]
where, \[E\] is the induced emf, \[d\phi \] is the change in magnetic flux and \[dt\] is a small time interval.
Complete step by step answer:
The dot product of the magnetic field \[\overrightarrow B \]and the area element \[d\overrightarrow A \] is called magnetic flux. The magnetic flux is denoted by \[\phi \]. If \[\overrightarrow B \]is the magnetic field through the area element \[d\overrightarrow A \].Then the flux through the area is given by
\[d\phi = \overrightarrow B .d\overrightarrow A \]
When the magnetic flux linked with the circuit changes, emf set up in the circuit is called induced emf. The current due to induced emf is called induced current. The Lenz’s law states that induced opposes the cause that produces it. If \[d\phi \] is the change in magnetic flux during time \[dt\], then the Lenz’s law is given by
\[E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\]
In the problem, it is given that the magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. Therefore, the magnetic flux will also increase causing an induced emf to oppose increasing magnetic flux. Therefore, the magnetic flux will decrease. Hence, an induced current will be generated in the loop.This can only happen if there is a magnetic field directed outside the paper. And, then the current in the loop will flow in an anticlockwise direction. The direction of the current will be \[A \to D \to C \to B \to A\]. In the loop \[ADCB\], direction of current in segment \[AB\] is from \[B \to A\] and that segment \[CD\] is from \[D \to C\].
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:The magnetic flux that tends to increase due to the magnetic field that is directed inside the paper. If the induced current is generated in opposing this magnetic flux then according to the Right Hand Thumb rule, that current should flow in an anticlockwise direction. That is, it will form a loop as \[A \to D \to C \to B \to A\].
The negative sign in Lenz’s law indicates that the induced emf opposes the change in magnetic field. The induced emf lasts as long as the magnetic field continues.
Formula Used:
The magnetic flux is given by: \[d\phi = \overrightarrow B .d\overrightarrow A \]
where, \[\overrightarrow B \] is the magnetic field, \[d\overrightarrow A \] is the area element and \[\phi \] is the magnetic flux.
The Lenz’s law is given by: \[E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\]
where, \[E\] is the induced emf, \[d\phi \] is the change in magnetic flux and \[dt\] is a small time interval.
Complete step by step answer:
The dot product of the magnetic field \[\overrightarrow B \]and the area element \[d\overrightarrow A \] is called magnetic flux. The magnetic flux is denoted by \[\phi \]. If \[\overrightarrow B \]is the magnetic field through the area element \[d\overrightarrow A \].Then the flux through the area is given by
\[d\phi = \overrightarrow B .d\overrightarrow A \]
When the magnetic flux linked with the circuit changes, emf set up in the circuit is called induced emf. The current due to induced emf is called induced current. The Lenz’s law states that induced opposes the cause that produces it. If \[d\phi \] is the change in magnetic flux during time \[dt\], then the Lenz’s law is given by
\[E = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\]
In the problem, it is given that the magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. Therefore, the magnetic flux will also increase causing an induced emf to oppose increasing magnetic flux. Therefore, the magnetic flux will decrease. Hence, an induced current will be generated in the loop.This can only happen if there is a magnetic field directed outside the paper. And, then the current in the loop will flow in an anticlockwise direction. The direction of the current will be \[A \to D \to C \to B \to A\]. In the loop \[ADCB\], direction of current in segment \[AB\] is from \[B \to A\] and that segment \[CD\] is from \[D \to C\].
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:The magnetic flux that tends to increase due to the magnetic field that is directed inside the paper. If the induced current is generated in opposing this magnetic flux then according to the Right Hand Thumb rule, that current should flow in an anticlockwise direction. That is, it will form a loop as \[A \to D \to C \to B \to A\].
The negative sign in Lenz’s law indicates that the induced emf opposes the change in magnetic field. The induced emf lasts as long as the magnetic field continues.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




