
A conducting rod of length $l$ and mass m is moving down a smooth inclined plane of inclination $\theta $ with constant velocity $v$. A current $i$ is flowing in the conductor in a direction perpendicular to paper inwards. The magnitude of field $B$ is:(Given acceleration due to gravity $ = g$)
A. $\dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\sin \theta $
B. $\dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\tan \theta $
C. $\dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\cos \theta $
D. $\dfrac{{mg}}{{il\sin \theta }}$

Answer
479.7k+ views
Hint: Determine the direction of all the forces acting on the conducting rod.The velocity of the rod is constant i.e., acceleration is zero. Therefore, the net force acting on the rod is zero.The magnetic force on the conducting rod is ${F_m} = ilB\sin \theta $. Where, $\theta $ is the angle between the length $l$ and magnetic field $\left( {\overrightarrow B } \right)$. $i$ is the current flowing through the rod.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s redraw the diagram showing all the forces acting on the rod.
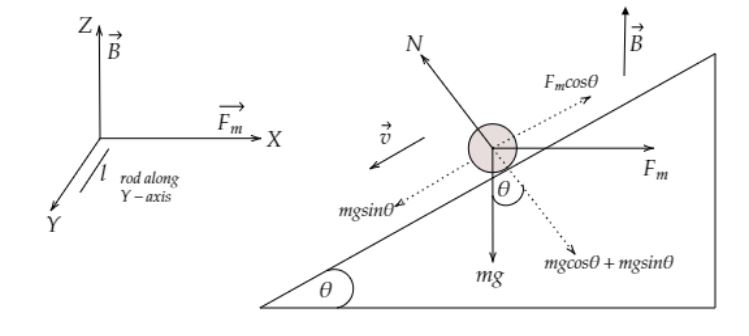
From the above diagram, the magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ is in the Z-axis direction.The length $l$ of the rod is in Y-axis direction.It is given that the current $i$ is flowing in the conductor (rod) in a direction perpendicular to paper inwards i.e. negative Y-axis direction.
Apply the Fleming’s Left-hand rule, the magnetic force ${\overrightarrow F _m}$ will be in positive X-axis direction.The gravity $mg$ will act on the rod vertically downward i.e., negative Z-axis.Now resolving both $mg$ and ${\overrightarrow F _m}$ into different components. The normal force $N$ acting on the body will be balanced by the $mg\cos \theta + {F_m}\sin \theta $. Since the rod is moving with constant velocity, the net force acting on the rod must be zero. So, we got
${F_m}\cos \theta = mg\sin \theta $ …… (1)
But we know that the magnitude of magnetic force ${F_m} = ilB\sin {90^0}$
Or ${F_m} = ilB$
Substitute the value of ${F_m}$ in the equation (1).
$ilB\cos \theta = mg\sin \theta $
Further simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
$ \therefore B = \dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\tan \theta $
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: To determine the direction of magnetic force acting on the rod , apply the Fleming’s left hand rule. Stretch the forefinger, middle finger and thumb of your left hand in mutually perpendicular directions. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field, middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb gives the direction of magnetic force on the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s redraw the diagram showing all the forces acting on the rod.

From the above diagram, the magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ is in the Z-axis direction.The length $l$ of the rod is in Y-axis direction.It is given that the current $i$ is flowing in the conductor (rod) in a direction perpendicular to paper inwards i.e. negative Y-axis direction.
Apply the Fleming’s Left-hand rule, the magnetic force ${\overrightarrow F _m}$ will be in positive X-axis direction.The gravity $mg$ will act on the rod vertically downward i.e., negative Z-axis.Now resolving both $mg$ and ${\overrightarrow F _m}$ into different components. The normal force $N$ acting on the body will be balanced by the $mg\cos \theta + {F_m}\sin \theta $. Since the rod is moving with constant velocity, the net force acting on the rod must be zero. So, we got
${F_m}\cos \theta = mg\sin \theta $ …… (1)
But we know that the magnitude of magnetic force ${F_m} = ilB\sin {90^0}$
Or ${F_m} = ilB$
Substitute the value of ${F_m}$ in the equation (1).
$ilB\cos \theta = mg\sin \theta $
Further simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
$ \therefore B = \dfrac{{mg}}{{il}}\tan \theta $
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: To determine the direction of magnetic force acting on the rod , apply the Fleming’s left hand rule. Stretch the forefinger, middle finger and thumb of your left hand in mutually perpendicular directions. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field, middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb gives the direction of magnetic force on the conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




