
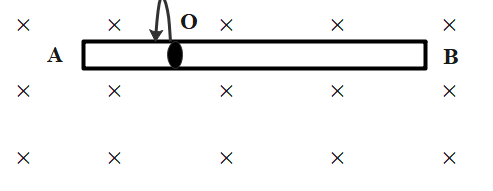
A conducting rod AC of length 4l is rotated about a point O in a uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow{B}$direction into the paper AO=l and OC=3l. Then
A. ${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{O}}=\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2}$
B. ${{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}=\dfrac{7}{2}B\omega {{l}^{2}}$
C. ${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=4B\omega {{l}^{2}}$
D. ${{V}_{C}}-{{V}_{O}}=\dfrac{9}{2}B\omega {{l}^{2}}$

Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: When a conducting rod is placed in a magnetic field B then it experiences a certain force. The rotating rod will contain some amount of emf. Thus, the potential difference between two points can be calculated.
Complete answer:
The potential difference between point O and A is \[{{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}\].
The potential difference between point O and C is \[{{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}\].
Thus, the potential difference between A and C is,
${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=({{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}})-({{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}).......(i)$
For a rotating rod, the electromotive force (emf) is given as,
$e=\dfrac{BVl}{2}$
Since, the angular velocity $(\omega )$ is
$\omega =V/l$
Rewriting the equations, we get,
$e=\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2}$
Thus, to calculate total emf for the length, we write,
$de=B\omega l.dl$
For the potential difference between A and O,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}=\int\limits_{0}^{l}{B\omega l.dl} \\
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}=\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
For the potential difference between O and C,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}=\int\limits_{0}^{3l}{B\omega l.dl} \\
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}=\dfrac{9B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the potential difference between the point A and C from equation (i),
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=\dfrac{9B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=4B\omega {{l}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the option C is correct.
Note:
The potential difference depends on the length of the conducting rod. When a conducting rod is placed in a magnetic field then the direction of the flow of electrons and the direction of magnetic field turns to rod producing a torque which results in an electromotive force.
Complete answer:
The potential difference between point O and A is \[{{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}\].
The potential difference between point O and C is \[{{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}\].
Thus, the potential difference between A and C is,
${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=({{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}})-({{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}).......(i)$
For a rotating rod, the electromotive force (emf) is given as,
$e=\dfrac{BVl}{2}$
Since, the angular velocity $(\omega )$ is
$\omega =V/l$
Rewriting the equations, we get,
$e=\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2}$
Thus, to calculate total emf for the length, we write,
$de=B\omega l.dl$
For the potential difference between A and O,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}=\int\limits_{0}^{l}{B\omega l.dl} \\
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{A}}=\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
For the potential difference between O and C,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}=\int\limits_{0}^{3l}{B\omega l.dl} \\
& {{V}_{O}}-{{V}_{C}}=\dfrac{9B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the potential difference between the point A and C from equation (i),
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=\dfrac{9B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{B\omega {{l}^{2}}}{2} \\
& {{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{C}}=4B\omega {{l}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the option C is correct.
Note:
The potential difference depends on the length of the conducting rod. When a conducting rod is placed in a magnetic field then the direction of the flow of electrons and the direction of magnetic field turns to rod producing a torque which results in an electromotive force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




