
A conducting loop in the shape of a right angled isosceles triangle of height $10cm$ is kept such that the ${90^ \circ }$ vertex is very close to an infinitely long conducting wire (see the figure). The wire is electrically insulated from the loop . The hypotenuse of the triangle is parallel to the wire. The current in the triangular loop is in the counter clockwise direction and increases at a constant rate of $10A/s$ Which of the following statements(s) is(are) true?
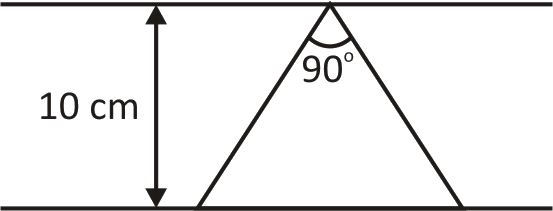
A. There is a repulsive force between the wire and the loop
B. If the loop is rotated at a constant angular speed about the wire, an additional emf of $(\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi })$ volt is inducted in the wire.
C. The magnitude of induced emf in the wire is $(\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi })$ volt
D. The induced current in the wire is in opposite direction to the current along the hypotenuse

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Find the flux through the wire assuming assuming some value of current and rate of change of current is given using that find mutual inductance of the system once you know the mutual inductance use faraday's law to find the magnitude of induced emf and use lenz's law to find the direction of induced emf or induced current.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's take a strip of width dx in the triangle perpendicular to the length of infinite wire
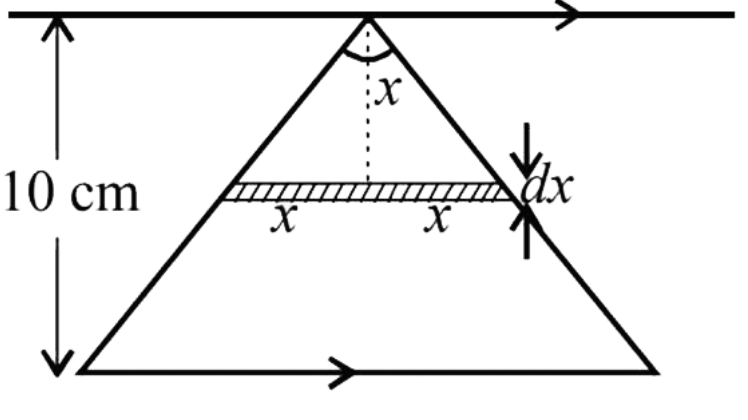
Now,
The flux passing through triangular wire when i current is passing through the infinite wire is
$\phi = \int {B.dA} = \int\limits_0^{0.1} {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{2\pi x}}} \times 2x.dx$ where 0.1 is the height of triangle
$ \Rightarrow \phi = \int\limits_0^{0.1} {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{2\pi x}}} \times 2x.dx = \left[ {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{\pi }x} \right]_0^{0.1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{10\pi }}$
We can also write flux as $\phi = Mi$
Therefore, $M = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }}$
Rate of change of current is given as $\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = 10A/s$
So induced emf $\varepsilon = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
$ \Rightarrow \varepsilon = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }} \times 10 = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }$
If loop rotates then emf is produced which must be opposed and in order to do so force on the loop should be outwards therefore,
There will be repulsion between loop and wire and direction of current will be the same as the direction of current in hypotenuse.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and C”.
Note:
Here finding the value of mutual inductance is crucial and to do that you will have to use integration there is no other shortcut way once you know the value of mutual inductance then simply use faraday's law and lenz's law to get to the answer.The hypotenuse of the triangle is parallel to the wire.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's take a strip of width dx in the triangle perpendicular to the length of infinite wire

Now,
The flux passing through triangular wire when i current is passing through the infinite wire is
$\phi = \int {B.dA} = \int\limits_0^{0.1} {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{2\pi x}}} \times 2x.dx$ where 0.1 is the height of triangle
$ \Rightarrow \phi = \int\limits_0^{0.1} {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{2\pi x}}} \times 2x.dx = \left[ {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{\pi }x} \right]_0^{0.1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}i}}{{10\pi }}$
We can also write flux as $\phi = Mi$
Therefore, $M = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }}$
Rate of change of current is given as $\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} = 10A/s$
So induced emf $\varepsilon = M\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}$
$ \Rightarrow \varepsilon = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }} \times 10 = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }$
If loop rotates then emf is produced which must be opposed and in order to do so force on the loop should be outwards therefore,
There will be repulsion between loop and wire and direction of current will be the same as the direction of current in hypotenuse.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and C”.
Note:
Here finding the value of mutual inductance is crucial and to do that you will have to use integration there is no other shortcut way once you know the value of mutual inductance then simply use faraday's law and lenz's law to get to the answer.The hypotenuse of the triangle is parallel to the wire.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




