
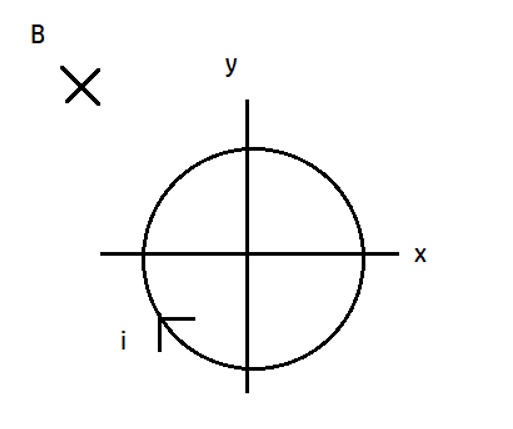
A conducting loop carrying a current i is placed in a uniform magnetic field pointing into the plane of the paper as shown. The loop will have a tendency to
(a) Contract
(b) Expand
(c) Move towards + ve x-axis
(d) Move towards – ve x-axis

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: We know a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a magnetic force, so this conductor will also experience the force. The figure shows a metallic frame of a conductor in a magnetic field directed into the page. The current is flowing in the conductor and the direction of current is shown by the arrows.
Complete Step by step answer: The formula for the force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is \[\overrightarrow{F}=i(\overrightarrow{l}\times \overrightarrow{B})\]
First of all we need to know the direction of the length, since, it is a circle at any point to find the direction of length we draw a tangent at that point and if we apply \[\overrightarrow{F}=i(\overrightarrow{l}\times \overrightarrow{B})\]then at every point the direction of force is radially outwards. Thus, the overall effect will be the expansion.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional information: This is an example of how to use the vector addition and what are the special cases when the vectors are perpendicular to each other or parallel to each other, here force is a vector quantity. While adding or subtracting the two or more vectors we have to keep in mind what is the angle between them. This explains the vector law of addition.
Note: The point to keep is that the direction of magnetic force will be the cross product of length and the field. Fleming’s left-hand rule is used here to find out the direction of force on each edge.
Complete Step by step answer: The formula for the force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is \[\overrightarrow{F}=i(\overrightarrow{l}\times \overrightarrow{B})\]
First of all we need to know the direction of the length, since, it is a circle at any point to find the direction of length we draw a tangent at that point and if we apply \[\overrightarrow{F}=i(\overrightarrow{l}\times \overrightarrow{B})\]then at every point the direction of force is radially outwards. Thus, the overall effect will be the expansion.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional information: This is an example of how to use the vector addition and what are the special cases when the vectors are perpendicular to each other or parallel to each other, here force is a vector quantity. While adding or subtracting the two or more vectors we have to keep in mind what is the angle between them. This explains the vector law of addition.
Note: The point to keep is that the direction of magnetic force will be the cross product of length and the field. Fleming’s left-hand rule is used here to find out the direction of force on each edge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




