
A concave mirror produces a real image of half of the size of an object placed at \[60cm\] in front of it. Where the object should be placed to obtain a virtual image of double the size of the object?
Answer
529.1k+ views
Hint: Here the magnification formula should be used to find out the answer. Virtual images are usually formed when the object is placed in front of the lens. These details should be used to solve this problem.
Complete step by step answer:
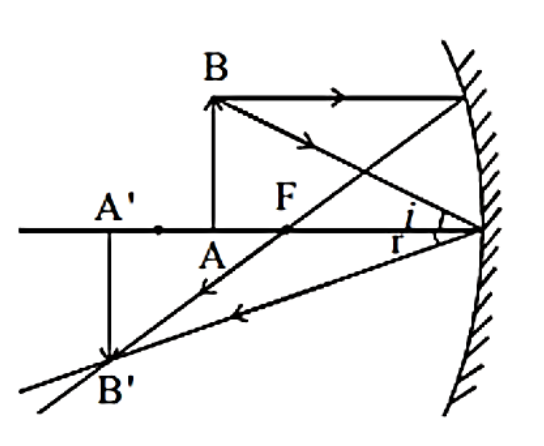
First of all let us discuss the real image and virtual image. The real image is the image produced when rays of light meet at a specific point after the process of reflection or refraction is called a real image. In other ways virtual images are the images formed when rays of light appear to be met at a point is called a virtual image. This is possible when the diverging rays are made an extension and get to meet at a point. As we all know the real images are always inverted. And also virtual images are upright in nature. In this question
The initial distance to the object is $u=-60cm$
Magnification is given by
$m=\dfrac{-f}{u-f}$
Magnification (m) = -1/2 (as both obj and image are real)
$-\dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{-f}{-60-f}$
From the above equation we will get,
$f=-20cm$
Let the final object distance be ${{u}^{1}}$ and magnification can be written as
$m=\dfrac{-f}{{{u}^{1}}-f}$
As the magnification is 2.
Then
$2=\dfrac{20}{{{u}^{1}}+20}$
Therefore the object distance will become,
${{u}^{1}}=10cm$
So, the correct answer is 10cm.
Note: A real image is defined as the collection of points of light rays which is coming from an object in which the rays are converging in nature. A virtual image is defined as the group of points of light rays which is coming from an object in which the rays are diverging in nature.
Complete step by step answer:

First of all let us discuss the real image and virtual image. The real image is the image produced when rays of light meet at a specific point after the process of reflection or refraction is called a real image. In other ways virtual images are the images formed when rays of light appear to be met at a point is called a virtual image. This is possible when the diverging rays are made an extension and get to meet at a point. As we all know the real images are always inverted. And also virtual images are upright in nature. In this question
The initial distance to the object is $u=-60cm$
Magnification is given by
$m=\dfrac{-f}{u-f}$
Magnification (m) = -1/2 (as both obj and image are real)
$-\dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{-f}{-60-f}$
From the above equation we will get,
$f=-20cm$
Let the final object distance be ${{u}^{1}}$ and magnification can be written as
$m=\dfrac{-f}{{{u}^{1}}-f}$
As the magnification is 2.
Then
$2=\dfrac{20}{{{u}^{1}}+20}$
Therefore the object distance will become,
${{u}^{1}}=10cm$
So, the correct answer is 10cm.
Note: A real image is defined as the collection of points of light rays which is coming from an object in which the rays are converging in nature. A virtual image is defined as the group of points of light rays which is coming from an object in which the rays are diverging in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




