
A concave mirror of focal length $10{\text{ }}cm$. A square wire of side $3{\text{ }}cm$ is placed $23{\text{ }}cm$ away from the mirror. The centre of the square lies on the principal axis. What is the area enclosed by the image?
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: For this type of question, we have to find the unknown variable from the mirror formula. Mirror formula is $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$. Here, $u$ is the object distance, $v$ is the image distance and $f$ is the focal length of the mirror.
Here, the unknown variable is image distance. Then after finding the image distance, we have to find the magnification of the image. This magnification will also increase the side of the image of the wire which will eventually lead us to find the area that the image encloses.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the question that the focal length of a concave mirror is $10{\text{ }}cm$. A square wire of side $3{\text{ }}cm$ is placed $23{\text{ }}cm$ away from the mirror which is placed on the principal axis. We have to find the area enclosed by the image.
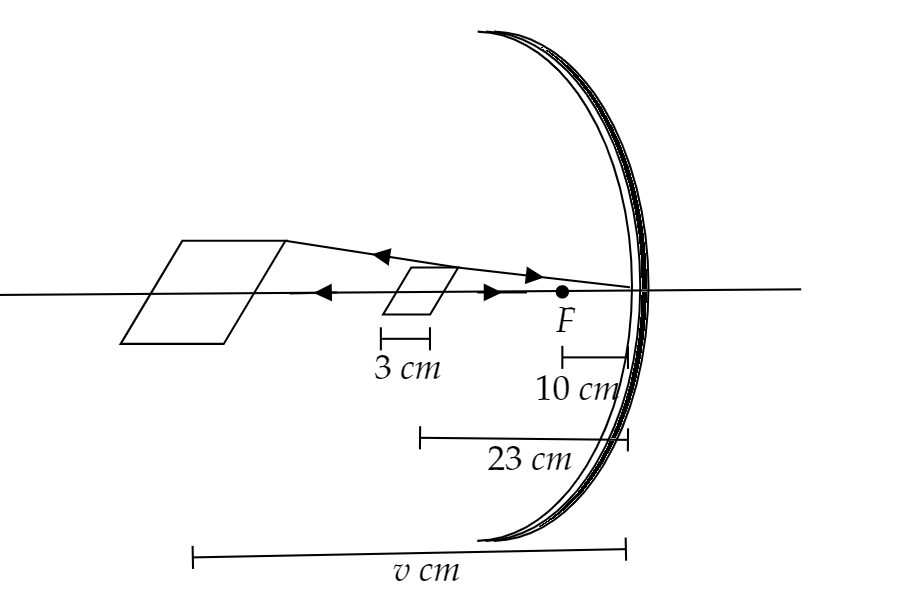
Firstly, we have to find the image distance of the given square wire.
Let us consider the image distance as $v$, the object distance $u$ and the focal length of the concave mirror $f$.
From the mirror formula we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
It is given in the question that the object distance $u = - 23{\text{ }}cm$ and the focal length $f = - 10{\text{ }}cm$.
Substituting the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{23}} = - \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
Arranging the equation we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{23}} - \dfrac{1}{{10}} = - \dfrac{{13}}{{230}}$
Reciprocal of this equation we get,
$v = - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}$
The image distance of the square wire is $v = - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}{\text{ }}cm$
To find the area enclosed by the wire, we have to find the magnification of the given object.
The formula of magnification $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$ where $m = $ magnification, $v = $ image distance and $u = $ object distance.
Substituting the values we get,
$m = \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}}}{{ - 23}} = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$
Now, as the magnification of the given image is $\dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$. Hence, side of the wire which is the object also increases by $\dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$ times.
The original side of the wire $a = 3{\text{ }}cm$
Let the new side of the wire be $a'$.
Therefore, $a' = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}} \times a = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}} \times 3 = \dfrac{{30}}{{13}}$
The new side of the wire is $\dfrac{{30}}{{13}}{\text{ }}cm$.
So, the new area of the wire is $ = {\left( {a'} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{30}}{{13}}} \right)^2} = 5.32$
The area enclosed by the image is $5.32{\text{ }}c{m^2}$.
Note:
It must be noted that we had given a negative sign in front of the focal length and the object distance which is due to the fact that according to mirror formulas anything which lies on the left of the mirror is given a negative sign while to the right of the mirror gives a positive side.
Here, the unknown variable is image distance. Then after finding the image distance, we have to find the magnification of the image. This magnification will also increase the side of the image of the wire which will eventually lead us to find the area that the image encloses.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the question that the focal length of a concave mirror is $10{\text{ }}cm$. A square wire of side $3{\text{ }}cm$ is placed $23{\text{ }}cm$ away from the mirror which is placed on the principal axis. We have to find the area enclosed by the image.

Firstly, we have to find the image distance of the given square wire.
Let us consider the image distance as $v$, the object distance $u$ and the focal length of the concave mirror $f$.
From the mirror formula we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
It is given in the question that the object distance $u = - 23{\text{ }}cm$ and the focal length $f = - 10{\text{ }}cm$.
Substituting the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{23}} = - \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
Arranging the equation we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{23}} - \dfrac{1}{{10}} = - \dfrac{{13}}{{230}}$
Reciprocal of this equation we get,
$v = - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}$
The image distance of the square wire is $v = - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}{\text{ }}cm$
To find the area enclosed by the wire, we have to find the magnification of the given object.
The formula of magnification $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$ where $m = $ magnification, $v = $ image distance and $u = $ object distance.
Substituting the values we get,
$m = \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{{230}}{{13}}}}{{ - 23}} = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$
Now, as the magnification of the given image is $\dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$. Hence, side of the wire which is the object also increases by $\dfrac{{10}}{{13}}$ times.
The original side of the wire $a = 3{\text{ }}cm$
Let the new side of the wire be $a'$.
Therefore, $a' = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}} \times a = \dfrac{{10}}{{13}} \times 3 = \dfrac{{30}}{{13}}$
The new side of the wire is $\dfrac{{30}}{{13}}{\text{ }}cm$.
So, the new area of the wire is $ = {\left( {a'} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{30}}{{13}}} \right)^2} = 5.32$
The area enclosed by the image is $5.32{\text{ }}c{m^2}$.
Note:
It must be noted that we had given a negative sign in front of the focal length and the object distance which is due to the fact that according to mirror formulas anything which lies on the left of the mirror is given a negative sign while to the right of the mirror gives a positive side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




