
A compound whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though they contain asymmetric carbon atoms is called:
A.A threo compound
B.A erythro compound
C.A meso compound
D.None of these
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:A compound whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though they contain asymmetric carbon atoms is called a meso compound. Compounds whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images are achiral compounds.
Complete answer:
There are two types of compounds when it comes to rotating the compound structure with respect to the bonds. These are chiral and achiral compounds. A chiral compound is a compound which is not identical to its mirror image, that is, it is not superimposable on its mirror image and achiral compounds are those compounds which are superimposable on their mirror image. This property is known as chirality.
Lets understand this with the help of examples propan-2-ol has no asymmetric carbon atom and all the four different groups attached to it are not different and thus it is superimposable on its mirror image so it is achiral and butan-2-ol has four different groups attached to it which makes it not identical to its mirror image and is thus a chiral compound.
A compound which is not capable of optical rotation is called optically inactive and the compounds which can rotate optically are known as optically active and achiral compounds are optically inactive. The stereoisomers which are related to each other as non-superimposable mirror images, that is, if they are chiral compounds then these are called enantiomers.
So, according to the question, compounds whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though it contains asymmetric carbon atoms are called a meso compound. They are optically inactive even though they contain chiral carbon atoms but due to plane of symmetry they are inactive optically.
So, the correct option of the question is option (C) A meso compound.
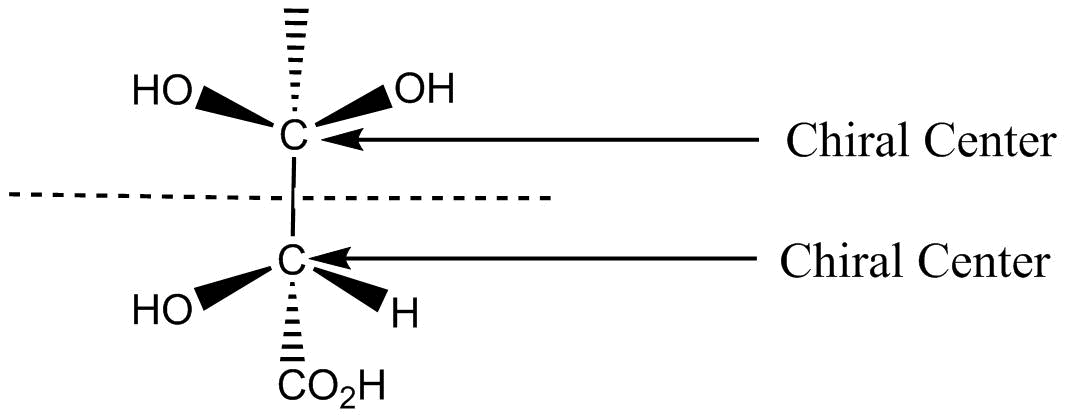
Example of meso compound
Note:
A mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportions will have zero optical rotation. This is because the rotation of one is cancelled out by the other isomer. This kind of mixture is known as the racemic mixture or racemic modification.
Complete answer:
There are two types of compounds when it comes to rotating the compound structure with respect to the bonds. These are chiral and achiral compounds. A chiral compound is a compound which is not identical to its mirror image, that is, it is not superimposable on its mirror image and achiral compounds are those compounds which are superimposable on their mirror image. This property is known as chirality.
Lets understand this with the help of examples propan-2-ol has no asymmetric carbon atom and all the four different groups attached to it are not different and thus it is superimposable on its mirror image so it is achiral and butan-2-ol has four different groups attached to it which makes it not identical to its mirror image and is thus a chiral compound.
A compound which is not capable of optical rotation is called optically inactive and the compounds which can rotate optically are known as optically active and achiral compounds are optically inactive. The stereoisomers which are related to each other as non-superimposable mirror images, that is, if they are chiral compounds then these are called enantiomers.
So, according to the question, compounds whose molecules are superimposable on their mirror images even though it contains asymmetric carbon atoms are called a meso compound. They are optically inactive even though they contain chiral carbon atoms but due to plane of symmetry they are inactive optically.
So, the correct option of the question is option (C) A meso compound.

Example of meso compound
Note:
A mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportions will have zero optical rotation. This is because the rotation of one is cancelled out by the other isomer. This kind of mixture is known as the racemic mixture or racemic modification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




