
(a) Compound (A) with molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\] gives a violet color with neutral\[\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]. (A) Reacts with \[\text{CHC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\] and \[\text{NaOH}\] gives two isomers (B) and (C) with the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]. Compound (A) reacts with ammonia at 473K in the presence of \[\text{ZnC}{{\text{1}}_{\text{2}}}\] gives compound (D) with the molecular formula\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{7}}}\text{N}\]. Compound (D) undergoes a carbylamine test. Identify (A), (B), (C), and (D) and explain the reactions.
(b) (A) is reddish-brown metal. It belongs to group 11 and period 4 of the periodic table. When heated below 1370K. (A) Given a black compound (B). When heated 1370K (A) gives a red compound (C). With concentrated nitric acid, (A) liberates \[\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] gas and gives compound (D). Identify (A), (B), (C) and (D). Explain the reactions.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The conversion of reactant to the product depending on the reaction conditions mentioned on the arrow. Each reactant forms different products under the effect of reagents. Thus name reactions are the reactions that are carried out to get the determined product under the progress of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
a) Let’s find out the A, B, C, and D for the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\] compound.
-First, we need to find compound A. According to the data given, the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\] reacts with the neutral $\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$to give a violet color.
-We know that a compound with a phenolic group reacts with the aqueous $\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ solution to give a violet, purple, blue color solution. The general reaction as shown below:
$\text{3}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{OH+FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{Fe(O}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3HCl}$
Thus the given compound A is the phenol ,structure of it is as shown below,
Structure of compound A: \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\]
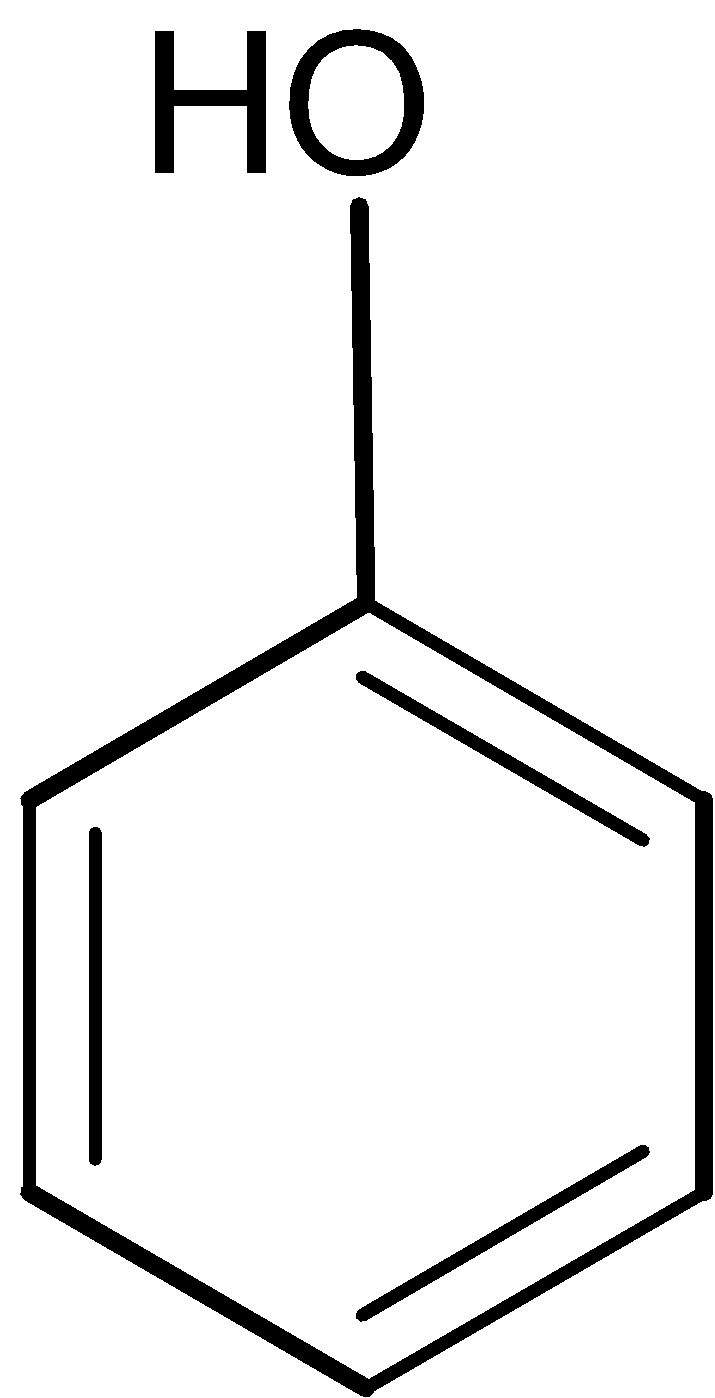
A=Phenol
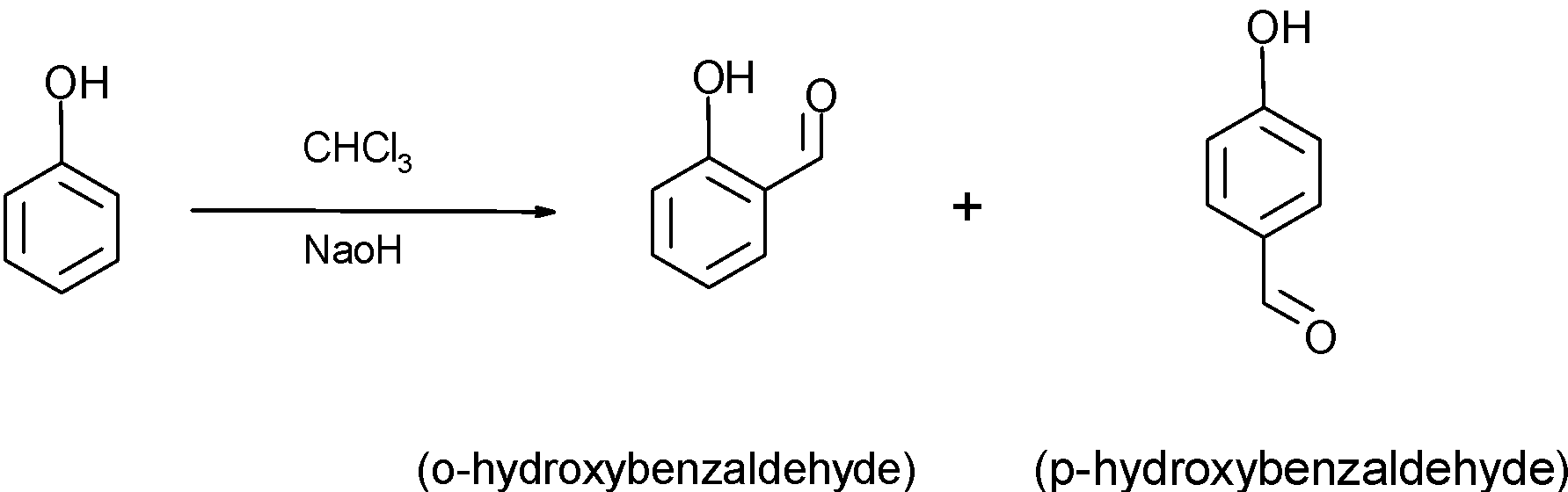
-The compound A which is phenol reacts with the chloroform $\text{(CHC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}})$ a presence of $\text{NaOH}$ to give phenol substituted with an aldehyde at ortho and para position to the benzene ring is called the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. The isomers have the formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]. The ortho-substituted phenol is the major product of the reaction. The reaction of phenol to give o-hydroxybenzaldehyde and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde is as shown below:
Reaction:
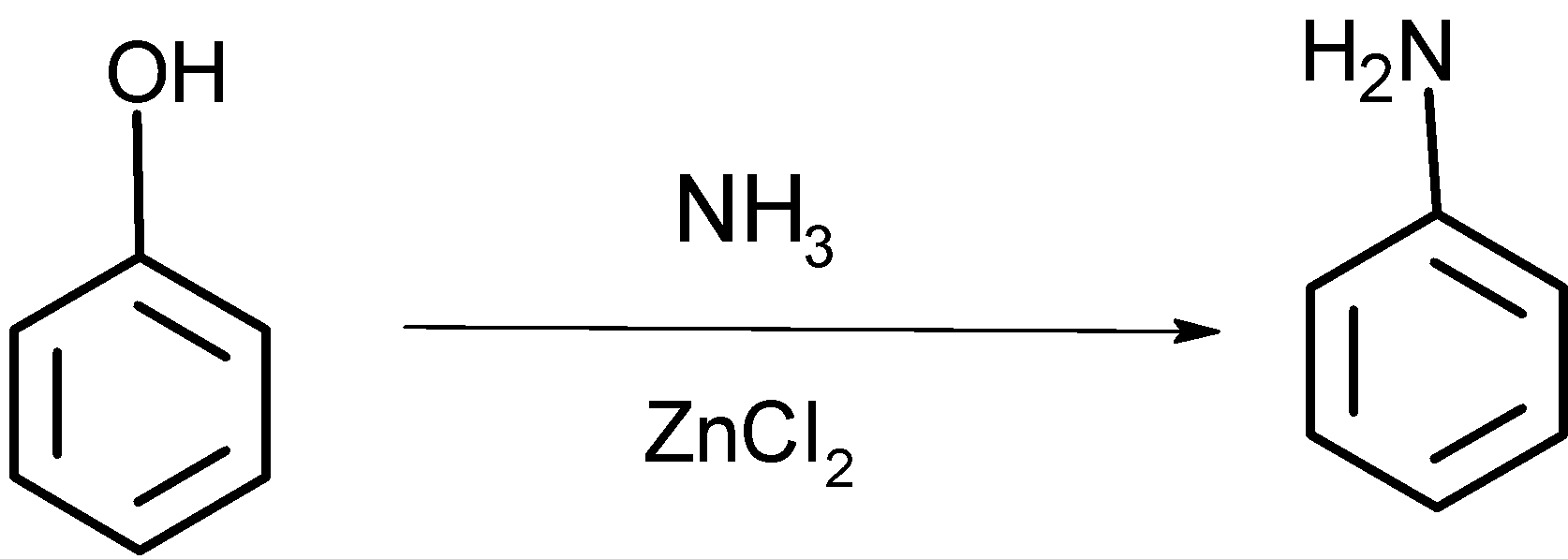
-when phenol reacts with the ammonia in presence of $\text{ZnC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ at the temperature 47K, the $\text{-OH}$ group of phenol reacts within $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and comes out as a water molecule, such that $\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ the group attaches to the benzene ring to give the compound D as shown below,
Reaction:
The compound D formed by the treatment of ammonia and zinc chloride undergoes a carbylamine test. As below:
Reaction:
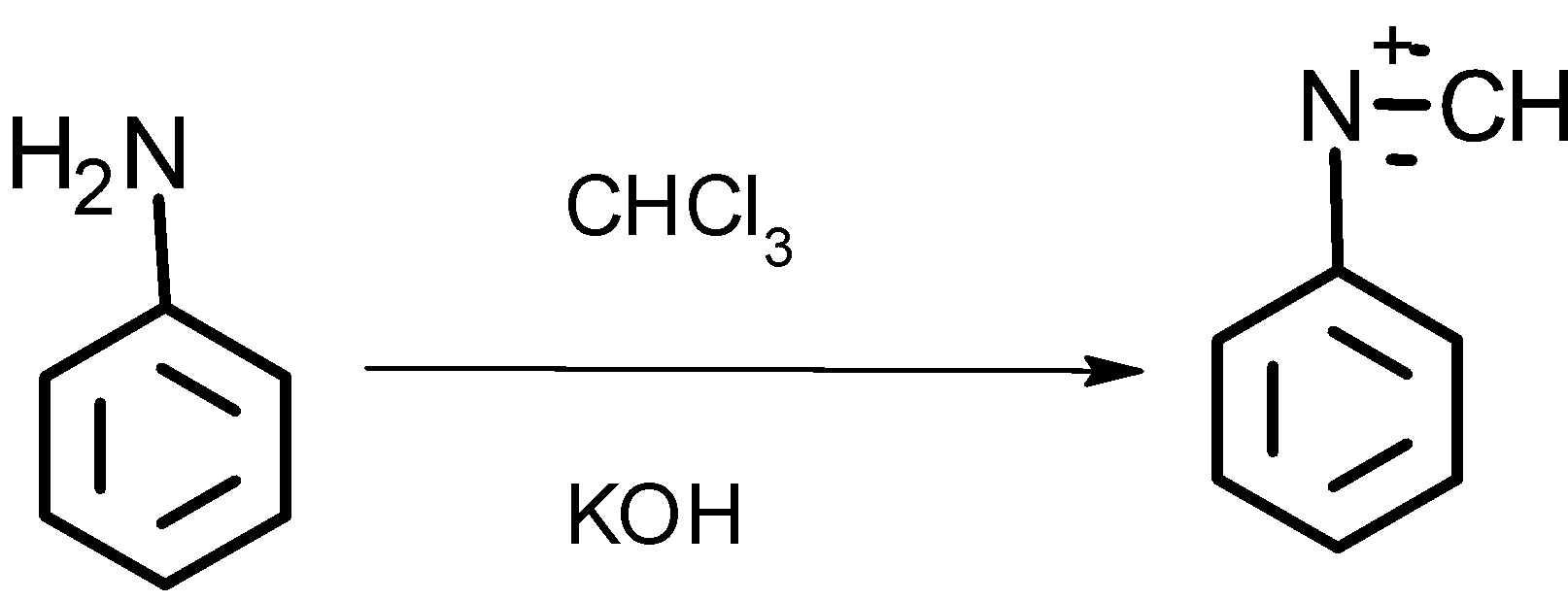
Thus compound D is a primary amine and its name is aniline
b) We are interested to find out the A, B, C, and D
-A is said to be the reddish-brown metal which belongs to group 11 and period 4 of the periodic table. If we search for the element in the periodic table, it is in the 3d transition metal series and group 11, the metal A is Copper ($\text{Cu}$).
-Copper is the reddish-brown metal that is lustrous. Its atomic number is 29 and it belongs to the 3d transition metal series.it is inorganic metal.
-Let's find out B,
When copper is heated to the 1370K it turns into the black. This is because when it is heated it reacts with the oxygen to form the black copper oxide. The reaction is as follows,
$\text{2Cu+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2CuO}$
$\text{CuO}$ Is the black compound. Thus B is $\text{CuO}$.
-Let's find out the C,
When the copper is heated to the 1370K it turns into the black. This is because when it is heated it reacts with the oxygen to form the red copper (I) oxide or cuprous oxide .the reaction is as follows
$\text{4Cu+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2C}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
It is the oxide of copper when an excess of copper is heated in the presence of oxygen, thus cuprous oxide $\text{C}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$ is compound C.
-When the copper is treated with concentrated nitric acid, the copper nitrate is formed along with the liberation of nitro $\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ gas. The reaction is as follows,
$\text{Cu+HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{Cu(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}+2{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
Thus, compound D is copper nitrate$\text{Cu(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Note: These are concept based questions. The reagents play a very important role in the progress of the reaction. Thus to carry out the transformation of reactant to product always remember what is written on the arrow. For example, phenol undergoes the reaction in the presence of chloroform and alkali to give hydroxybenzaldehyde as the product. Try to figure out the line out for the mechanistic approach of reagent.
Complete step by step answer:
a) Let’s find out the A, B, C, and D for the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\] compound.
-First, we need to find compound A. According to the data given, the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\] reacts with the neutral $\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$to give a violet color.
-We know that a compound with a phenolic group reacts with the aqueous $\text{FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ solution to give a violet, purple, blue color solution. The general reaction as shown below:
$\text{3}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{OH+FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{Fe(O}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3HCl}$
Thus the given compound A is the phenol ,structure of it is as shown below,
Structure of compound A: \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\text{O}\]

A=Phenol
-The compound A which is phenol reacts with the chloroform $\text{(CHC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}})$ a presence of $\text{NaOH}$ to give phenol substituted with an aldehyde at ortho and para position to the benzene ring is called the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. The isomers have the formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]. The ortho-substituted phenol is the major product of the reaction. The reaction of phenol to give o-hydroxybenzaldehyde and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde is as shown below:
Reaction:

-when phenol reacts with the ammonia in presence of $\text{ZnC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ at the temperature 47K, the $\text{-OH}$ group of phenol reacts within $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and comes out as a water molecule, such that $\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ the group attaches to the benzene ring to give the compound D as shown below,
Reaction:

The compound D formed by the treatment of ammonia and zinc chloride undergoes a carbylamine test. As below:
Reaction:

Thus compound D is a primary amine and its name is aniline
b) We are interested to find out the A, B, C, and D
-A is said to be the reddish-brown metal which belongs to group 11 and period 4 of the periodic table. If we search for the element in the periodic table, it is in the 3d transition metal series and group 11, the metal A is Copper ($\text{Cu}$).
-Copper is the reddish-brown metal that is lustrous. Its atomic number is 29 and it belongs to the 3d transition metal series.it is inorganic metal.
-Let's find out B,
When copper is heated to the 1370K it turns into the black. This is because when it is heated it reacts with the oxygen to form the black copper oxide. The reaction is as follows,
$\text{2Cu+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2CuO}$
$\text{CuO}$ Is the black compound. Thus B is $\text{CuO}$.
-Let's find out the C,
When the copper is heated to the 1370K it turns into the black. This is because when it is heated it reacts with the oxygen to form the red copper (I) oxide or cuprous oxide .the reaction is as follows
$\text{4Cu+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2C}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
It is the oxide of copper when an excess of copper is heated in the presence of oxygen, thus cuprous oxide $\text{C}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$ is compound C.
-When the copper is treated with concentrated nitric acid, the copper nitrate is formed along with the liberation of nitro $\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ gas. The reaction is as follows,
$\text{Cu+HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{Cu(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}+2{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
Thus, compound D is copper nitrate$\text{Cu(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Note: These are concept based questions. The reagents play a very important role in the progress of the reaction. Thus to carry out the transformation of reactant to product always remember what is written on the arrow. For example, phenol undergoes the reaction in the presence of chloroform and alkali to give hydroxybenzaldehyde as the product. Try to figure out the line out for the mechanistic approach of reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




