
A complex of the type $ {\left[ {M{{\left( {AA} \right)}_2}{X_2}} \right]^{n + }} $ is known to be optically active. What does this indicate about the structure of the complex? Give one example of such a complex.
Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: In order to answer the question let us first understand what optically active means. The capacity to rotate the plane of polarisation of a linearly polarised light is known as optical activity. This effect can only be seen in chiral materials, which lack mirror symmetry.
Complete answer:
When a molecule is chiral, it is the cause of its optical activity. The property demonstrated by substances in which the plane of polarisation is rotated for plane-polarized light is known as optical activity.
An optically active complex of the type $ {\left[ {M{{\left( {AA} \right)}_2}{X_2}} \right]^{n + }} $ indicates cis-octahedral structure, e.g., $ cis - {\left[ {\operatorname{P} t{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]^{2 + }} $ or $ cis - {[Cr{(en)_2}C{l_2}]^ + } $ because the mirror image isomers aren't superimposable.
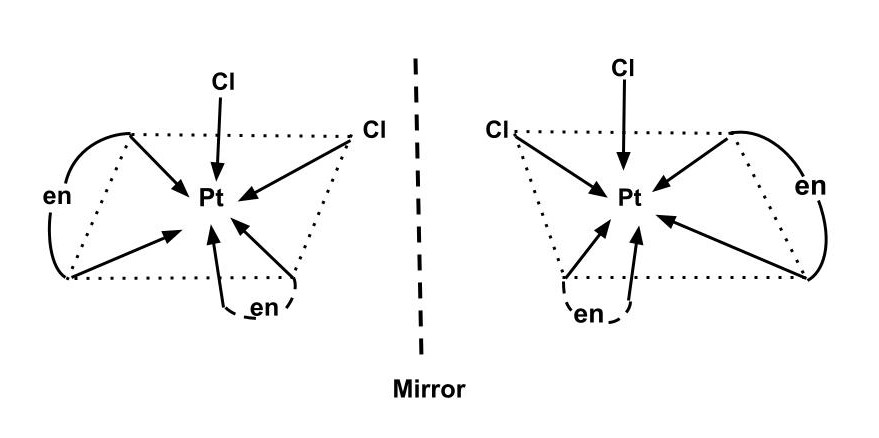
Additional Information:
In chemistry, the words dextrorotation and laevorotation (sometimes spelled levorotation) are used to describe the optical rotation of plane-polarized light. Dextrorotation refers to clockwise or right-handed rotation from the observer's perspective, while laevorotation refers to counter clockwise or left-handed rotation.
Note:
It should be known that Dextrorotatory or dextrorotatory refers to a chemical compound that causes dextrorotation, whereas laevorotatory or laevorotatory refers to a chemical component that causes laevorotation. Compounds with these features are said to have optical activity since they are made up of chiral molecules.] A chiral molecule's enantiomer (geometric mirror image) will be laevorotatory if it is dextrorotatory, and vice versa. Enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions by the same amount of degrees.
Complete answer:
When a molecule is chiral, it is the cause of its optical activity. The property demonstrated by substances in which the plane of polarisation is rotated for plane-polarized light is known as optical activity.
An optically active complex of the type $ {\left[ {M{{\left( {AA} \right)}_2}{X_2}} \right]^{n + }} $ indicates cis-octahedral structure, e.g., $ cis - {\left[ {\operatorname{P} t{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}C{l_2}} \right]^{2 + }} $ or $ cis - {[Cr{(en)_2}C{l_2}]^ + } $ because the mirror image isomers aren't superimposable.

Additional Information:
In chemistry, the words dextrorotation and laevorotation (sometimes spelled levorotation) are used to describe the optical rotation of plane-polarized light. Dextrorotation refers to clockwise or right-handed rotation from the observer's perspective, while laevorotation refers to counter clockwise or left-handed rotation.
Note:
It should be known that Dextrorotatory or dextrorotatory refers to a chemical compound that causes dextrorotation, whereas laevorotatory or laevorotatory refers to a chemical component that causes laevorotation. Compounds with these features are said to have optical activity since they are made up of chiral molecules.] A chiral molecule's enantiomer (geometric mirror image) will be laevorotatory if it is dextrorotatory, and vice versa. Enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions by the same amount of degrees.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




