
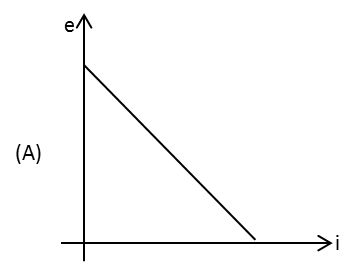
A coil of inductance L and zero resistance is connected to a source of variable emf at t=0. The emf of source is varied with time according to the graph shown on the right above. What will be the average current that flows through the coil during time T?

A.\[{V_0}T/2L\]
B.\[{V_0}T/6L\]
C.\[3{V_0}T/2L\]
D.\[{V_0}T/L\]





Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Determine the equation for the given curve emf of source versus time graph. Use the formula for the emf in the coil. This equation gives the relation between the inductance, change in current in the time interval.
Formula Used: The emf in the coil is given by
\[e = - L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[e\] is the emf in the coil, \[L\] is the inductance and \[di\] is the change in current during the time interval \[dt\].
Complete step by step answer:A coil of inductance L and zero resistance is connected to a source of variable emf at t=0. The emf of source is varied with time according to the graph shown below.
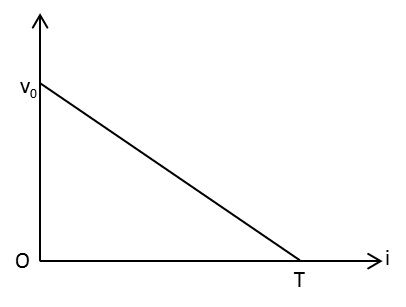
The equation of the above graph is
\[e = - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t\]
Here, \[{V_0}\] is the peak emf from the graph, \[T\] is the time during which the current flows and \[t\] is the time.
Rearrange equation (1) for the small current \[di\].
\[di = - \dfrac{{edt}}{L}\]
Substitute \[ - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t\] for \[e\] in the above equation.
\[di = - \dfrac{{\left( { - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t} \right)dt}}{L}\]
\[ \Rightarrow di = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}tdt\]
Determine the current through the coil in time \[T\].
Integrate on both sides of the above equation.
\[\int {di} = \int {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}tdt} \]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}\int {tdt} \]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}\dfrac{{{t^2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\]
Hence, the total current flowing is \[\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\].
Now determine the average current \[{i_{avg}}\] from time \[t = 0\] to \[t = T\].
The average current through the coil is
\[{i_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int {idt} \]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\] for \[i\] in the above equation and integrate the above equation of current from time \[t = 0\] to \[t = T\].
\[{i_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T} {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}} dt\]
\[{i_{avg}} = \int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T} {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}} dt\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2L{T^2}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_{t = 0}^{t = T}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2L{T^2}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{T^3}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{0^3}}}{3}} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{{6L}}\]
Therefore, the average current that flows through the coil during time T will be \[\dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{{6L}}\] and the corresponding graph is shown in option B.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The equation of the emf from the graph is negative as the graph has a negative slope.
Formula Used: The emf in the coil is given by
\[e = - L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[e\] is the emf in the coil, \[L\] is the inductance and \[di\] is the change in current during the time interval \[dt\].
Complete step by step answer:A coil of inductance L and zero resistance is connected to a source of variable emf at t=0. The emf of source is varied with time according to the graph shown below.

The equation of the above graph is
\[e = - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t\]
Here, \[{V_0}\] is the peak emf from the graph, \[T\] is the time during which the current flows and \[t\] is the time.
Rearrange equation (1) for the small current \[di\].
\[di = - \dfrac{{edt}}{L}\]
Substitute \[ - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t\] for \[e\] in the above equation.
\[di = - \dfrac{{\left( { - \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}t} \right)dt}}{L}\]
\[ \Rightarrow di = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}tdt\]
Determine the current through the coil in time \[T\].
Integrate on both sides of the above equation.
\[\int {di} = \int {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}tdt} \]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}\int {tdt} \]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{LT}}\dfrac{{{t^2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\]
Hence, the total current flowing is \[\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\].
Now determine the average current \[{i_{avg}}\] from time \[t = 0\] to \[t = T\].
The average current through the coil is
\[{i_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int {idt} \]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}\] for \[i\] in the above equation and integrate the above equation of current from time \[t = 0\] to \[t = T\].
\[{i_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T} {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}} dt\]
\[{i_{avg}} = \int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T} {\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2LT}}{t^2}} dt\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2L{T^2}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_{t = 0}^{t = T}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2L{T^2}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{T^3}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{0^3}}}{3}} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {i_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{{6L}}\]
Therefore, the average current that flows through the coil during time T will be \[\dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{{6L}}\] and the corresponding graph is shown in option B.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The equation of the emf from the graph is negative as the graph has a negative slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




