
A circular wire of diameter 30 mm is placed 25 cm away from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. If the area of the image is Xπ mm2, what is the value of x? The center of the wire is on the axis of the mirror, with its plane normal to the axis.
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: Here we will use the mirror formula for magnification and how the distance of the object related to the focal length and the distance of the image from the mirror to find the magnification of the radius and then use the radius of the circle in the image to find the area of the image.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& M=-\dfrac{v}{u} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
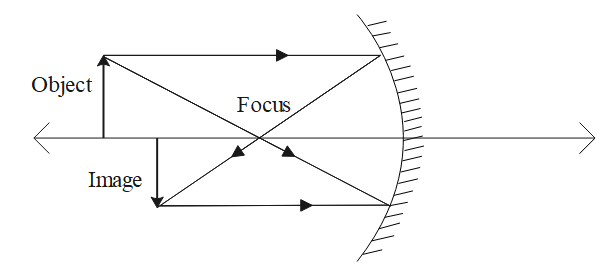
Let’s consider a radius extending from the center of the circle made by the wire to one of the ends and then find the radius in the image. Then, that value of radius can be used to find the area of the image. To find the length of the radius we need to use the magnification formula. But, to use the magnification formula we need to have the value of ‘v’ that is the distance from the mirror at which the image is formed. To find the value of ‘v’ we will use the mirror formula
\[\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Here v is the distance of image from the mirror.
u is the distance of an object from the mirror. Which is given to be 25 cm in the question
f is the focal length of the mirror. The focal length has been given as 10 cm in the question
As it is a concave mirror both the object and the focal point will be to the left of the mirror and thus will have a negative sign according to the sign convention.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{-25}=\dfrac{-(5-2)}{50} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-50}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will use this value of ‘v’ in magnification formula
$M=-\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{\dfrac{-50}{3}}{-25}=-\dfrac{2}{3}$
We will ignore the negative sign as we only need the length of the radius negative sign indicates that the image will be inverted.
So, The radius will be M times the initial radius. Initial diameter is given as 30 mm. So, the initial radius will be 15 mm. And the radius of the image will be $15\times \dfrac{2}{3}=10$mm. The area of the image will be \[\pi {{10}^{2}}=100\pi \]mm2. So, x will be equal to 100.
One unit = 5 centimetres
Note:
Take care of the sign conventions when using the mirror formulae. Taking wrong signs can change the answer. The most widely accepted form of sing convention assumes the zero at the centre of the mirror/lens and any distance to its left is considered negative and on the right is considered positive.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& M=-\dfrac{v}{u} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
Let’s consider a radius extending from the center of the circle made by the wire to one of the ends and then find the radius in the image. Then, that value of radius can be used to find the area of the image. To find the length of the radius we need to use the magnification formula. But, to use the magnification formula we need to have the value of ‘v’ that is the distance from the mirror at which the image is formed. To find the value of ‘v’ we will use the mirror formula
\[\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Here v is the distance of image from the mirror.
u is the distance of an object from the mirror. Which is given to be 25 cm in the question
f is the focal length of the mirror. The focal length has been given as 10 cm in the question
As it is a concave mirror both the object and the focal point will be to the left of the mirror and thus will have a negative sign according to the sign convention.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{-25}=\dfrac{-(5-2)}{50} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-50}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will use this value of ‘v’ in magnification formula
$M=-\dfrac{v}{u}=-\dfrac{\dfrac{-50}{3}}{-25}=-\dfrac{2}{3}$
We will ignore the negative sign as we only need the length of the radius negative sign indicates that the image will be inverted.
So, The radius will be M times the initial radius. Initial diameter is given as 30 mm. So, the initial radius will be 15 mm. And the radius of the image will be $15\times \dfrac{2}{3}=10$mm. The area of the image will be \[\pi {{10}^{2}}=100\pi \]mm2. So, x will be equal to 100.

One unit = 5 centimetres
Note:
Take care of the sign conventions when using the mirror formulae. Taking wrong signs can change the answer. The most widely accepted form of sing convention assumes the zero at the centre of the mirror/lens and any distance to its left is considered negative and on the right is considered positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




