
A circular insulated copper wire loop is twisted to form two loops of area A and 2A as shown in the figure. At the point of crossing the wires remain electrically insulated from each other. The entire loop lies in the plane (of the paper). A uniform magnetic field B points into the plane of paper. At $t = 0$, the loop starts rotating about the common diameter as an axis with a constant angular velocity in the magnetic field. Which of the following options is/are correct?
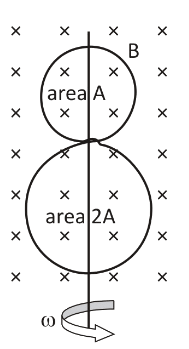
A. The amplitude of the maximum net emf induced due to both the loops is equal to the amplitude of maximum emf induced in the smaller loop alone.
B. The rate of change of the flux is maximum when the plane of the loops is perpendicular to the plane of the paper.
C. The emf induced in the loop is proportional to the sum of the areas of the two loops.
D. The net emf induced due to both the loops is proportional to \[\cos \omega t\].

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:First find the rate of change of the magnetic flux passing through the smaller loop. This will give you the value of \[\omega t\] and hence the direction. Then find the emf produced in the bigger loop and the smaller loop. Find the difference in the emfs to find the net emf produced.
Complete step by step answer:
The magnetic flux passing through the smaller loop is given by $\phi = BA\sin \omega t$ where B is the magnetic field intensity, A is the area of cross section and \[\omega \] is the angular velocity in the magnetic field.
The rate of change of the magnetic flux is given by,
\[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - BA\sin \omega t\]
Now, B and A are constants, therefore \[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\] will be maximum when \[\sin \omega t\] will be maximum. This is possible only when \[\omega t = 90^\circ \], that is the plane of loop is perpendicular to the plane of the paper.
Also, the emfs produced in both the loops will oppose each other. The net emf will also be proportional to \[\sin \omega t\].
Net emf = \[B(2A)\sin \omega t - BA\sin \omega t = BA\sin \omega t\],
where $2A$ is the area of the cross section of the bigger loop.
Hence the correct options are B and D.
Note:As the magnetic flux passing through both the loops will be different due to the different area of cross sections. The amplitude of the net emf produced due to both the loops is equal to the emf produced by the smaller loop alone.
Complete step by step answer:
The magnetic flux passing through the smaller loop is given by $\phi = BA\sin \omega t$ where B is the magnetic field intensity, A is the area of cross section and \[\omega \] is the angular velocity in the magnetic field.
The rate of change of the magnetic flux is given by,
\[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - BA\sin \omega t\]
Now, B and A are constants, therefore \[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}\] will be maximum when \[\sin \omega t\] will be maximum. This is possible only when \[\omega t = 90^\circ \], that is the plane of loop is perpendicular to the plane of the paper.
Also, the emfs produced in both the loops will oppose each other. The net emf will also be proportional to \[\sin \omega t\].
Net emf = \[B(2A)\sin \omega t - BA\sin \omega t = BA\sin \omega t\],
where $2A$ is the area of the cross section of the bigger loop.
Hence the correct options are B and D.
Note:As the magnetic flux passing through both the loops will be different due to the different area of cross sections. The amplitude of the net emf produced due to both the loops is equal to the emf produced by the smaller loop alone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




