
A charge of $5 \times {10^{10}}C$ is given to a metal cylinder of length $10cm$, placed in the air. The electric intensity due to the cylinder at a distance of $0.2m$form its axis is: -
A. $150V/m$
B. $250V/m$
C. $350V/m$
D. $450V/m$
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Use the concept of Gaussian surface and gausses’ law for electric field intensity at a point due long current carrying conductor of cylindrical shape OR wine.
Formulae used:
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$
$\lambda $ is linear change density
$r$ is the radius of a Gaussian cylinder.
${ \in _0}$ is permittivity in the free space
Complete step by step answer:
Observe the diagram
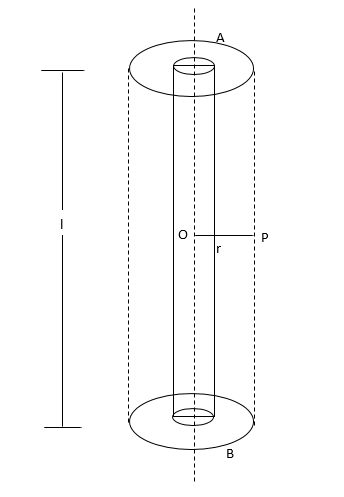
Let \[AB\] be a cylinder of length,
$l = 10cm = 0.1m$
Let $O$ be some point on the axis of the cylinder.
Let $P$ be some point, close to cylinder such that,
$OP = r = 0.2m$
$Q = 5 \times {10^{ - 10}}C$ is the given change on the cylinder.
Now, assume a cylinder, concurrent to the given cylinder, such that the radius of the Gaussian cylinder is $r = 0.2m$.
Then the point P lies on the edge of the Gaussian surface.
Now, according to Gauss’s law. Electric field intensity due to a large cylindrical current carrying conductor is at point $P$ given by,
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$ . . . (1)
Where,
$\lambda $ is linear change density
$r$ is the radius of a Gaussian cylinder.
${ \in _0}$ is permittivity in the free space
${ \in _0} = 8.85 \times {10^{ - 12}}{c^2}N{m^{ - 2}}$
To solve equation (1), we need, value of$\lambda $
For that we know,
Linear change density is the ratio of total change on the conductor and the length of the conductor
i.e. $\lambda = \dfrac{Q}{l}$
By substituting the given values, we get
$\lambda = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 5 \times {10^{ - 9}}C/m$ $\left( {\because \dfrac{{{a^m}}}{{{a^n}}} = {a^{m - n}}} \right)$
Substituting this values in equation (1), we get
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{2 \times 3.14 \times 0.2 \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$ $\left( {\because \pi = 3.14 = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{2 \times 314 \times {{10}^{ - 2}} \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 1}} \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 2}} \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{11}^{ - 9}}}}{{4 \times 314 \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 17}}}}$ $\left( {\because {a^m}{a^n} = {a^{m - n}}} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^{ - 9 + 17}}}}{{1256 \times 177}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{{1256 \times 177}} \times {10^8}$
$ \Rightarrow E = 449.8V/m$
$ \Rightarrow E \approx 450V/m$
Therefore, the electric field intensity at point $P$ is $450V/m$.
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (D) $450V/m$
Note:
Calculation can be difficult in such questions. You should use a log table for complex calculation.
Since this question is objective, single current type, we can simplify the calculation by approximating the calculation as well.
For example, one of the steps in above solution is
$E = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 11}}}}{{2 \times 3.14 \times 0.2 \times {{10}^{ - 1}} \times 8.85 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
Write, $3.14 \approx 3$, and$8.85 \approx 9$
We get,
$E = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times {{10}^{12}}}}{{2 \times 3 \times 0.2 \times 9}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times 10}}{{54 \times 0.2}}$.
Formulae used:
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$
$\lambda $ is linear change density
$r$ is the radius of a Gaussian cylinder.
${ \in _0}$ is permittivity in the free space
Complete step by step answer:
Observe the diagram

Let \[AB\] be a cylinder of length,
$l = 10cm = 0.1m$
Let $O$ be some point on the axis of the cylinder.
Let $P$ be some point, close to cylinder such that,
$OP = r = 0.2m$
$Q = 5 \times {10^{ - 10}}C$ is the given change on the cylinder.
Now, assume a cylinder, concurrent to the given cylinder, such that the radius of the Gaussian cylinder is $r = 0.2m$.
Then the point P lies on the edge of the Gaussian surface.
Now, according to Gauss’s law. Electric field intensity due to a large cylindrical current carrying conductor is at point $P$ given by,
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$ . . . (1)
Where,
$\lambda $ is linear change density
$r$ is the radius of a Gaussian cylinder.
${ \in _0}$ is permittivity in the free space
${ \in _0} = 8.85 \times {10^{ - 12}}{c^2}N{m^{ - 2}}$
To solve equation (1), we need, value of$\lambda $
For that we know,
Linear change density is the ratio of total change on the conductor and the length of the conductor
i.e. $\lambda = \dfrac{Q}{l}$
By substituting the given values, we get
$\lambda = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}}{{0.1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 5 \times {10^{ - 9}}C/m$ $\left( {\because \dfrac{{{a^m}}}{{{a^n}}} = {a^{m - n}}} \right)$
Substituting this values in equation (1), we get
$E = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\pi r{ \in _0}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{2 \times 3.14 \times 0.2 \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$ $\left( {\because \pi = 3.14 = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}}{{2 \times 314 \times {{10}^{ - 2}} \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 1}} \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 2}} \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times {{11}^{ - 9}}}}{{4 \times 314 \times 885 \times {{10}^{ - 17}}}}$ $\left( {\because {a^m}{a^n} = {a^{m - n}}} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^{ - 9 + 17}}}}{{1256 \times 177}}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{{1256 \times 177}} \times {10^8}$
$ \Rightarrow E = 449.8V/m$
$ \Rightarrow E \approx 450V/m$
Therefore, the electric field intensity at point $P$ is $450V/m$.
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (D) $450V/m$
Note:
Calculation can be difficult in such questions. You should use a log table for complex calculation.
Since this question is objective, single current type, we can simplify the calculation by approximating the calculation as well.
For example, one of the steps in above solution is
$E = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 11}}}}{{2 \times 3.14 \times 0.2 \times {{10}^{ - 1}} \times 8.85 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
Write, $3.14 \approx 3$, and$8.85 \approx 9$
We get,
$E = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times {{10}^{12}}}}{{2 \times 3 \times 0.2 \times 9}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times 10}}{{54 \times 0.2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




