
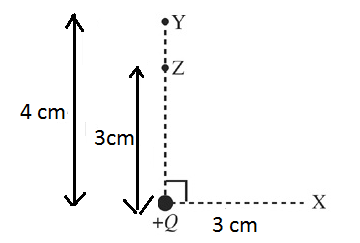
A charge of ${{10}^{-9}}C$ moves from $X$ to $Z$. Find the work done by the electric field due to the charge $Q=2C$ in moving the charge from $X$ to $Z$. The value of coulomb's constant is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$.
A. $0J$
B. $150J$
C. $300J$
D. $500J$
E. $1000J$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The concept to be used is that change in electrostatic potential energy due to a conservative force is equal to negative of work done by that force.Electrostatic force is a conservative force.The electrostatic potential energy of charges is product of charge and potential at that point
Difference in electrostatic potential energy is charge multiplied by the potential difference between two points.
Complete answer:
The electrostatic potential will be developed by the electric field of bigger charge of $Q=2C$in which the smaller charge of ${{10}^{-9}}C$ in moving from $X$ to $Z$ point
The electric potential due to a charge $Q$ is defined as$\dfrac{kQ}{R}$ where $k$ is Coulombs’ constant and R is distance from charge .
Since change in potential from $X$ to $Z$ point when multiplied by smaller charge will be responsible for change in electrostatic potential energy which will be the work done by the electric field of bigger stationary charge in moving from $X$ to$Z$ .
Work done=change in potential energy = charge $\times$ change in potential from $X$ to $Z$ .
Since the points $X$ and $Z$ are at the same distance from charge $Q$ so potential at both points will be the same as seen from the formula and hence change in potential and potential energy will be $0$ and hence work done by electric field will be $0$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Electrostatic potential and electrostatic potential energy are both scalar quantities and electric fields are vector quantities.The above said rule of change in potential energy is equal to work done is not applicable when non-conservative forces are acting.
Difference in electrostatic potential energy is charge multiplied by the potential difference between two points.
Complete answer:
The electrostatic potential will be developed by the electric field of bigger charge of $Q=2C$in which the smaller charge of ${{10}^{-9}}C$ in moving from $X$ to $Z$ point
The electric potential due to a charge $Q$ is defined as$\dfrac{kQ}{R}$ where $k$ is Coulombs’ constant and R is distance from charge .
Since change in potential from $X$ to $Z$ point when multiplied by smaller charge will be responsible for change in electrostatic potential energy which will be the work done by the electric field of bigger stationary charge in moving from $X$ to$Z$ .
Work done=change in potential energy = charge $\times$ change in potential from $X$ to $Z$ .
Since the points $X$ and $Z$ are at the same distance from charge $Q$ so potential at both points will be the same as seen from the formula and hence change in potential and potential energy will be $0$ and hence work done by electric field will be $0$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Electrostatic potential and electrostatic potential energy are both scalar quantities and electric fields are vector quantities.The above said rule of change in potential energy is equal to work done is not applicable when non-conservative forces are acting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




