
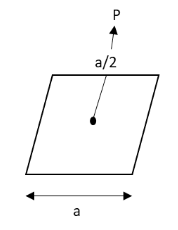
A charge is placed at a distance \[a/2\] above the centre of a square surface of edge \[a\] as shown in the figure. The electric flux through the square surface is:
A. \[\dfrac{Q}{{3{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{Q}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{Q}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:Use the formula for the electric flux through a closed surface. This formula gives the relation between the electric flux through the closed surface, charge and permittivity of free space. First draw an imaginary cube around the charge with the charge placed at the centre of the cube. Then determine the electric flux through only one face of the cube which is the required answer.
Formula used:
The electric flux \[\phi \] passing through a closed area is given by
\[\phi = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[Q\] is the charge enclosed in the area and \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that a charge is placed at a distance \[a/2\] above the centre of a square surface of edge \[a\] as shown in the figure.We have asked to determine the electric flux through the square surface.We know that the electric flux through any closed surface is the number of electric field lines passing through that surface.
We have given that the charge is placed above the square surface. To determine the electric flux through the given surface, we need to construct an imaginary cube around the charge with the charge placed at the centre of the cube.Let us draw the diagram of the imaginary cube around the charge.
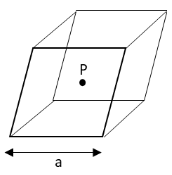
We can see that the electric flux due to this charge Q passes through all the six sides of the imaginary cube.But we have asked for the electric flux through only one given square shaped surface of the cube.Thus, the net electric flux through one square shaped surface is one sixth of the total electric flux through the whole imaginary cube.
According to equation (1), the electric flux through one surface is
\[\phi = \dfrac{1}{6} \times \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
\[ \therefore \phi = \dfrac{Q}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Therefore, the electric flux through the square surface is \[\dfrac{Q}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should keep in mind that we have asked to determine the electric flux through only one given square shaped surface. The students may get confused and determine the electric flux through the whole imaginary cube around the charge. But this is not the required answer. One should determine one sixth of the total flux through the cube.
Formula used:
The electric flux \[\phi \] passing through a closed area is given by
\[\phi = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[Q\] is the charge enclosed in the area and \[{\varepsilon _0}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that a charge is placed at a distance \[a/2\] above the centre of a square surface of edge \[a\] as shown in the figure.We have asked to determine the electric flux through the square surface.We know that the electric flux through any closed surface is the number of electric field lines passing through that surface.
We have given that the charge is placed above the square surface. To determine the electric flux through the given surface, we need to construct an imaginary cube around the charge with the charge placed at the centre of the cube.Let us draw the diagram of the imaginary cube around the charge.

We can see that the electric flux due to this charge Q passes through all the six sides of the imaginary cube.But we have asked for the electric flux through only one given square shaped surface of the cube.Thus, the net electric flux through one square shaped surface is one sixth of the total electric flux through the whole imaginary cube.
According to equation (1), the electric flux through one surface is
\[\phi = \dfrac{1}{6} \times \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
\[ \therefore \phi = \dfrac{Q}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Therefore, the electric flux through the square surface is \[\dfrac{Q}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should keep in mind that we have asked to determine the electric flux through only one given square shaped surface. The students may get confused and determine the electric flux through the whole imaginary cube around the charge. But this is not the required answer. One should determine one sixth of the total flux through the cube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




