
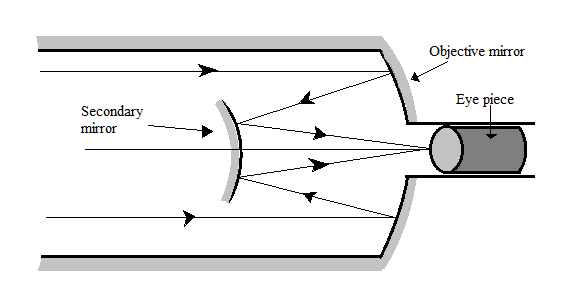
A Cassegrain telescope uses two mirrors as shown in the above figure. Such a telescope is built with the mirrors $20mm$ apart. If the radius of curvature of the large mirror is $220mm$ and the small mirror is $140mm$, where will the final image of an object at infinity be?

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question you have to know the concept of mirror formula for concave and convex mirror. Always remember that when there is given a Cassegrain telescope like in above diagram then the image formed by the objective will act as a virtual object for the secondary mirror.
Formula used:
Mirror formula is given as
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where $v$ is the distance where the final image formed
$u$ is the distance of the object from the mirror
$f$ is the focal length of the mirror
Complete step by step solution:
The distance between the objective mirror and the secondary mirror is given in the question, $d = 20mm$
The radius of the curvature of the objective mirror is also given in the question, ${R_1} = 220mm$
Hence, the focal length of the objective mirror is, ${f_1} = \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{2} = 110mm$
Also the radius of curvature of the secondary mirror is given in the question, ${R_2} = 70mm$
Hence, the focal length of the secondary mirror is, ${f_2} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{2} = 70mm$
The image formed by the objective mirror with an object placed at infinity, will act as a virtual object for the secondary mirror.
Hence, the image distance which acts as an object for the secondary mirror is,
$u = {f_1} - d$
On putting the values, we get
$ \Rightarrow u = 110 - 20 = 90mm$
Now, Applying the mirror formula for the secondary mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}$
On putting all the values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{90}} = \dfrac{1}{{70}}$
On solving this we get
$ \Rightarrow v = 315mm$
Hence, the final image of an object at infinity will be formed $315mm$ away from the secondary mirror.
Note:The Cassegrain telescope is an reflecting astronomical telescope, in which light ray is incident on a concave mirror known as objective mirror and then the reflected ray incident on a smaller convex mirror known as secondary mirror and then finally this ray is also gets reflected through a hole in the concave mirror onto a eyepiece to finally form the image.
Formula used:
Mirror formula is given as
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where $v$ is the distance where the final image formed
$u$ is the distance of the object from the mirror
$f$ is the focal length of the mirror
Complete step by step solution:
The distance between the objective mirror and the secondary mirror is given in the question, $d = 20mm$
The radius of the curvature of the objective mirror is also given in the question, ${R_1} = 220mm$
Hence, the focal length of the objective mirror is, ${f_1} = \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{2} = 110mm$
Also the radius of curvature of the secondary mirror is given in the question, ${R_2} = 70mm$
Hence, the focal length of the secondary mirror is, ${f_2} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{2} = 70mm$
The image formed by the objective mirror with an object placed at infinity, will act as a virtual object for the secondary mirror.
Hence, the image distance which acts as an object for the secondary mirror is,
$u = {f_1} - d$
On putting the values, we get
$ \Rightarrow u = 110 - 20 = 90mm$
Now, Applying the mirror formula for the secondary mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}$
On putting all the values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{90}} = \dfrac{1}{{70}}$
On solving this we get
$ \Rightarrow v = 315mm$
Hence, the final image of an object at infinity will be formed $315mm$ away from the secondary mirror.
Note:The Cassegrain telescope is an reflecting astronomical telescope, in which light ray is incident on a concave mirror known as objective mirror and then the reflected ray incident on a smaller convex mirror known as secondary mirror and then finally this ray is also gets reflected through a hole in the concave mirror onto a eyepiece to finally form the image.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




