
A car starts from the rest and accelerates at $5m{s^{ - 2}}$ for some time. Then the car moves with the uniform velocity for 1.5 sec. again, it deaccelerates at $5m{s^{ - 2}}$ and comes to rest. If the total time for the journey is 25seconds, then what is the average speed for the journey?
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Calculate the average time and the average distance using their mathematical expression. As the average speed is the ratio of the average distance to the average time. By using this relation, we can calculate the average speed for the journey.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at \cr
& s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \cr
& {V^2} - {U^2} = 2aS \cr} $
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the average speed of an object in a time interval is defined as the distance traveled by the object divided by the time interval. Additionally, we know the three equations of motions in their mathematical expressions as:
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at \cr
& s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \cr
& {V^2} - {U^2} = 2aS \cr} $
where v represents the final velocity,
$u$ represents the initial velocity,
$t$ represents the time period,
$a$ represents the acceleration,
$S$ represents the displacement.
Using this expression, we will calculate the required result of the given question.
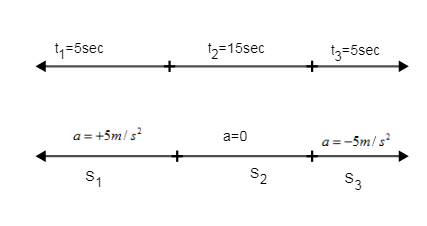
Consider the time taken for ${S_1} = 5\sec ,$ the time taken for ${S_2} = 15\sec $ and the time taken for ${S_3} = 5\sec $. Now the total time taken will be given by:
$\eqalign{
& t = {t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3} \cr
& \Rightarrow t = 5 + 15 + 5 \cr
& \therefore t = 25\sec \cr} $
Using the formula, $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
For ${S_1}$ as we know that u = 0 (at rest)
$\eqalign{
& {S_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t_1}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times {(5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 25 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 125 \cr
& \therefore {S_1} = \dfrac{{125}}{2} = 62.5m \cr} $
For ${S_2}$, we know,
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at = 0 + 5\left( 5 \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow V = 25m/s \cr
& {S_2} = 25 \times 15 + \dfrac{1}{2}a{(15)^2} \cr
& {\text{since }}a = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_2} = 25 \times 15 + 0 \cr
& \therefore {S_2} = 375m \cr} $
Clearly, ${{\text{V}}^2}{\text{ - }}{{\text{U}}^2} = 2a{S_3}$
Put ${\text{V = 0, U = 25m/s, a = - 5m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$
So, we have :
$\eqalign{
& 0 - {\left( {25} \right)^2} = 2\left( { - 5} \right){S_3} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_3} = \dfrac{{ - 25 \times 25}}{{ - 2 \times 5}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_3} = \dfrac{{625}}{{10}} \cr
& \therefore {S_3} = 62.5m \cr} $
Now the average distance $S = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3}$
$\eqalign{
& S = 6.25 + 375 + 62.5 \cr
& \therefore S = 500m \cr} $
Let’s find the average speed that is
Average speed = $\dfrac{S}{t} = \dfrac{{500}}{{25}}$
Average speed = 20m/s
Hence the average speed for the journey will be 20m/s.
Note:
Average speed is a scalar quantity and SI units are $m{s^{ - 1}}$ average speed can be calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the total time taken. Average distance is the sum of all the distances traveled by body or object. The average speed gives the overall “rapidity” with which the particle moves in a certain interval.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at \cr
& s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \cr
& {V^2} - {U^2} = 2aS \cr} $
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the average speed of an object in a time interval is defined as the distance traveled by the object divided by the time interval. Additionally, we know the three equations of motions in their mathematical expressions as:
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at \cr
& s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \cr
& {V^2} - {U^2} = 2aS \cr} $
where v represents the final velocity,
$u$ represents the initial velocity,
$t$ represents the time period,
$a$ represents the acceleration,
$S$ represents the displacement.
Using this expression, we will calculate the required result of the given question.

Consider the time taken for ${S_1} = 5\sec ,$ the time taken for ${S_2} = 15\sec $ and the time taken for ${S_3} = 5\sec $. Now the total time taken will be given by:
$\eqalign{
& t = {t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3} \cr
& \Rightarrow t = 5 + 15 + 5 \cr
& \therefore t = 25\sec \cr} $
Using the formula, $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
For ${S_1}$ as we know that u = 0 (at rest)
$\eqalign{
& {S_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t_1}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times {(5)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 25 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 125 \cr
& \therefore {S_1} = \dfrac{{125}}{2} = 62.5m \cr} $
For ${S_2}$, we know,
$\eqalign{
& V = U + at = 0 + 5\left( 5 \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow V = 25m/s \cr
& {S_2} = 25 \times 15 + \dfrac{1}{2}a{(15)^2} \cr
& {\text{since }}a = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_2} = 25 \times 15 + 0 \cr
& \therefore {S_2} = 375m \cr} $
Clearly, ${{\text{V}}^2}{\text{ - }}{{\text{U}}^2} = 2a{S_3}$
Put ${\text{V = 0, U = 25m/s, a = - 5m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$
So, we have :
$\eqalign{
& 0 - {\left( {25} \right)^2} = 2\left( { - 5} \right){S_3} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_3} = \dfrac{{ - 25 \times 25}}{{ - 2 \times 5}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {S_3} = \dfrac{{625}}{{10}} \cr
& \therefore {S_3} = 62.5m \cr} $
Now the average distance $S = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3}$
$\eqalign{
& S = 6.25 + 375 + 62.5 \cr
& \therefore S = 500m \cr} $
Let’s find the average speed that is
Average speed = $\dfrac{S}{t} = \dfrac{{500}}{{25}}$
Average speed = 20m/s
Hence the average speed for the journey will be 20m/s.
Note:
Average speed is a scalar quantity and SI units are $m{s^{ - 1}}$ average speed can be calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the total time taken. Average distance is the sum of all the distances traveled by body or object. The average speed gives the overall “rapidity” with which the particle moves in a certain interval.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




