
A capillary tube of radius $r$ is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height $h$. The water of mass there in the capillary tube is $5g$. Some other capillary tube of radius $2r$ is immersed in water. The mass of the water which rise in this tube will be given as,
$\begin{align}
& A.2.5g \\
& B.5.0g \\
& C.10g \\
& D.20g \\
\end{align}$
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The product of radius and the height will be a constant. Using this relation, find the height of the second capillary tube. Mass of the water in the capillary can be calculated as the product of the density of the water and the volume of the container.
Complete answer:
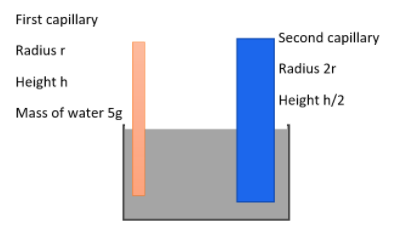
The radius of the first capillary tube is given as,
${{r}_{1}}=r$
The height of the first capillary tube will be,
${{h}_{1}}=h$
The radius of the second capillary will be,
${{r}_{2}}=2r$
Here the product of the height and the radius will be a constant, that is we can write that,
$rh=\text{constant}$
Substituting the parameters mentioned in the question will give,
${{r}_{1}}{{h}_{1}}={{r}_{2}}{{h}_{2}}$
That is,
$\begin{align}
& rh=2r{{h}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{h}{2} \\
\end{align}$
The mass of the water in the capillary can be found using the equation,
$M=\rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right)$
Here $\rho $be the density of water.
For the first capillary tube, the mass of the water in it is given as,
${{M}_{1}}=5g$
Substituting this in the equation of mass will give,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{1}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{1}}^{2}{{h}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 5=\rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now in the case of second capillary tube, we can write that,
${{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{2}}^{2}{{h}_{2}} \right)$
Substitute the values in it will give,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{2}}^{2}{{h}_{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}\dfrac{h}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Simplifying the equation can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{2}}=2\times \rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}=2\times \left[ \text{mass of the water in first capillary} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the mass of water in the second capillary will be,
${{M}_{2}}=2\times 5=10g$
The answer for this question is option C.
Note:
Capillary action is the property of a liquid to flow in narrow regions without the assistance or any opposition of external forces like gravity. A capillary tube is a tube with a minute cavity. The capillary action is also known as capillarity.
Complete answer:

The radius of the first capillary tube is given as,
${{r}_{1}}=r$
The height of the first capillary tube will be,
${{h}_{1}}=h$
The radius of the second capillary will be,
${{r}_{2}}=2r$
Here the product of the height and the radius will be a constant, that is we can write that,
$rh=\text{constant}$
Substituting the parameters mentioned in the question will give,
${{r}_{1}}{{h}_{1}}={{r}_{2}}{{h}_{2}}$
That is,
$\begin{align}
& rh=2r{{h}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{h}{2} \\
\end{align}$
The mass of the water in the capillary can be found using the equation,
$M=\rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right)$
Here $\rho $be the density of water.
For the first capillary tube, the mass of the water in it is given as,
${{M}_{1}}=5g$
Substituting this in the equation of mass will give,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{1}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{1}}^{2}{{h}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 5=\rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now in the case of second capillary tube, we can write that,
${{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{2}}^{2}{{h}_{2}} \right)$
Substitute the values in it will give,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{r}_{2}}^{2}{{h}_{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}=\rho \left( \pi {{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}\dfrac{h}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Simplifying the equation can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{M}_{2}}=2\times \rho \left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}=2\times \left[ \text{mass of the water in first capillary} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the mass of water in the second capillary will be,
${{M}_{2}}=2\times 5=10g$
The answer for this question is option C.
Note:
Capillary action is the property of a liquid to flow in narrow regions without the assistance or any opposition of external forces like gravity. A capillary tube is a tube with a minute cavity. The capillary action is also known as capillarity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




