
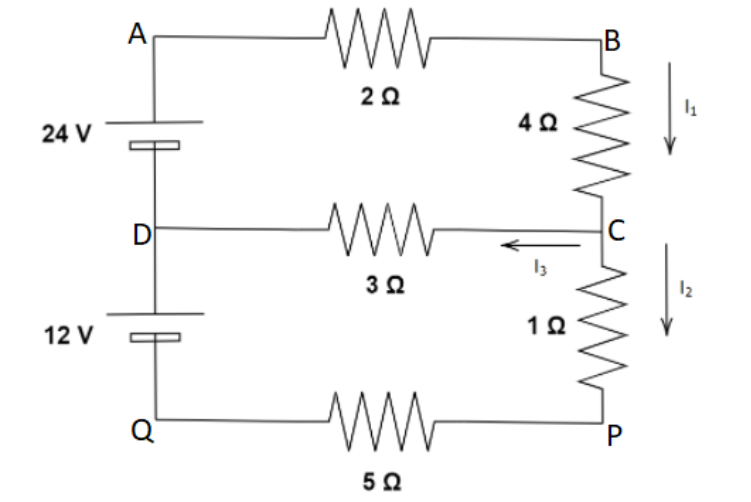
(A) Can the circuit shown in Figure be reduced to a single resistor connected to a battery? Explain. Calculate the currents
(B) \[{I_1}\]
(C) \[{I_2}\]
(D) \[{I_3}\]

Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find three quantities of current in the figure by using Kirchhoff's laws. Initially we are asked if the given circuit can be reduced into one resistor and a battery. We can start by looking at the circuit and observing it will lead us to the solution to the first part of the question. Then we can solve for the three asked quantities using Kirchhoff’s laws.
Formulas used: Kirchhoff’s loop law states that the algebraic sum of potential difference, and resistive elements, in any loop must be equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
We can start one by one.
(A) The given circuit cannot be converted into one resistor and a battery as there are already two voltage sources present (the two batteries).
(B) Applying Kirchhoff’s law
We can see that from the figure \[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3}\]
In the upper loop ABCD, we can apply Kirchhoff’s law and get,
\[24 = 2{I_1} + 4{I_1} + 3{I_3}\]
Then we can use the relation between all the three current and get,
\[3{I_3} + 2{I_2} = 8\]
We also divided the whole equation by three to get the above simpler equation.
Now applying the loop DCPQ, we get
\[12 = - 3{I_3} + {I_2} + 5{I_2}\]
We can simplify this in order to get,
\[4 = 2{I_2} - {I_3}\]
We can solve the final equations we got from solving the two loops using Kirchhoff’s loop rule and get,
\[{I_3} = 1A\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_2} = 2.5\,A\]
Now we have already seen that the relationships between the three values of current is given by
\[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3}\]
We now substitute the values in the above equation and get,
\[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3} \\
\Rightarrow {I_1} = 1 + 2.5 \\
\therefore {I_1} = 3.5\,A\]
In conclusion the values of the three unknown values of current is \[{I_1} = 3.5\,A\] , \[{I_3} = 1\,A\] , and, \[{I_2} = 2.5\,A\].
Note: Kirchhoff’s laws are usually used to analyze circuits. There are two, namely the current law and a voltage law. At every node, the sum of all current coming in the node must be zero. Nodes are places that attach to each other.
Formulas used: Kirchhoff’s loop law states that the algebraic sum of potential difference, and resistive elements, in any loop must be equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
We can start one by one.
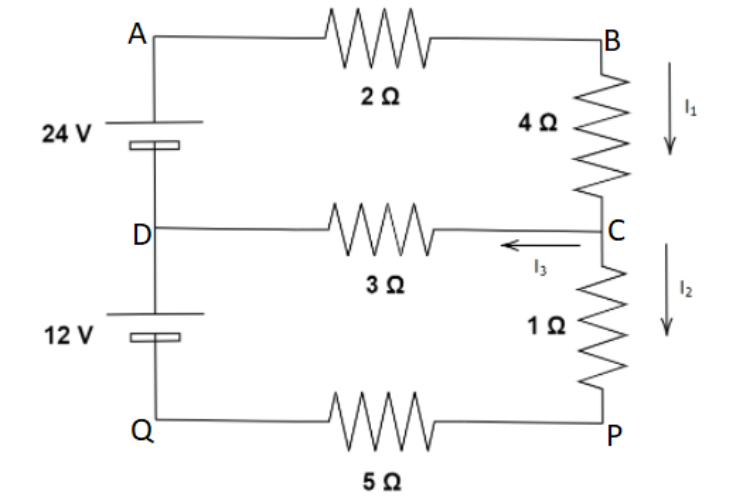
(A) The given circuit cannot be converted into one resistor and a battery as there are already two voltage sources present (the two batteries).
(B) Applying Kirchhoff’s law
We can see that from the figure \[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3}\]

In the upper loop ABCD, we can apply Kirchhoff’s law and get,
\[24 = 2{I_1} + 4{I_1} + 3{I_3}\]
Then we can use the relation between all the three current and get,
\[3{I_3} + 2{I_2} = 8\]
We also divided the whole equation by three to get the above simpler equation.
Now applying the loop DCPQ, we get
\[12 = - 3{I_3} + {I_2} + 5{I_2}\]
We can simplify this in order to get,
\[4 = 2{I_2} - {I_3}\]
We can solve the final equations we got from solving the two loops using Kirchhoff’s loop rule and get,
\[{I_3} = 1A\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_2} = 2.5\,A\]
Now we have already seen that the relationships between the three values of current is given by
\[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3}\]
We now substitute the values in the above equation and get,
\[{I_1} = {I_2} + {I_3} \\
\Rightarrow {I_1} = 1 + 2.5 \\
\therefore {I_1} = 3.5\,A\]
In conclusion the values of the three unknown values of current is \[{I_1} = 3.5\,A\] , \[{I_3} = 1\,A\] , and, \[{I_2} = 2.5\,A\].
Note: Kirchhoff’s laws are usually used to analyze circuits. There are two, namely the current law and a voltage law. At every node, the sum of all current coming in the node must be zero. Nodes are places that attach to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




