
A bullet fired into a fixed target loses half of its velocity after penetrating 3cm. How much further it will penetrate before coming to rest assuming that it faces constant resistance to motion?
A. 2.0cm
B. 3.0cm
C. 1.0cm
D. 1.5cm
Answer
529.3k+ views
Hint: Firstly, you could make a neat diagram of the situation that is discussed in the question. Then you could first find the acceleration of the body by applying an equation of motion for the motion of 3cm. Then you could use the equation of motion for finding the distance penetrated by the bullet before coming to rest.
Formula used:
Equation of motion,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are told that a bullet is being fired into a fixed target. While penetrating into this fixed target, the bullet loses half of its velocity after 3cm. We are asked to find the distance penetrated by this bullet before coming to rest. Assume that the bullet faces constant resistance to motion.
As a first step, let us depict the given situation in a neat diagram.
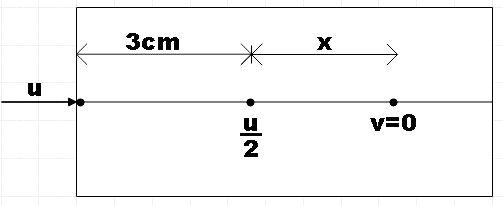
Let the initial and final velocities of the bullet be u and v respectively while penetrating the first 3cm. Then, from Newton’s equations of motion, we have,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
Where, $a$ is the constant acceleration of the bullet and $s=3cm$
Also,
$v=\dfrac{u}{2}$
So,
${{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2a\left( 3 \right)$
$\Rightarrow a=-\dfrac{3{{u}^{2}}}{24}$
$\therefore a=-\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{8}$ …………………………………………….. (1)
Now for finding the distance penetrated by the bullet after this, let us use the same equation of motion again. But, the initial velocity now will be $\dfrac{u}{2}$ and final velocity is zero. So,
$0-{{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}=2ax$
Substituting (1) we get,
$-{{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}=2\left( -\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{8} \right)x$
$\therefore x=1cm$
Therefore, we found that the bullet will penetrate 1cm more into the fixed target before coming to rest.
Hence, option C is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
We should understand that, it is the acceleration of the bullet that is being described as the resistance to motion in the question. From that sentence, it is very clear that the bullet is having constant acceleration of motion. We have assumed this condition throughout the solution.
Formula used:
Equation of motion,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are told that a bullet is being fired into a fixed target. While penetrating into this fixed target, the bullet loses half of its velocity after 3cm. We are asked to find the distance penetrated by this bullet before coming to rest. Assume that the bullet faces constant resistance to motion.
As a first step, let us depict the given situation in a neat diagram.

Let the initial and final velocities of the bullet be u and v respectively while penetrating the first 3cm. Then, from Newton’s equations of motion, we have,
${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
Where, $a$ is the constant acceleration of the bullet and $s=3cm$
Also,
$v=\dfrac{u}{2}$
So,
${{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2a\left( 3 \right)$
$\Rightarrow a=-\dfrac{3{{u}^{2}}}{24}$
$\therefore a=-\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{8}$ …………………………………………….. (1)
Now for finding the distance penetrated by the bullet after this, let us use the same equation of motion again. But, the initial velocity now will be $\dfrac{u}{2}$ and final velocity is zero. So,
$0-{{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}=2ax$
Substituting (1) we get,
$-{{\left( \dfrac{u}{2} \right)}^{2}}=2\left( -\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{8} \right)x$
$\therefore x=1cm$
Therefore, we found that the bullet will penetrate 1cm more into the fixed target before coming to rest.
Hence, option C is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
We should understand that, it is the acceleration of the bullet that is being described as the resistance to motion in the question. From that sentence, it is very clear that the bullet is having constant acceleration of motion. We have assumed this condition throughout the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




