
A boy with a normal brother and colourblind sister has
A. Father normal, mother colourblind
B. Both normal
C. Both colourblind
D. Father colourblind, mother normal
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Color blindness is associated with the X chromosome. A person suffering from colour blindness is unable to identify the difference between certain colours, mostly they cannot distinguish between green and red colours and rarely blue.
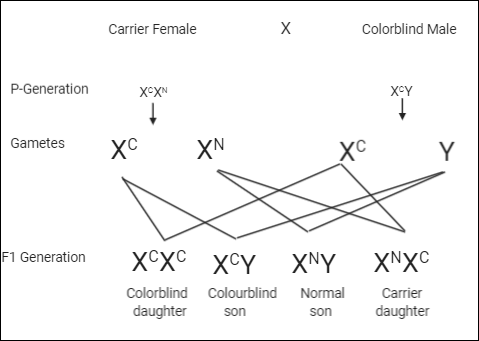
Complete answer: The whole genome or a part of a DNA sequence might get altered in genetic disorders. They are hierarchical, i.e. they are passed from parents to offsprings. Cystic fibrosis, down syndrome, haemophilia, sickle cell anaemia, etc. are few types of genetic disorders. A genetic disorder like colour blindness is usually seen in males. The gene responsible for colour blindness is located on the X-chromosome, hence, it is also known as X-linked inheritance. In this disorder, the person cannot identify colours. It is also called an X-linked recessive disorder because the gene for colour blindness present on the X chromosome always causes expression of the phenotype in male progeny and in females, only if it is homozygous. Let’s consider,
${{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}$ = Defective allele for color blindness
${{\text{X}}^{\text{N}}}$ = Normal allele for color blindness
For the given question, as it says the boy has a normal brother and colourblind sister. Normal brother will be ${{\text{X}}^{\text{N}}}\text{Y}$ and the colorblind sister will be ${{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}$, hence parents of these children can be a colourblind father and a normal mother.
Note: Color blindness is referred to as red-green colour blindness because our retina contains cone cells that perceive colours and can absorb different wavelengths with the help of pigments called opsins also called photo opsins. Opsins are of three types based on the type of wavelength absorption. S-type: absorbs small wavelength (blue-sensitive opsin); M-type: absorbs medium wavelength (green-sensitive opsin); L-type: absorbs large wavelength (red-sensitive opsin). Gene encoding S-type opsin is found on chromosome number 7 whereas M-type and L-type are found exclusively on X-chromosome.
Complete answer: The whole genome or a part of a DNA sequence might get altered in genetic disorders. They are hierarchical, i.e. they are passed from parents to offsprings. Cystic fibrosis, down syndrome, haemophilia, sickle cell anaemia, etc. are few types of genetic disorders. A genetic disorder like colour blindness is usually seen in males. The gene responsible for colour blindness is located on the X-chromosome, hence, it is also known as X-linked inheritance. In this disorder, the person cannot identify colours. It is also called an X-linked recessive disorder because the gene for colour blindness present on the X chromosome always causes expression of the phenotype in male progeny and in females, only if it is homozygous. Let’s consider,
${{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}$ = Defective allele for color blindness
${{\text{X}}^{\text{N}}}$ = Normal allele for color blindness
For the given question, as it says the boy has a normal brother and colourblind sister. Normal brother will be ${{\text{X}}^{\text{N}}}\text{Y}$ and the colorblind sister will be ${{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{C}}}$, hence parents of these children can be a colourblind father and a normal mother.

Note: Color blindness is referred to as red-green colour blindness because our retina contains cone cells that perceive colours and can absorb different wavelengths with the help of pigments called opsins also called photo opsins. Opsins are of three types based on the type of wavelength absorption. S-type: absorbs small wavelength (blue-sensitive opsin); M-type: absorbs medium wavelength (green-sensitive opsin); L-type: absorbs large wavelength (red-sensitive opsin). Gene encoding S-type opsin is found on chromosome number 7 whereas M-type and L-type are found exclusively on X-chromosome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




