
A body of mass m and velocity 9 m/s collides with a stationary body of mass 2m and stick to. Now the combined mass starts to move. What will be combined velocity (in m/s)
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: This question is an easy application of the law of conservation of linear momentum. In this question, the stationary body is having a velocity of 0 m/s. So, the final combine body will have the momentum equal to that of the moving body.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving this question. Let us take a look at all the parameters that have been given to us in the above stated question.
Mass of the moving body = m
Velocity if the moving body = 9 m/s
Now, for the stationary body
The mass of the stationary body = 2m
Now,
We must use the help of the diagram for better clarification
Before the collision
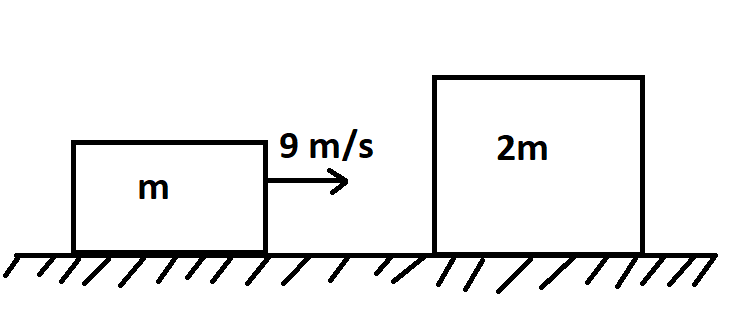
Now,
After the collision, the body of mass m will stick to the body of mass 2m and this combined mass will start moving at some velocity.
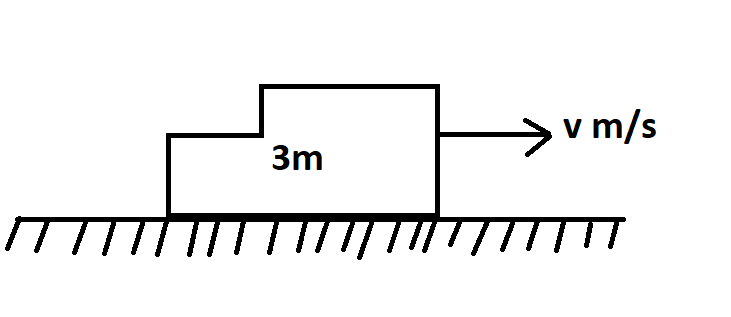
Let us assume the velocity of the combined mass after the collision to be equal to v m/s
Now,
By applying the law of conservation of linear momentum
We have
${{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}=Mv$
Here,
${{m}_{1}}$= m
${{u}_{1}}$ = 9m/s
And,
${{m}_{2}}$= 2m
${{u}_{2}}$= 0 m/s
Also,
M = 3m
Now, using the above value in the formula for the law of conservation of linear momentum
We have
$\Rightarrow m\times 9+m\times 0=3m\times v$
\[\Rightarrow 9m=3mv\]
\[\Rightarrow v=3\]
So, the velocity of the combined mass will be 3 m/s
Note: The law of conservation of momentum says in physics and chemistry that the momentum of an independent device remains constant. Therefore, momentum is said to be preserved over time; that is, momentum is not produced or lost, only converted or moved from one shape to another. Isaac Newton discovered the law of conservation of momentum while he was formulating his laws of motion.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving this question. Let us take a look at all the parameters that have been given to us in the above stated question.
Mass of the moving body = m
Velocity if the moving body = 9 m/s
Now, for the stationary body
The mass of the stationary body = 2m
Now,
We must use the help of the diagram for better clarification
Before the collision

Now,
After the collision, the body of mass m will stick to the body of mass 2m and this combined mass will start moving at some velocity.

Let us assume the velocity of the combined mass after the collision to be equal to v m/s
Now,
By applying the law of conservation of linear momentum
We have
${{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}=Mv$
Here,
${{m}_{1}}$= m
${{u}_{1}}$ = 9m/s
And,
${{m}_{2}}$= 2m
${{u}_{2}}$= 0 m/s
Also,
M = 3m
Now, using the above value in the formula for the law of conservation of linear momentum
We have
$\Rightarrow m\times 9+m\times 0=3m\times v$
\[\Rightarrow 9m=3mv\]
\[\Rightarrow v=3\]
So, the velocity of the combined mass will be 3 m/s
Note: The law of conservation of momentum says in physics and chemistry that the momentum of an independent device remains constant. Therefore, momentum is said to be preserved over time; that is, momentum is not produced or lost, only converted or moved from one shape to another. Isaac Newton discovered the law of conservation of momentum while he was formulating his laws of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




