
A body is thrown upwards and reaches its maximum height. At that position
A) its acceleration is minimum
B) its velocity is zero and its acceleration is also zero
C) its velocity is zero but its acceleration is maximum
D) its velocity is zero and its acceleration is the acceleration due to gravity
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The total energy for the motion of the body will remain constant. The total energy of the body is the sum of its kinetic energy and its potential energy. So by the conservation of energy theorem, only a transfer of energy takes place. Thus the loss in kinetic energy will be equal to the gain in potential energy.
Formula used:
The kinetic energy of a moving body is given by,
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$, where $m$ is the mass of the body and $v$ is the velocity of the body.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure describing the problem at hand.
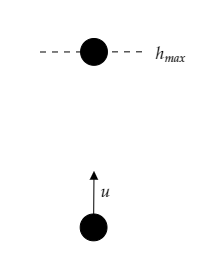
In the above figure, the body is thrown upwards with an initial velocity $u$ and reaches a maximum height ${h_{\max }}$ .
Step 2: Based on the conservation of energy theorem, obtain the acceleration and velocity of the body when it reaches its maximum height.
The thrown body consists of kinetic energy but on reaching the maximum height, all the kinetic energy of the body gets converted to the potential energy of the body.
So at the maximum height, the kinetic energy of the body will be zero.
i.e., at ${h_{\max }}$, $K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = 0$, where $m$ is the mass of the body and $v$ is the final velocity of the body.
$\Rightarrow v = 0$
So at the maximum height, the velocity of the body is zero.
Also at the maximum height, the acceleration of the body will be constant. This acceleration will be the acceleration due to gravity i.e., $a = g$ at ${h_{\max }}$ .
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Initially at the moment the body is thrown upwards, the body only possesses kinetic energy $K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$. Over the course of its motion upwards the velocity decreases and finally becomes zero at the maximum height so that at this point, it only possesses potential energy. The potential energy at this point will be the work done by the body to have displacement ${h_{\max }}$ . Here the force acting on the body is its weight $F = mg$ and thus the potential energy will be $U = mg{h_{\max }}$.
Formula used:
The kinetic energy of a moving body is given by,
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$, where $m$ is the mass of the body and $v$ is the velocity of the body.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure describing the problem at hand.

In the above figure, the body is thrown upwards with an initial velocity $u$ and reaches a maximum height ${h_{\max }}$ .
Step 2: Based on the conservation of energy theorem, obtain the acceleration and velocity of the body when it reaches its maximum height.
The thrown body consists of kinetic energy but on reaching the maximum height, all the kinetic energy of the body gets converted to the potential energy of the body.
So at the maximum height, the kinetic energy of the body will be zero.
i.e., at ${h_{\max }}$, $K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = 0$, where $m$ is the mass of the body and $v$ is the final velocity of the body.
$\Rightarrow v = 0$
So at the maximum height, the velocity of the body is zero.
Also at the maximum height, the acceleration of the body will be constant. This acceleration will be the acceleration due to gravity i.e., $a = g$ at ${h_{\max }}$ .
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Initially at the moment the body is thrown upwards, the body only possesses kinetic energy $K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$. Over the course of its motion upwards the velocity decreases and finally becomes zero at the maximum height so that at this point, it only possesses potential energy. The potential energy at this point will be the work done by the body to have displacement ${h_{\max }}$ . Here the force acting on the body is its weight $F = mg$ and thus the potential energy will be $U = mg{h_{\max }}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




