
A beam of light is incident on a glass plate at an angle of incidence \[60^\circ \]. The reflected ray is completely polarised. If a ray of light incident at angle of \[37^\circ \], then the angle of refraction will be:
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: If the reflected ray of light is completely polarized then the ray of light that is refracted will be perpendicular to the refracted ray of light. We can use this condition to determine the refractive index of the medium which we will then use to determine the angle of refraction when the light ray is incident at \[37^\circ \].
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Snell's law: ${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2}$ where ${\mu _1}$ and ${\mu _2}$ are the refractive index of two different mediums and ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ are the angles made by the ray of light with the normal to the surface of refraction.
Complete step by step answer
Whenever a ray of light interacts with an interface, some part of it is reflected, while some part of it is refracted in the other medium. If the reflected ray is perpendicular to the refracted ray only then will the reflected ray be completely polarized. Let us start by drawing a diagram of this situation.
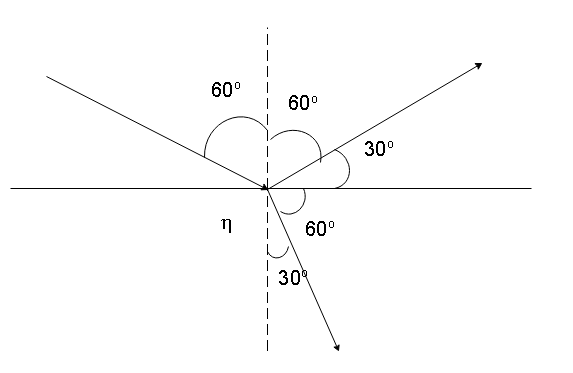
As we can see, for the refracted ray to be perpendicular to the reflected ray, the refracted ray must form an angle of $30^\circ $ with the normal.
Using Snell’s’ law we can write
${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2}$
Since the first medium is air, we can write
$1\sin 60^\circ = {\mu _2}\sin 30^\circ $
$1\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = {\mu _2}\dfrac{1}{2}$
Which gives us the refractive index of the medium as,
${\mu _2} = \sqrt 3 $
Now that we know the refractive index of the second medium, if the ray of light is incident at \[37^\circ \], the angle of refraction can be calculated using Snell’s law as
$1\sin 37^\circ = \sqrt 3 \sin {\theta _2}$
Which gives us,
\[\sin {\theta _2} = \dfrac{3}{{5\sqrt 3 }}\]
Hence the angle of refraction is,
\[\therefore {\theta _2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{{5\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\]
Note
The relation of reflected and refracted rays is only provided to us to determine the refractive index of the second medium. When the light ray is incident at \[37^\circ \] there is no direct relation between the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction and the reflected light will also not be completely polarised.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Snell's law: ${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2}$ where ${\mu _1}$ and ${\mu _2}$ are the refractive index of two different mediums and ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ are the angles made by the ray of light with the normal to the surface of refraction.
Complete step by step answer
Whenever a ray of light interacts with an interface, some part of it is reflected, while some part of it is refracted in the other medium. If the reflected ray is perpendicular to the refracted ray only then will the reflected ray be completely polarized. Let us start by drawing a diagram of this situation.

As we can see, for the refracted ray to be perpendicular to the reflected ray, the refracted ray must form an angle of $30^\circ $ with the normal.
Using Snell’s’ law we can write
${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2}$
Since the first medium is air, we can write
$1\sin 60^\circ = {\mu _2}\sin 30^\circ $
$1\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = {\mu _2}\dfrac{1}{2}$
Which gives us the refractive index of the medium as,
${\mu _2} = \sqrt 3 $
Now that we know the refractive index of the second medium, if the ray of light is incident at \[37^\circ \], the angle of refraction can be calculated using Snell’s law as
$1\sin 37^\circ = \sqrt 3 \sin {\theta _2}$
Which gives us,
\[\sin {\theta _2} = \dfrac{3}{{5\sqrt 3 }}\]
Hence the angle of refraction is,
\[\therefore {\theta _2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{{5\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\]
Note
The relation of reflected and refracted rays is only provided to us to determine the refractive index of the second medium. When the light ray is incident at \[37^\circ \] there is no direct relation between the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction and the reflected light will also not be completely polarised.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




