
A bar magnet of dipole moment $M$ is bent at midpoint by ${90^ \circ }$(in the form of English alphabet ‘L’). The new magnetic dipole moment of the magnet will be
A. $M$
B. $\dfrac{M}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
C. $\sqrt 2 M$
D. $\dfrac{M}{2}$
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: We can find the resultant magnetic dipole moment by using the concept of magnetic dipole moment and resultant of two vectors. The dipole moment of the magnet is the product of its pole strength and its magnetic length.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a bar magnet whose pole strength is $m$. When the bar magnet is bent at midpoint by ${90^ \circ }$, the magnetic dipole moment of each bar magnet is changed.The length of the original bar magnet is gets halved and hence, the magnetic dipole moment of each bar magnet is also gets halved as magnetic dipole moment , $M = m2l$. Here, $m$ is pole strength and $2l$ is magnetic length of the bar magnet.
Now, we know that the magnetic dipole moment is the vector quantity which directs from the South pole to North pole of the magnet. Hence, the resultant magnetic dipole moment of the new arrangement is shown as
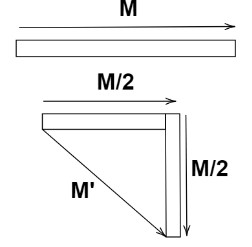
Magnitude of the resultant dipole moment is
$M' = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow M' = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{M^2}}}{2}} $
We get, $M' = \dfrac{M}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
So, the new magnetic dipole moment of the magnet is $M' = \dfrac{M}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
Note: The magnetic dipole moment of the bar magnet is proportional to its length. It is a vector quantity which is directed from $ - m$ to $ + m$ i.e. from south to north pole. The unit of the dipole moment is $A{m^2}$ . This is because the pole strength of the bar magnet depends on the current flowing through the area of the bar magnet.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a bar magnet whose pole strength is $m$. When the bar magnet is bent at midpoint by ${90^ \circ }$, the magnetic dipole moment of each bar magnet is changed.The length of the original bar magnet is gets halved and hence, the magnetic dipole moment of each bar magnet is also gets halved as magnetic dipole moment , $M = m2l$. Here, $m$ is pole strength and $2l$ is magnetic length of the bar magnet.
Now, we know that the magnetic dipole moment is the vector quantity which directs from the South pole to North pole of the magnet. Hence, the resultant magnetic dipole moment of the new arrangement is shown as

Magnitude of the resultant dipole moment is
$M' = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{M}{2}} \right)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow M' = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{M^2}}}{2}} $
We get, $M' = \dfrac{M}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
So, the new magnetic dipole moment of the magnet is $M' = \dfrac{M}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
Note: The magnetic dipole moment of the bar magnet is proportional to its length. It is a vector quantity which is directed from $ - m$ to $ + m$ i.e. from south to north pole. The unit of the dipole moment is $A{m^2}$ . This is because the pole strength of the bar magnet depends on the current flowing through the area of the bar magnet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




