
A ball with charge $-50\;e$ is placed at the centre of a hollow spherical shell that has a net charge $-50\;e$. What is the charge on the shell’s outer surface?
A. -50e
B. Zero
C. -100e
D. +100e
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: Recall that like charges repel and unlike charges attract. We are given the total charge of the shell, which is the sum of the charges on the inner surface of the shell and the outer shell surface. Now, we have a negatively charged ball placed at the centre of the hollow sphere. This ball induces a positive charge of same magnitude on the inner shell, and consequently a negative charge of the outer shell. Use this to substitute values into the total shell-charge equation and obtain the appropriate result.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that the net charge of the hollow spherical shell is $-50\;e$. This means that the sum of charges on the inner surface and outer surface of the shell is $-50\;e$. If $q_1$ is the charge on the inner surface of the shell and $q_2$ is the charge on the outer surface of the shell, then,
$q_1+q_2 = -50\;e$
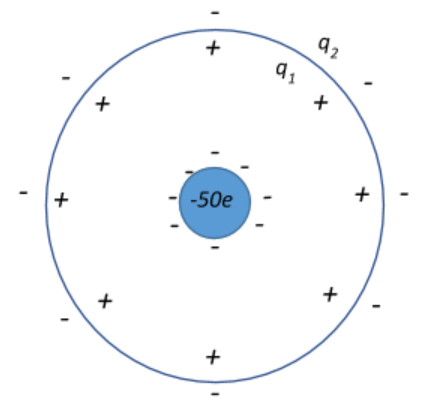
Now, the charge on the inner surface of the shell is the charge induced by the presence of the ball of charge $-50\;e$. Since the ball has a charge of $-50\;e$, it induces an equal but opposite charge of the inner surface of the sphere due to electrostatic attraction. This means that $q_1 = +50\;e$
Substituting this back in our first equation, we can get the charge on the shell’s outer surface.
$+50\;e+q_2=-50\;e$
$\Rightarrow q_2 = -50\;e-50\;e = -100\;e$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Recall that the charges get distributed over the surface of the shell. This is because like charges move away from each other and finally orient themselves at the farthest distance. These collective distribution of charges farthest distances from the centre forms an equipotential surface. Thus, all the charge carried by the shell gets distributed over the inner and outer surface of the shell with no charges constituting the mass of the shell.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that the net charge of the hollow spherical shell is $-50\;e$. This means that the sum of charges on the inner surface and outer surface of the shell is $-50\;e$. If $q_1$ is the charge on the inner surface of the shell and $q_2$ is the charge on the outer surface of the shell, then,
$q_1+q_2 = -50\;e$

Now, the charge on the inner surface of the shell is the charge induced by the presence of the ball of charge $-50\;e$. Since the ball has a charge of $-50\;e$, it induces an equal but opposite charge of the inner surface of the sphere due to electrostatic attraction. This means that $q_1 = +50\;e$
Substituting this back in our first equation, we can get the charge on the shell’s outer surface.
$+50\;e+q_2=-50\;e$
$\Rightarrow q_2 = -50\;e-50\;e = -100\;e$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Recall that the charges get distributed over the surface of the shell. This is because like charges move away from each other and finally orient themselves at the farthest distance. These collective distribution of charges farthest distances from the centre forms an equipotential surface. Thus, all the charge carried by the shell gets distributed over the inner and outer surface of the shell with no charges constituting the mass of the shell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




