
A ball of mass $m$ approaches a wall of mass $M$( $ > > m$ ) with a speed $4m{s^{ - 1}}$ along the normal to the wall. The speed of the wall is $1m{s^{ - 1}}$ towards the ball. Find the speed of the ball after an elastic collision with the wall.
A. $5m{s^{ - 1}}$ away from the wall
B. $3m{s^{ - 1}}$ away from the wall
C. $9m{s^{ - 1}}$ away from the wall
D. $6m{s^{ - 1}}$ away from the wall
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint:-Here it is mentioned that the collision of the ball with the wall is elastic. For an elastic collision, the ratio of the relative velocity of separation to the relative velocity of approach will be equal to one. Since the mass of the wall is very much greater than the ball, its change in velocity can be assumed to be zero.
Formulas used:
The relative velocity of separation of two bodies is given by, ${v_{sep}} = {v_2} - {v_1}$ where ${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first body and ${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second body.
The relative velocity of approach of two bodies is given by, ${v_{app}} = {v_2} - {v_1}$ where ${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first body and ${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second body.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a figure depicting the collision of the ball and the wall and list the parameters known from the question.
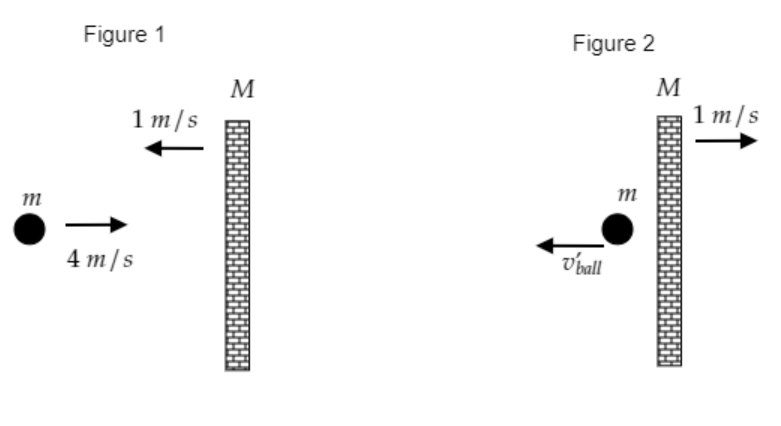
Figure 1 depicts the state of the system before collision and figure 2 depicts the state of the system after the collision.
The velocity with which the ball approaches is given to be ${v_{ball}} = 4m{s^{ - 1}}$ and the velocity with which the wall approaches is given to be ${v_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
After the collision, the velocity of the wall does not change i.e., ${v_{wall}} = {v'_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Let ${v'_{ball}}$ be the velocity with which the ball moves after the collision.
Step 2: Express the relative velocity of approach and separation for the given collision.
The relative velocity of approach of the ball and the wall will be ${v_{app}} = {v_{ball}} - {v_{wall}}$ ------- (1).
Substituting for ${v_{ball}} = 4m{s^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_{wall}} = - 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (1) we get, ${v_{app}} = 4 - \left( { - 1} \right) = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus the relative velocity of approach is ${v_{app}} = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Now the relative velocity of separation of the ball and the wall will be ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - {v'_{wall}}$ -------(2).
Substituting for ${v'_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (2) we get, ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - 1$
Thus the relative velocity of separation is ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - 1$ .
Step 3: Express the ratio $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}}$ for the elastic collision to find ${v'_{ball}}$ .
Now the ratio of the relative velocity of separation to the relative velocity of approach of the above mentioned elastic collision can be expressed as $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}} = 1$ ------- (3)
Substituting for ${v_{app}} = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} + 1$ in equation (3) we get, $\dfrac{{{{v'}_{ball}} + 1}}{5} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {v'_{ball}} = 5 + 1 = 6{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus the velocity of the ball after the collision is ${v'_{ball}} = 6{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ and it moves away from the wall.
So the correct option is D.
Additional information: The ratio $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}}$ is referred to as the coefficient of restitution and is denoted by $e$. It is a number which determines the amount of kinetic energy lost during a collision. For a perfectly inelastic collision, $e = 0$ .
Note:- Here the ball is considered to move in the positive x-direction as it approaches the wall to collide with it, whereas the wall moves in the negative x-direction. So we substitute ${v_{wall}} = - 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (1). After the collision, the wall moves with the same velocity in the positive x-direction and so we substitute ${v_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (2).
Formulas used:
The relative velocity of separation of two bodies is given by, ${v_{sep}} = {v_2} - {v_1}$ where ${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first body and ${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second body.
The relative velocity of approach of two bodies is given by, ${v_{app}} = {v_2} - {v_1}$ where ${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first body and ${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second body.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a figure depicting the collision of the ball and the wall and list the parameters known from the question.

Figure 1 depicts the state of the system before collision and figure 2 depicts the state of the system after the collision.
The velocity with which the ball approaches is given to be ${v_{ball}} = 4m{s^{ - 1}}$ and the velocity with which the wall approaches is given to be ${v_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
After the collision, the velocity of the wall does not change i.e., ${v_{wall}} = {v'_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Let ${v'_{ball}}$ be the velocity with which the ball moves after the collision.
Step 2: Express the relative velocity of approach and separation for the given collision.
The relative velocity of approach of the ball and the wall will be ${v_{app}} = {v_{ball}} - {v_{wall}}$ ------- (1).
Substituting for ${v_{ball}} = 4m{s^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_{wall}} = - 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (1) we get, ${v_{app}} = 4 - \left( { - 1} \right) = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus the relative velocity of approach is ${v_{app}} = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Now the relative velocity of separation of the ball and the wall will be ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - {v'_{wall}}$ -------(2).
Substituting for ${v'_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (2) we get, ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - 1$
Thus the relative velocity of separation is ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} - 1$ .
Step 3: Express the ratio $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}}$ for the elastic collision to find ${v'_{ball}}$ .
Now the ratio of the relative velocity of separation to the relative velocity of approach of the above mentioned elastic collision can be expressed as $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}} = 1$ ------- (3)
Substituting for ${v_{app}} = 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ and ${v_{sep}} = {v'_{ball}} + 1$ in equation (3) we get, $\dfrac{{{{v'}_{ball}} + 1}}{5} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {v'_{ball}} = 5 + 1 = 6{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus the velocity of the ball after the collision is ${v'_{ball}} = 6{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ and it moves away from the wall.
So the correct option is D.
Additional information: The ratio $\dfrac{{{v_{sep}}}}{{{v_{app}}}}$ is referred to as the coefficient of restitution and is denoted by $e$. It is a number which determines the amount of kinetic energy lost during a collision. For a perfectly inelastic collision, $e = 0$ .
Note:- Here the ball is considered to move in the positive x-direction as it approaches the wall to collide with it, whereas the wall moves in the negative x-direction. So we substitute ${v_{wall}} = - 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (1). After the collision, the wall moves with the same velocity in the positive x-direction and so we substitute ${v_{wall}} = 1{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ in equation (2).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




