
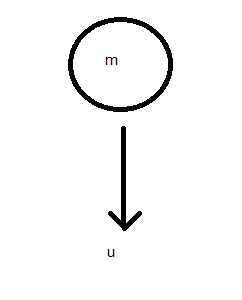
A ball is approaching ground with speed u. If the coefficient of restitution is e. Find the impulse exerted by the normal due to ground on the ball.

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Impulse is a vector quantity. The impulse comes into play when a very large force acts on an object and that too for a very short time. It quantifies the overall effect of a force acting over time. According to Newton’s third law, forces always occur in pairs. So, when the ball applies force on the ground, the ground also applies an equivalent and equal force on the ball.
Complete step by step answer:
Let before collision velocity=u and after collision velocity=v
The coefficient of restitution always satisfies \[0\le e\le 1\]
When e=0, the balls remain in contact after the collision. When e=1, the collision is elastic: there is no loss of kinetic energy. The relationship between the coefficient of restitution and impulse can be written as \[v=eu\]
Where Impulse due to normal = change in momentum
Putting it mathematically we get,
\[J=mv-(-mu)\]
But\[v=eu\]
So, \[J=meu+mu\]
\[J=mu(e+1)\]
Hence this is the required answer.
Additional Information:
'e' is a consequence of Newton's Experimental Law of Impact. the coefficient of restitution has no unit; it is a dimensionless ratio. It is the ratio of the relative velocity of an object after collision to the relative velocity of the object before collision. It lies between 0 to 1
Note:
In such problems we have to keep in mind that velocity is a vector quantity and hence, such we have to also take into account its direction. If the top to down direction is taking positive then its opposite will be taken negative and vice-versa.
Complete step by step answer:
Let before collision velocity=u and after collision velocity=v
The coefficient of restitution always satisfies \[0\le e\le 1\]
When e=0, the balls remain in contact after the collision. When e=1, the collision is elastic: there is no loss of kinetic energy. The relationship between the coefficient of restitution and impulse can be written as \[v=eu\]
Where Impulse due to normal = change in momentum
Putting it mathematically we get,
\[J=mv-(-mu)\]
But\[v=eu\]
So, \[J=meu+mu\]
\[J=mu(e+1)\]
Hence this is the required answer.
Additional Information:
'e' is a consequence of Newton's Experimental Law of Impact. the coefficient of restitution has no unit; it is a dimensionless ratio. It is the ratio of the relative velocity of an object after collision to the relative velocity of the object before collision. It lies between 0 to 1
Note:
In such problems we have to keep in mind that velocity is a vector quantity and hence, such we have to also take into account its direction. If the top to down direction is taking positive then its opposite will be taken negative and vice-versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




