
A, B, C are three functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula \[{{{C}}_4}{{{H}}_8}{{O}}\]. Isomers A and C give positive Tollens test whereas B does not give Tollen’s test but gives iodoform test. Isomers A and B on reduction with ${{Zn}}\left( {{{Hg}}} \right)/{{HCl}}$ give the same product D. Write the structures of A, B, C, D.
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: Only aldehydes give positive results for the Tollens test. The compounds which have a carbonyl carbon which is attached to a methyl group give positive result for Iodoform test. ${{Zn}}\left( {{{Hg}}} \right)/{{HCl}}$ reagent is used for Clemmenson’s reduction of carbonyl carbon to methylene.
Complete step by step solution:
The first hint given was that A, B, C are non-cyclic, i.e. they are aliphatic compounds and they do not have a ring structure. And the chemical formula is \[{{{C}}_4}{{{H}}_8}{{O}}\]. Since four carbon atoms are there, the parent name starts with “but”.
Now let’s consider the Tollen’s test. This is mainly used to check whether there is an aldehyde group or not. The chemical name of Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate, ${\left[ {{{Ag}}{{\left( {{{N}}{{{H}}_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + }$. When a mixture containing an aldehydic group reacts with Tollen’s reagent, a silver mirror is formed. This is done in an alkaline medium with exposure of heat. The reaction is given below:
${{RCHO}} + 2{\left[ {{{Ag}}{{\left( {{{N}}{{{H}}_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + } + 3{{O}}{{{H}}^ - } \to {{RCO}}{{{O}}^ - } + 2{{Ag}} + 2{{{H}}_2}{{O}} + 4{{N}}{{{H}}_3}$
This proves that isomers A and C are aldehydes.
We know that the compound B does not give Tollens test, but gives a positive result for the iodoform test. Only the compounds which have a carbonyl carbon which is attached to a methyl group react with this type of reaction. This indicates that the compound B is a methyl ketone.
When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with ${{Zn}}\left( {{{Hg}}} \right)/{{HCl}}$, oxygen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon is replaced with two hydrogen atoms. This gives the compound D as an alkane.
Considering all the hints given in the question, we get
B is
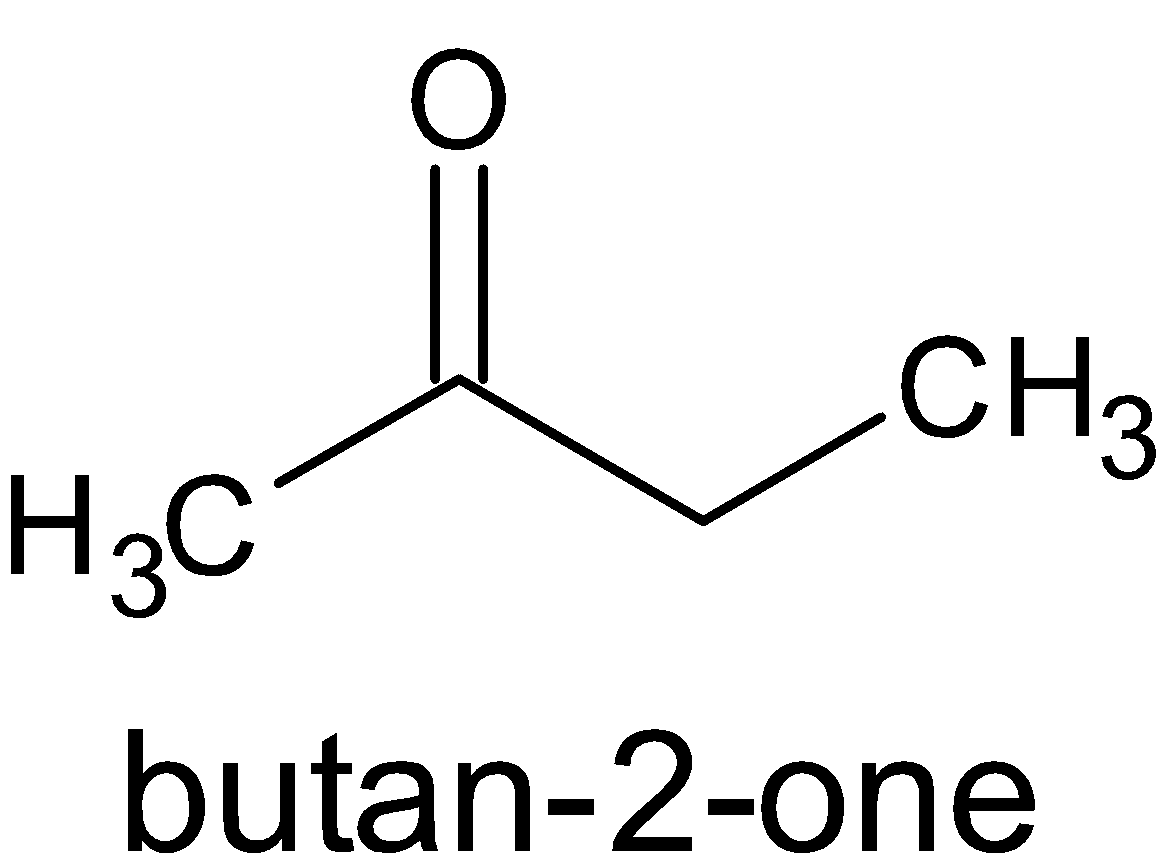 .
.
A is
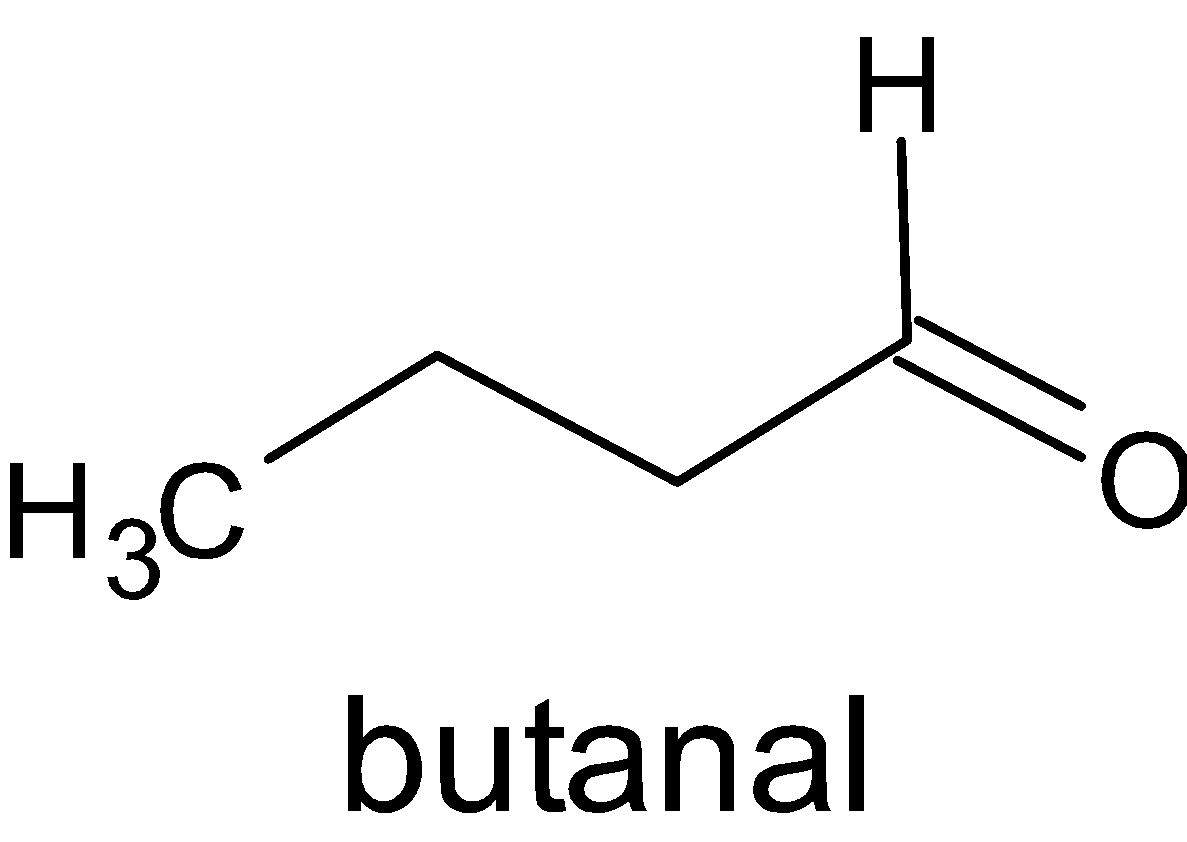 .
.
D is
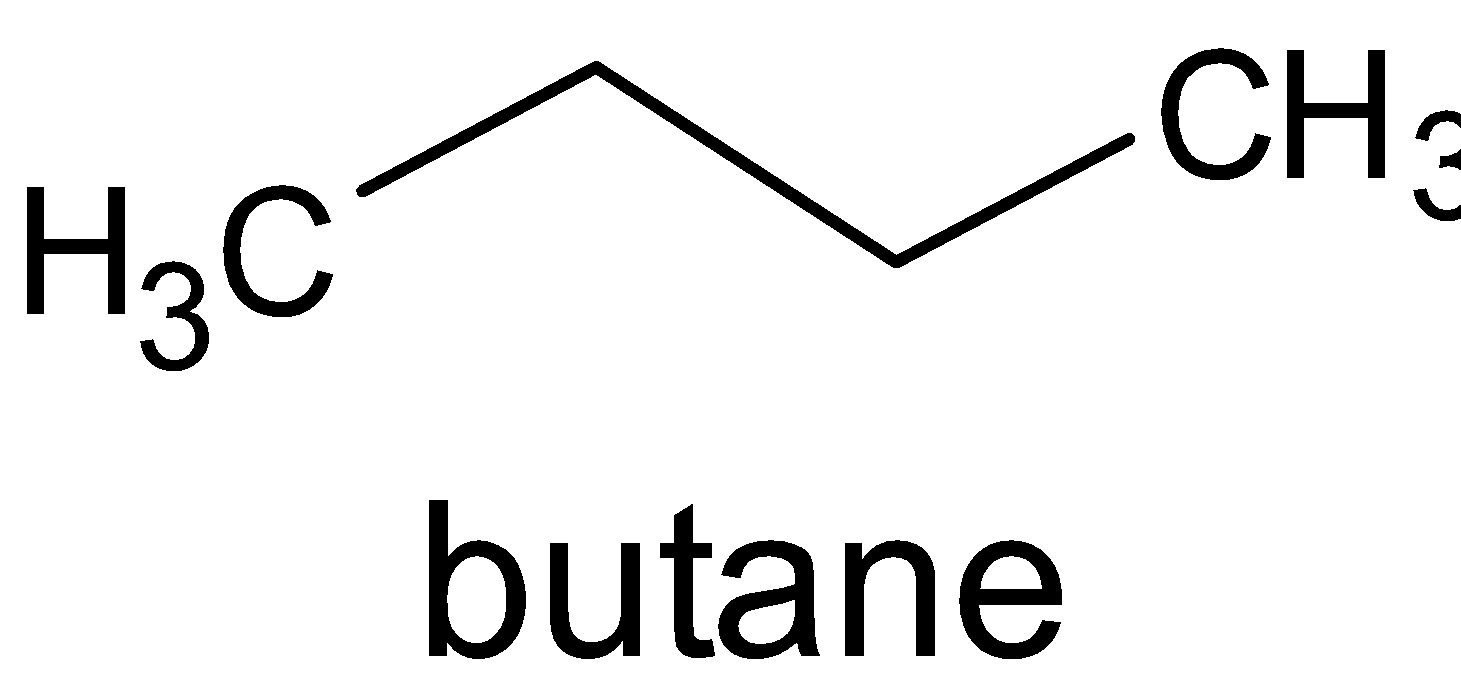 .
.
And C is
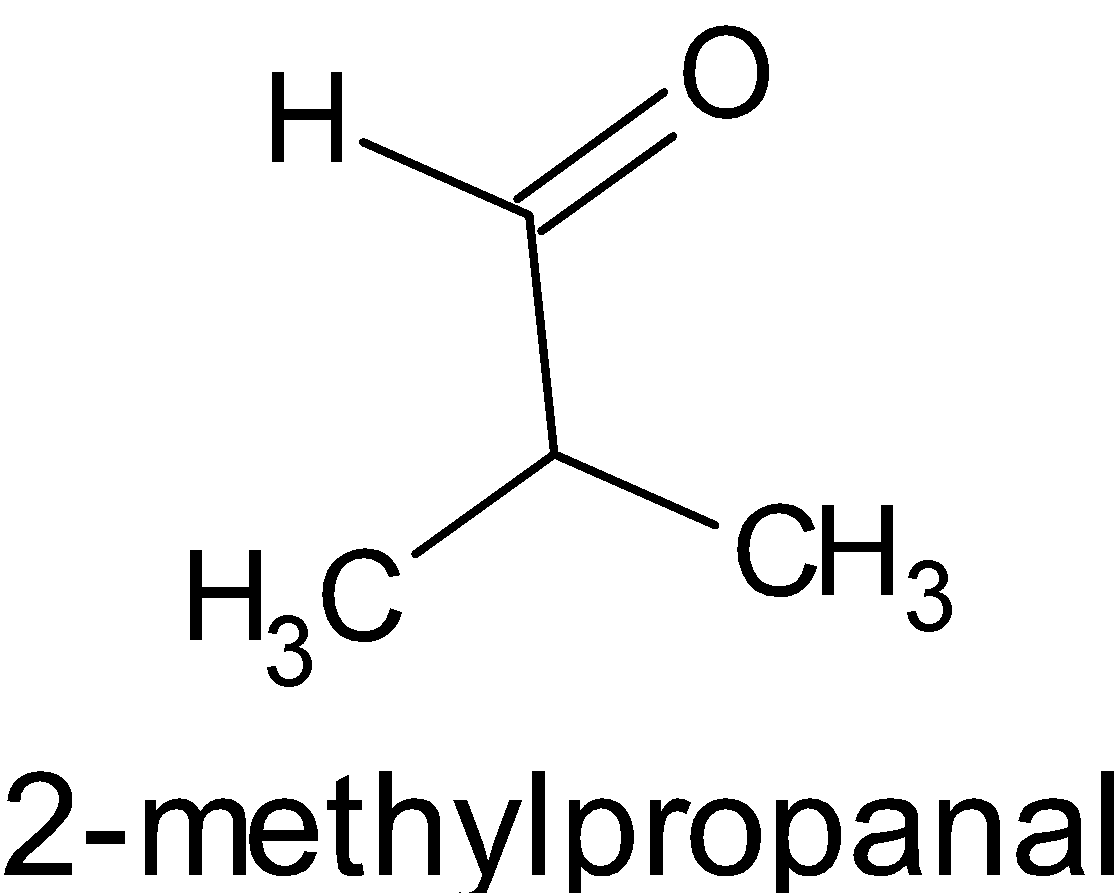 .
.
Note:
The silver mirror formed is due to the presence of element silver. Silver is reduced from $ + 1$ state to $0$. Also during Tollen’s test, aldehyde is converted to carboxylate anion which is an oxidation process.
Complete step by step solution:
The first hint given was that A, B, C are non-cyclic, i.e. they are aliphatic compounds and they do not have a ring structure. And the chemical formula is \[{{{C}}_4}{{{H}}_8}{{O}}\]. Since four carbon atoms are there, the parent name starts with “but”.
Now let’s consider the Tollen’s test. This is mainly used to check whether there is an aldehyde group or not. The chemical name of Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate, ${\left[ {{{Ag}}{{\left( {{{N}}{{{H}}_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + }$. When a mixture containing an aldehydic group reacts with Tollen’s reagent, a silver mirror is formed. This is done in an alkaline medium with exposure of heat. The reaction is given below:
${{RCHO}} + 2{\left[ {{{Ag}}{{\left( {{{N}}{{{H}}_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + } + 3{{O}}{{{H}}^ - } \to {{RCO}}{{{O}}^ - } + 2{{Ag}} + 2{{{H}}_2}{{O}} + 4{{N}}{{{H}}_3}$
This proves that isomers A and C are aldehydes.
We know that the compound B does not give Tollens test, but gives a positive result for the iodoform test. Only the compounds which have a carbonyl carbon which is attached to a methyl group react with this type of reaction. This indicates that the compound B is a methyl ketone.
When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with ${{Zn}}\left( {{{Hg}}} \right)/{{HCl}}$, oxygen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon is replaced with two hydrogen atoms. This gives the compound D as an alkane.
Considering all the hints given in the question, we get
B is

A is

D is

And C is

Note:
The silver mirror formed is due to the presence of element silver. Silver is reduced from $ + 1$ state to $0$. Also during Tollen’s test, aldehyde is converted to carboxylate anion which is an oxidation process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




