
(a) An unsaturated hydrocarbon ‘A’ adds two molecules of ${H_2}$ and on reductive ozonolysis gives butane-1,4-dial, ethanal and propanone. Give the structure of ‘A’, write the IUPAC name and explain the reaction involved.
(b) In the presence of peroxide addition of HBr to propene takes place according to anti markovnikov's rule but peroxide effect is not seen in the case of HCl and HI. Explain.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: The given question has two parts: (a) and (b). We solve both one by one. The first part is solved by the reaction of reductive ozonolysis on unsaturated hydrocarbons and explaining the reductive ozonolysis reaction. In the second part of question, the asked reaction is the reaction of halogenation of alkene.
(a) In organic chemistry, ozonolysis reaction is the breaking of unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes and azo compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
In the reductive ozonolysis of alkenes, the oxidation of alkenes occurs and forms the alcohol, aldehyde, ketones or carboxylic acids. The resultant product of the reaction depends upon the type of reactant and the mechanism of reaction. This reaction is an electrophilic addition reaction of ozone on alkene double bond to form ozonide intermediate which is unstable and after breaking it forms a carbonyl molecule and a carbonyl oxide molecule.
For the given question, reaction can be written as follows:
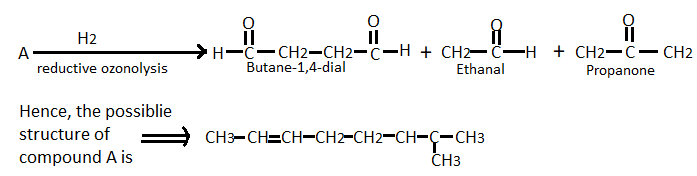
The IUPAC name of this organic compound: $2 - methyloct - 2,6 - diene$.
(b) In this question we have to explain the halogenation reaction of alkenes. In the alkene halogenation reaction, the halogens attack on the double bond and then give an additional product which is dihalide alkane. This alkane is formed according to the markovnikov and anti markovnikov rules.
HBr is added to the alkene according to a free radical mechanism in the presence of organic peroxides. In the reaction mechanism, Br radical is added on the less substituted side of alkene for forming the most stable free radical according to anti-markovnikov rule. While addition of Cl and I radical to alkene is unfavourable by the anti-markownikoff rule because this reaction is an endothermic reaction.
Note: All the halogen halides will add according to the markownikoff rule without the presence of peroxide.
Ozonolysis is of two types: reductive and oxidative ozonolysis and this reaction is an organic redox reaction.
(a) In organic chemistry, ozonolysis reaction is the breaking of unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes and azo compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
In the reductive ozonolysis of alkenes, the oxidation of alkenes occurs and forms the alcohol, aldehyde, ketones or carboxylic acids. The resultant product of the reaction depends upon the type of reactant and the mechanism of reaction. This reaction is an electrophilic addition reaction of ozone on alkene double bond to form ozonide intermediate which is unstable and after breaking it forms a carbonyl molecule and a carbonyl oxide molecule.
For the given question, reaction can be written as follows:
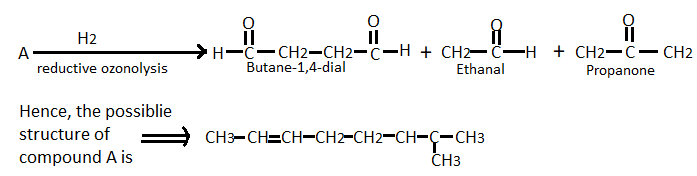
The IUPAC name of this organic compound: $2 - methyloct - 2,6 - diene$.
(b) In this question we have to explain the halogenation reaction of alkenes. In the alkene halogenation reaction, the halogens attack on the double bond and then give an additional product which is dihalide alkane. This alkane is formed according to the markovnikov and anti markovnikov rules.
HBr is added to the alkene according to a free radical mechanism in the presence of organic peroxides. In the reaction mechanism, Br radical is added on the less substituted side of alkene for forming the most stable free radical according to anti-markovnikov rule. While addition of Cl and I radical to alkene is unfavourable by the anti-markownikoff rule because this reaction is an endothermic reaction.
Note: All the halogen halides will add according to the markownikoff rule without the presence of peroxide.
Ozonolysis is of two types: reductive and oxidative ozonolysis and this reaction is an organic redox reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




