
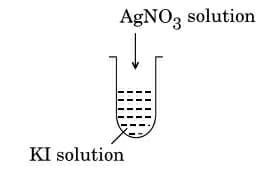
(a) A colloidal sol is prepared by the given method in figure. What is the charge of $AgI$ colloidal particles in the test tube? How is the sol formed, represented?
(b) Explain how the phenomenon of adsorption finds application in heterogeneous catalysis
(c) Which of the following electrolysis is the most effective for the coagulation of $NaCl,\,N{a_2}S{o_4},\,N{a_3}P{O_4}$ .

Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: A colloid is a mixture in which one material is suspended in another by microscopically scattered insoluble particles. Some definitions, however, stipulate that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the concept to include aerosols and gels.
Complete answer: (a) In the particles, a negative charge develops. This happens when one of the electrolyte's ions adsorbed on the precipitate surface.
\[AgI/I - \] is the formula for the resulting sol.
(b) One of the applications of adsorptions is heterogeneous catalysis -
The reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst's stable surface. As a result, the reaction rate may be increased.
Heterogeneous catalysis can be seen in the production of ammonia by the Haber process, which uses iron as a catalyst, and the production of sulphuric acid by the touch process, which uses finely divided nickel.
c) Sodium phosphate \[\left( {N{a_3}P{O_4}} \right)\]
The reason for this is that:
The Hardy - Schulze rule determines this. According to this law, the higher the valency of the flocculating ion, the greater its ability to precipitate.
\[P{O_4}^{3 - }\] has the greatest coagulating capacity in the above issue since it has the highest valency.
Note:
As silver nitrate solution is applied to \[KI\] solution, the precipitated \[AgI\] binds to the iodide ions in the dispersion medium, resulting in a negatively charged colloidal solution. Iodide ions \[\left( {I - } \right)\] can be adsorbed on the surface of \[AgI\] particles due to an excess of \[KI\] , giving them a negative charge.
Complete answer: (a) In the particles, a negative charge develops. This happens when one of the electrolyte's ions adsorbed on the precipitate surface.
\[AgI/I - \] is the formula for the resulting sol.
(b) One of the applications of adsorptions is heterogeneous catalysis -
The reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst's stable surface. As a result, the reaction rate may be increased.
Heterogeneous catalysis can be seen in the production of ammonia by the Haber process, which uses iron as a catalyst, and the production of sulphuric acid by the touch process, which uses finely divided nickel.
c) Sodium phosphate \[\left( {N{a_3}P{O_4}} \right)\]
The reason for this is that:
The Hardy - Schulze rule determines this. According to this law, the higher the valency of the flocculating ion, the greater its ability to precipitate.
\[P{O_4}^{3 - }\] has the greatest coagulating capacity in the above issue since it has the highest valency.
Note:
As silver nitrate solution is applied to \[KI\] solution, the precipitated \[AgI\] binds to the iodide ions in the dispersion medium, resulting in a negatively charged colloidal solution. Iodide ions \[\left( {I - } \right)\] can be adsorbed on the surface of \[AgI\] particles due to an excess of \[KI\] , giving them a negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




