
A 3kg mass and a 4kg mass are placed on x and y axes at a distance of 1m from the origin, and a l kg mass is placed at the origin. Then the resultant gravitational force on 1kg mass is
a) 7G
b) G
c) 5G
d) 3G
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: The gravitational force between two massive bodies is given as:
${{F}_{G}}=G\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 is the mass of two bodies and r is the distance between them.
By evaluating the gravitational force on the body having 1 Kg due bodies of masses 4 Kg and 3 Kg, separately, resultant vector calculation can be applied.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
Using the fact that the gravitational force between two bodies is always attractive, we can determine the direction of resultant force on the body under examination.
Figure given below depicts the scenario of given problem:
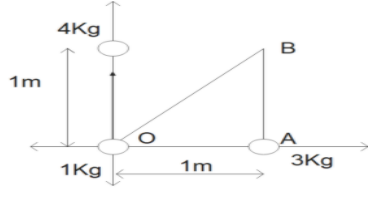
Force on 1 Kg due to 3 Kg ${{F}_{13}}$ = $G\dfrac{1\times 3}{{{1}^{2}}}=3G$
Force on 1 Kg due to 4 Kg ${{F}_{14}}$ =$G\dfrac{1\times 4}{{{1}^{2}}}=4G$
The magnitude of resultant force will be calculated by using vector law of addition. From figure given above:
\[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{OB}}\, \right|=\sqrt{{{\overset{\to }{\mathop{OA}}\,}^{2}}+{{\overset{\to }{\mathop{AB}}\,}^{2}}}\]
Where OB is the vector for resultant force, OA is the vector of force due to mass 3 Kg, and AB is the vector of force due to mass 4 Kg.
$\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{OB}}\, \right|=\sqrt{3{{G}^{2}}+4{{G}^{2}}}=5G$
Hence, resultant force will be 5G. Thus option (c) is correct.
Note:
The direction of the resultant force should be carefully examined. And the attractive nature of force here plays an important role in determining the direction of forces. As the values other than 3 Kg and 4 Kg are 1, one can directly apply the vector law of addition and can immediately get the resultant value without following the whole procedure.
${{F}_{G}}=G\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 is the mass of two bodies and r is the distance between them.
By evaluating the gravitational force on the body having 1 Kg due bodies of masses 4 Kg and 3 Kg, separately, resultant vector calculation can be applied.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
Using the fact that the gravitational force between two bodies is always attractive, we can determine the direction of resultant force on the body under examination.
Figure given below depicts the scenario of given problem:

Force on 1 Kg due to 3 Kg ${{F}_{13}}$ = $G\dfrac{1\times 3}{{{1}^{2}}}=3G$
Force on 1 Kg due to 4 Kg ${{F}_{14}}$ =$G\dfrac{1\times 4}{{{1}^{2}}}=4G$
The magnitude of resultant force will be calculated by using vector law of addition. From figure given above:
\[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{OB}}\, \right|=\sqrt{{{\overset{\to }{\mathop{OA}}\,}^{2}}+{{\overset{\to }{\mathop{AB}}\,}^{2}}}\]
Where OB is the vector for resultant force, OA is the vector of force due to mass 3 Kg, and AB is the vector of force due to mass 4 Kg.
$\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{OB}}\, \right|=\sqrt{3{{G}^{2}}+4{{G}^{2}}}=5G$
Hence, resultant force will be 5G. Thus option (c) is correct.
Note:
The direction of the resultant force should be carefully examined. And the attractive nature of force here plays an important role in determining the direction of forces. As the values other than 3 Kg and 4 Kg are 1, one can directly apply the vector law of addition and can immediately get the resultant value without following the whole procedure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




