
A $2.5dioptre$ lens forms a virtual image which is $4$ times the object placed perpendicularly on the lens. Then the required distance of the object from the lens is
A) $35$
B) $40$
C) $30$
D) $25$
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: You can calculate the focal length from the refractive power, by simply reciprocating. The virtual image clearly indicates that the object and the image both are on the same side. The object and image distances are also related to their heights and that is insightful to the relation between them which can be used here as well.
Formula used:
The lens formula can be written as
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$ ………………..(1)
where $f$ is the focal length of the lens, $v$ is the distance of the image from the image and $u$ is the distance between from the lens to the object.
You know that if the height of the object is ${h_o}$ and the height of the image is ${h_i}$, then
$\dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}}$ …………...(2)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The refractive power of the lens $P$ is $2.5dioptre$.
The height of the image is $4$ times the object’s height.
To get: The distance of the object from the lens.
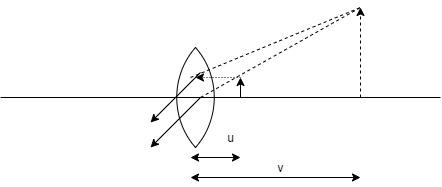
Step 1:
Calculate the focal length $f$ of the lens.
$f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
$\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2.5}}m $
$\therefore f = 40cm $
Step 2:
You have the relation between the object height ${h_O}$ and the image height ${h_i}$ :
${h_i} = 4 \times {h_o}$
Now, use the eq (2) and get
$ \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{4 \times {h_o}}} $
On substituting the corresponding values,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{1}{4} $
on simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow v = 4u $
Step 3:
Now the use the relation in eq (1).
$ \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
On substituting the corresponding values,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{1}{{4u}} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{{1 - 4}}{{4u}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{{4u}} $
solving for $u$,
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{4} \times 40 $
$ \Rightarrow u = - 30 $
Here, the sign is negative as the object is on the side of the lens from where the light comes from.
$\therefore u = 30cm$
If a $2.5dioptre$ lens forms a virtual image which is $4$ times the object placed perpendicularly on the lens, then the required distance of the object from the lens is $30$ cm. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
The image is imaginary here hence the signature of both the distance of the object from the image $u$ and the distance of the image from the image $v$ are the same. You should carefully use the relation of the ratio of $\dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}}$ and $\dfrac{u}{v}$. The height and the distance of the object are proportional and the same for the image as well.
Formula used:
The lens formula can be written as
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$ ………………..(1)
where $f$ is the focal length of the lens, $v$ is the distance of the image from the image and $u$ is the distance between from the lens to the object.
You know that if the height of the object is ${h_o}$ and the height of the image is ${h_i}$, then
$\dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}}$ …………...(2)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The refractive power of the lens $P$ is $2.5dioptre$.
The height of the image is $4$ times the object’s height.
To get: The distance of the object from the lens.

Step 1:
Calculate the focal length $f$ of the lens.
$f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
$\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2.5}}m $
$\therefore f = 40cm $
Step 2:
You have the relation between the object height ${h_O}$ and the image height ${h_i}$ :
${h_i} = 4 \times {h_o}$
Now, use the eq (2) and get
$ \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{4 \times {h_o}}} $
On substituting the corresponding values,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{1}{4} $
on simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow v = 4u $
Step 3:
Now the use the relation in eq (1).
$ \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
On substituting the corresponding values,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{1}{{4u}} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{{1 - 4}}{{4u}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{40}} = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{{4u}} $
solving for $u$,
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{4} \times 40 $
$ \Rightarrow u = - 30 $
Here, the sign is negative as the object is on the side of the lens from where the light comes from.
$\therefore u = 30cm$
If a $2.5dioptre$ lens forms a virtual image which is $4$ times the object placed perpendicularly on the lens, then the required distance of the object from the lens is $30$ cm. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
The image is imaginary here hence the signature of both the distance of the object from the image $u$ and the distance of the image from the image $v$ are the same. You should carefully use the relation of the ratio of $\dfrac{{{h_o}}}{{{h_i}}}$ and $\dfrac{u}{v}$. The height and the distance of the object are proportional and the same for the image as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




