
A 2 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image also find its magnification.
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the relations between the length parameters in a lens system such as the distance from the lens to the object, the focal length of the lens and the image distance from the lens to solve the required parameters in this problem.
Complete answer:
We are given an object of 2 cm height which is placed 15 cm from a convex lens, which has a focal length of 10 cm. We know that the three given parameters can be employed to find the distance of the image formed from the lens and the magnification of the image. These details will let us know the nature of the image formed by the convex lens.
We know that the lens formula can be used to calculate the image distance as the focal length and the object distance for this case is given already. The lens formula is given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
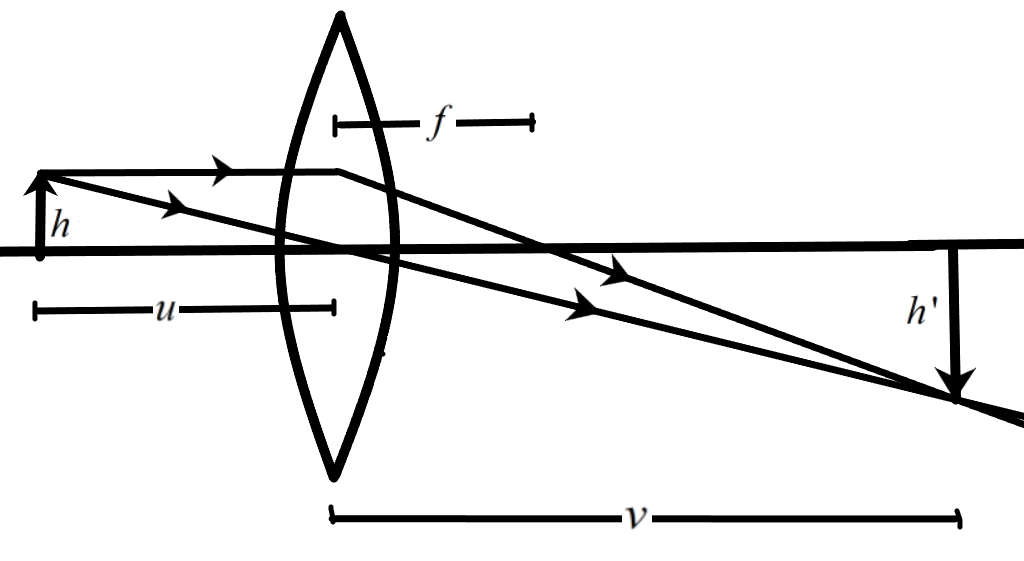
Now, we can substitute the values for ‘u’, the object distance and ‘f’, the focal length with the proper signs to get the image distance ‘v’ as –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{+10}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-15} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{15} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{30}{3-2} \\
& \therefore v=+30cm \\
\end{align}\]
The image distance from the lens is +30 cm.
Now, we can find the magnification of the image using the image distance and the object distance as –
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\dfrac{30}{-15} \\
& \therefore m=-2 \\
\end{align}\]
The image formed is enlarged twice as the object and is real and inverted, as we can conclude from the negative sign in the magnification.
We can find the height of the image from the magnification and the height of the object as –
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{h'}{h} \\
& \Rightarrow h'=mh \\
& \Rightarrow h'=(-2)(2cm) \\
& \therefore h'=-4cm \\
\end{align}\]
The image size is given as -4 cm for this case. We can conclude that the image formed by the convex lens has a size of 4 cm, it is real and inverted and is formed 30 cm away from the lens with a magnification of -2.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The properties of forming an image is highly dependent on the lens used, the medium in which the lens is kept and the object distance. The same lens when kept in water can give entirely opposite results and the object kept closer can give a virtual and erect image.
Complete answer:
We are given an object of 2 cm height which is placed 15 cm from a convex lens, which has a focal length of 10 cm. We know that the three given parameters can be employed to find the distance of the image formed from the lens and the magnification of the image. These details will let us know the nature of the image formed by the convex lens.
We know that the lens formula can be used to calculate the image distance as the focal length and the object distance for this case is given already. The lens formula is given by –
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]

Now, we can substitute the values for ‘u’, the object distance and ‘f’, the focal length with the proper signs to get the image distance ‘v’ as –
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{+10}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-15} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{15} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{30}{3-2} \\
& \therefore v=+30cm \\
\end{align}\]
The image distance from the lens is +30 cm.
Now, we can find the magnification of the image using the image distance and the object distance as –
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\dfrac{30}{-15} \\
& \therefore m=-2 \\
\end{align}\]
The image formed is enlarged twice as the object and is real and inverted, as we can conclude from the negative sign in the magnification.
We can find the height of the image from the magnification and the height of the object as –
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{h'}{h} \\
& \Rightarrow h'=mh \\
& \Rightarrow h'=(-2)(2cm) \\
& \therefore h'=-4cm \\
\end{align}\]
The image size is given as -4 cm for this case. We can conclude that the image formed by the convex lens has a size of 4 cm, it is real and inverted and is formed 30 cm away from the lens with a magnification of -2.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The properties of forming an image is highly dependent on the lens used, the medium in which the lens is kept and the object distance. The same lens when kept in water can give entirely opposite results and the object kept closer can give a virtual and erect image.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




