
A $10\mu F$ capacitor is connected across a $200V$, $50Hz$A.C. supply. The peak current through the circuit is:
$0.6A$
$0.6\sqrt{2}A$
$0.06\sqrt{2}A$
$0.6\pi A$
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:The energy source of this circuit is AC (alternating current). Also, it is a purely capacitive circuit. This means that only a capacitor is present in the circuit along with the alternating current source and no resistor or inductor is present. Therefore, only the capacitor is consuming energy and the current faces resistance only by the capacitive reactance of the capacitor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Impedance is the total resistance present against the current in the circuit.
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given as:
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{\left( {{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Where,
$R=$ Resistance of the resistor present
${{X}_{L}}=$Inductive reactance of the inductor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{L}}=\omega L$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{L}}=2\pi \nu L$
Where, $\nu =$ frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $L=$inductance of inductor
${{X}_{C}}=$Capacitive reactance of the capacitor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}$ ………….. equation (1)
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $C=$capacitance of capacitor
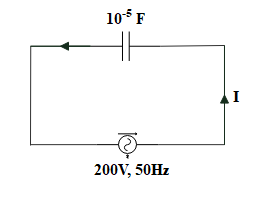
Since, no resistor or inductor is present in the circuit,
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& Z=\sqrt{0+{{\left( 0-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow Z={{X}_{C}} \\
\end{align}$
Now,
The voltage,$V$of the a.c. circuit is given as:
$V=IZ$
Here, $I=$current in circuit and $Z={{X}_{C}}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
From equation (1),
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
Given that voltage = 200 volts, frequency = $50Hz$ and capacitance =$10\mu F=10\times {{10}^{-6}}F={{10}^{-5}}F$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \left( 50 \right)\left( {{10}^{-5}} \right)}=\dfrac{200}{I} \\
& \Rightarrow I=\pi 200\left( 100 \right)\left( {{10}^{-5}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\pi \left( {{10}^{-1}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore I=0.2\pi A$ ……………. Equation (2)
The voltage given and current that we have just calculated are the rms voltage and rms current respectively (where rms stands for root mean square).
The rms voltage is related to the peak voltage as: ${{V}_{rms}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{peak}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
Similarly, the rms current is related to the peak current as: ${{I}_{rms}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{peak}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}{{I}_{rms}}$
From equation (2), we get ${{I}_{rms}}=0.2\pi A$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.2\pi \right)$
Substituting $\pi =3.14,$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.2 \right)\left( 3.14 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.628 \right) \\
& \therefore {{I}_{peak}}\approx 0.6\sqrt{2}A \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the peak current is $0.6\sqrt{2}A$.
Therefore, the correct option is (B)$0.6\sqrt{2}A$.
Note:
The voltage rating coming to our households is the rms voltage of the alternating current. Since the alternating current occurs as sine or cosine function of time, the value of this current is not constant and keeps fluctuating. This gives rise to the need of a more stable measurement such as rms current.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Impedance is the total resistance present against the current in the circuit.
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given as:
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{\left( {{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Where,
$R=$ Resistance of the resistor present
${{X}_{L}}=$Inductive reactance of the inductor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{L}}=\omega L$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{L}}=2\pi \nu L$
Where, $\nu =$ frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $L=$inductance of inductor
${{X}_{C}}=$Capacitive reactance of the capacitor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}$ ………….. equation (1)
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $C=$capacitance of capacitor

Since, no resistor or inductor is present in the circuit,
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& Z=\sqrt{0+{{\left( 0-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow Z={{X}_{C}} \\
\end{align}$
Now,
The voltage,$V$of the a.c. circuit is given as:
$V=IZ$
Here, $I=$current in circuit and $Z={{X}_{C}}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
From equation (1),
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
Given that voltage = 200 volts, frequency = $50Hz$ and capacitance =$10\mu F=10\times {{10}^{-6}}F={{10}^{-5}}F$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \left( 50 \right)\left( {{10}^{-5}} \right)}=\dfrac{200}{I} \\
& \Rightarrow I=\pi 200\left( 100 \right)\left( {{10}^{-5}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\pi \left( {{10}^{-1}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore I=0.2\pi A$ ……………. Equation (2)
The voltage given and current that we have just calculated are the rms voltage and rms current respectively (where rms stands for root mean square).
The rms voltage is related to the peak voltage as: ${{V}_{rms}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{peak}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
Similarly, the rms current is related to the peak current as: ${{I}_{rms}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{peak}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}{{I}_{rms}}$
From equation (2), we get ${{I}_{rms}}=0.2\pi A$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.2\pi \right)$
Substituting $\pi =3.14,$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.2 \right)\left( 3.14 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{peak}}=\sqrt{2}\left( 0.628 \right) \\
& \therefore {{I}_{peak}}\approx 0.6\sqrt{2}A \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the peak current is $0.6\sqrt{2}A$.
Therefore, the correct option is (B)$0.6\sqrt{2}A$.
Note:
The voltage rating coming to our households is the rms voltage of the alternating current. Since the alternating current occurs as sine or cosine function of time, the value of this current is not constant and keeps fluctuating. This gives rise to the need of a more stable measurement such as rms current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




