
2-phenylethyl bromide when heated with \[NaOEt\] , elimination takes place. No
deuterium exchange takes place when the reaction is carried out in \[{C_2}{H_5}OD\] solvent. The Mechanism will be:
A. E1 elimination
B. E2 elimination
C. E1cB elimination
D. E2 or E1cB
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: To find the elimination mechanism we need to know the difference between the three types of elimination reactions. Elimination is an organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in one or two step mechanisms.
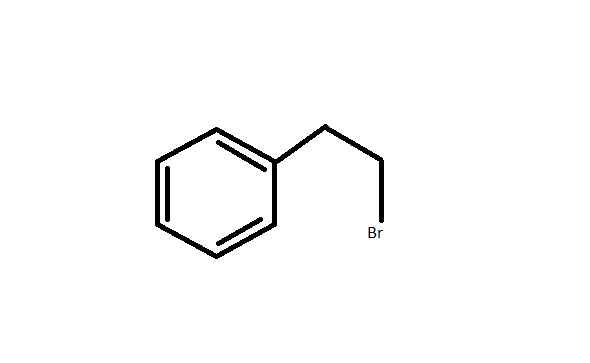
Step by step answer: 2-Ethyl Bromide is an organobromine with molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br\] . It is a colourless liquid but its older samples had appeared yellow. It is prepared by free radical addition of hydrogen bromide to styrene. Its structure is as given below:
\[NaOEt\] is commonly called Sodium ethoxide. It is an organic compound with the formula \[{C_2}{H_5}Na\] . It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol and is a strong base. It is a crystal structure which is determined by crystallography.
In the question \[{C_2}{H_5}OD\] is called Ethanol (ol-d). It is a deuterated NMR solvent useful in NMR based research and analysis. It can be prepared by reacting tetraethyorthosilicate with deuterium oxide. The hydrogen bonding in ethanol has been investigated based on Raman spectral data.
Now, as it is a primary bromide, it will undergo elimination either by E2 or E1cB. Since there is no deuterium exchange in the solvent, the C-H bond is not broken to form carbanion.
Hence the actual mechanism is E2 only. Therefore, the correct option is B.
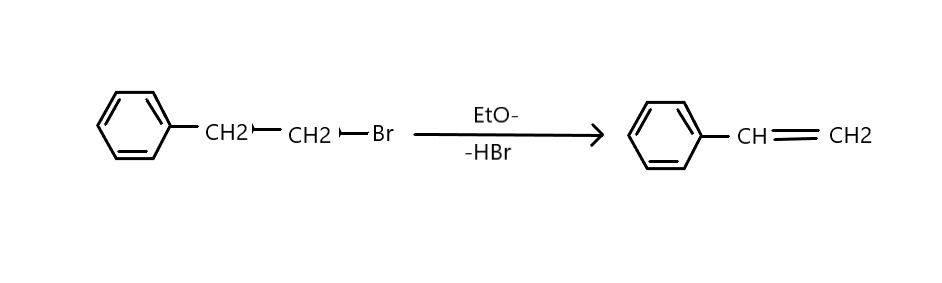
E2 stands for bimolecular elimination. This reaction is a one-step mechanism in which carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bonds break to form a double bond. The reaction rate is second order because it’s influenced by both the alkyl halide and the base.
E1 is an unimolecular elimination reaction in which the removal of an HX substituent results in the formation of a double bond. It is similar to a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
E1cB elimination reaction is a type which occurs under basic conditions where the hydrogen to be removed is acidic while the leaving group is a relatively poor one.
Hence the actual mechanism is E2 only. Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Here we noted the difference between the types of elimination which are E1, E2 and E1cB and also the difference between them. The student may get confused in the symbols used.
Step by step answer: 2-Ethyl Bromide is an organobromine with molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br\] . It is a colourless liquid but its older samples had appeared yellow. It is prepared by free radical addition of hydrogen bromide to styrene. Its structure is as given below:

\[NaOEt\] is commonly called Sodium ethoxide. It is an organic compound with the formula \[{C_2}{H_5}Na\] . It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol and is a strong base. It is a crystal structure which is determined by crystallography.
In the question \[{C_2}{H_5}OD\] is called Ethanol (ol-d). It is a deuterated NMR solvent useful in NMR based research and analysis. It can be prepared by reacting tetraethyorthosilicate with deuterium oxide. The hydrogen bonding in ethanol has been investigated based on Raman spectral data.
Now, as it is a primary bromide, it will undergo elimination either by E2 or E1cB. Since there is no deuterium exchange in the solvent, the C-H bond is not broken to form carbanion.
Hence the actual mechanism is E2 only. Therefore, the correct option is B.

E2 stands for bimolecular elimination. This reaction is a one-step mechanism in which carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bonds break to form a double bond. The reaction rate is second order because it’s influenced by both the alkyl halide and the base.
E1 is an unimolecular elimination reaction in which the removal of an HX substituent results in the formation of a double bond. It is similar to a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
E1cB elimination reaction is a type which occurs under basic conditions where the hydrogen to be removed is acidic while the leaving group is a relatively poor one.
Hence the actual mechanism is E2 only. Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Here we noted the difference between the types of elimination which are E1, E2 and E1cB and also the difference between them. The student may get confused in the symbols used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle-class-12-maths-CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE




