
2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is a:
(A) primary alcohol
(B) secondary alcohol
(C) tertiary alcohol
(D) dihydric alcohol
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The structure of 2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is :
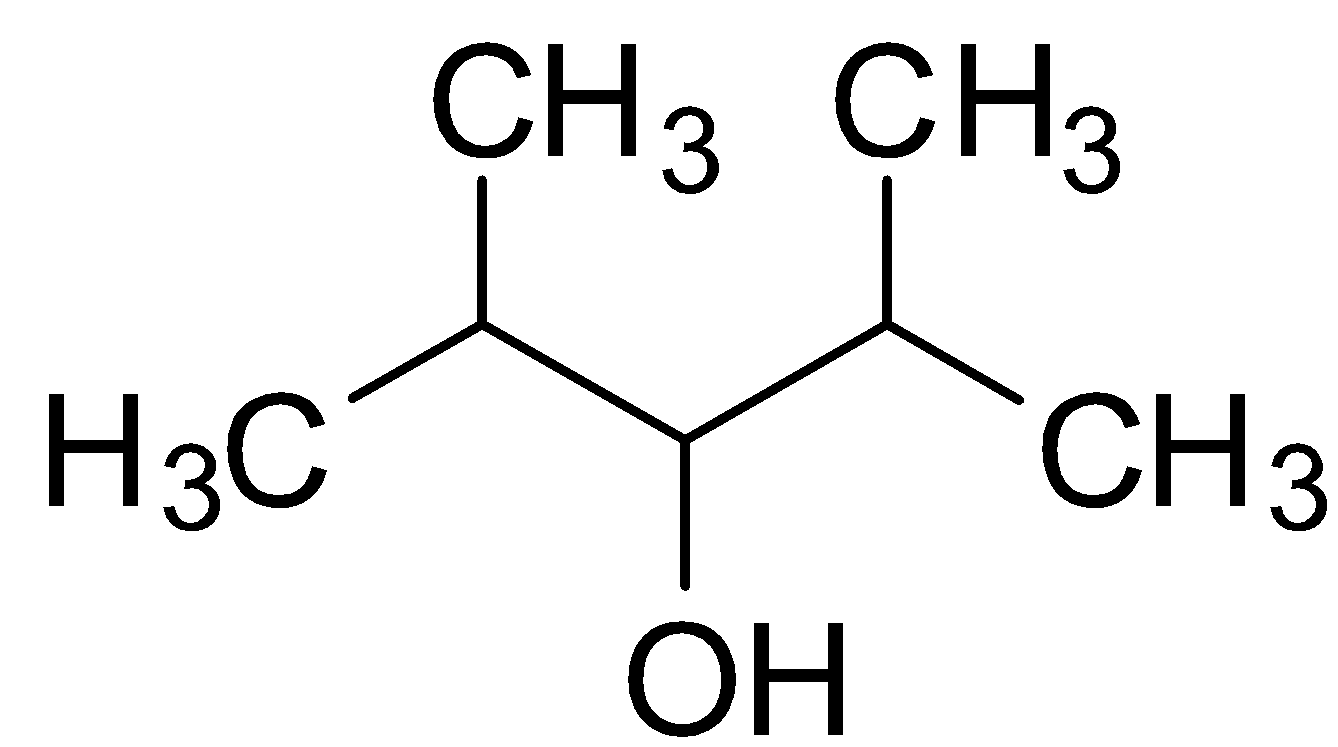
Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are classified on the basis of the number of other carbon atoms being attached to the carbon having the hydroxyl (OH) group.
Complete answer:
The classification of alcohols is done on the basis of the attachment of the carbon atom holding the hydroxyl group (OH) to other alkyl groups and is classified as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols.
In a primary alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group as shown below-
\[{{R}_{1}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\]
In a secondary alcohol, the carbon atom with which the -OH group is attached, is further joined directly to two alkyl groups, which may be the same or different.
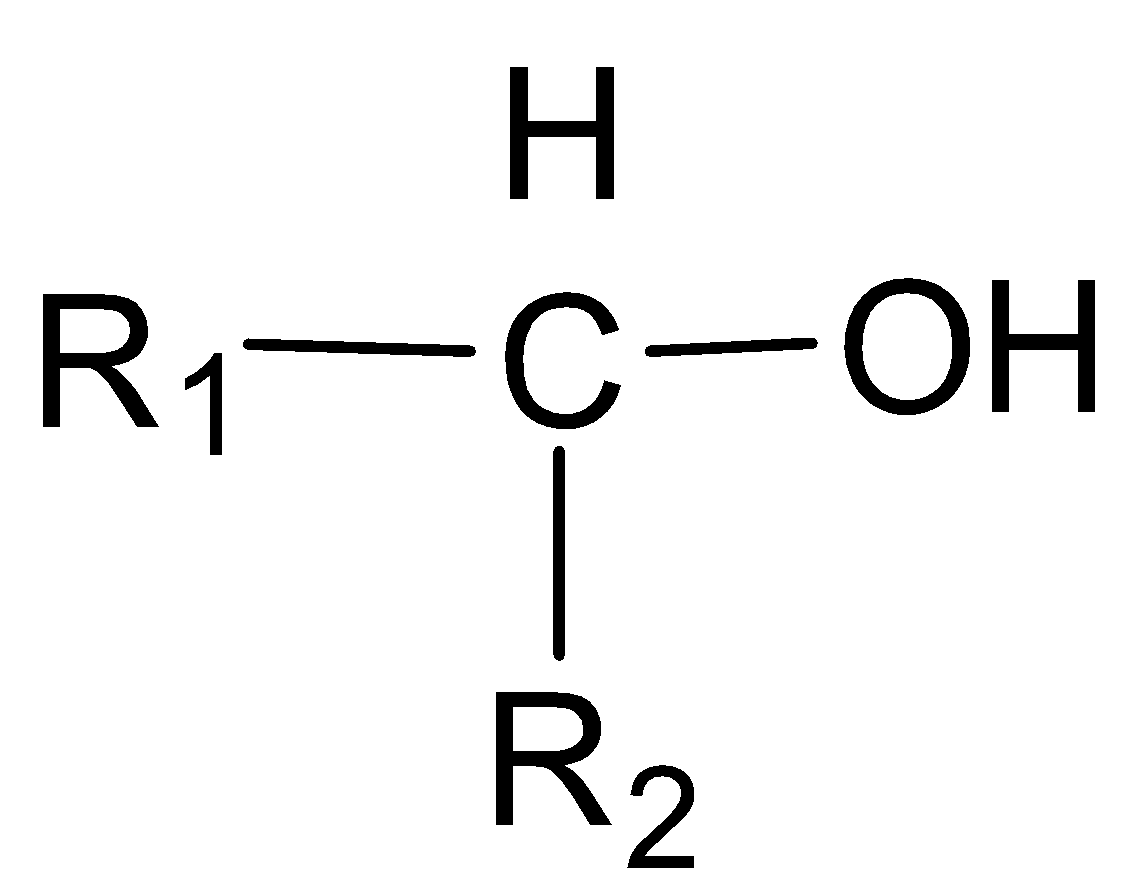 Secondary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
In a tertiary alcohol, the carbon atom with which the -OH group is attached, is further joined directly to three alkyl groups and is not attached to any hydrogen atom.
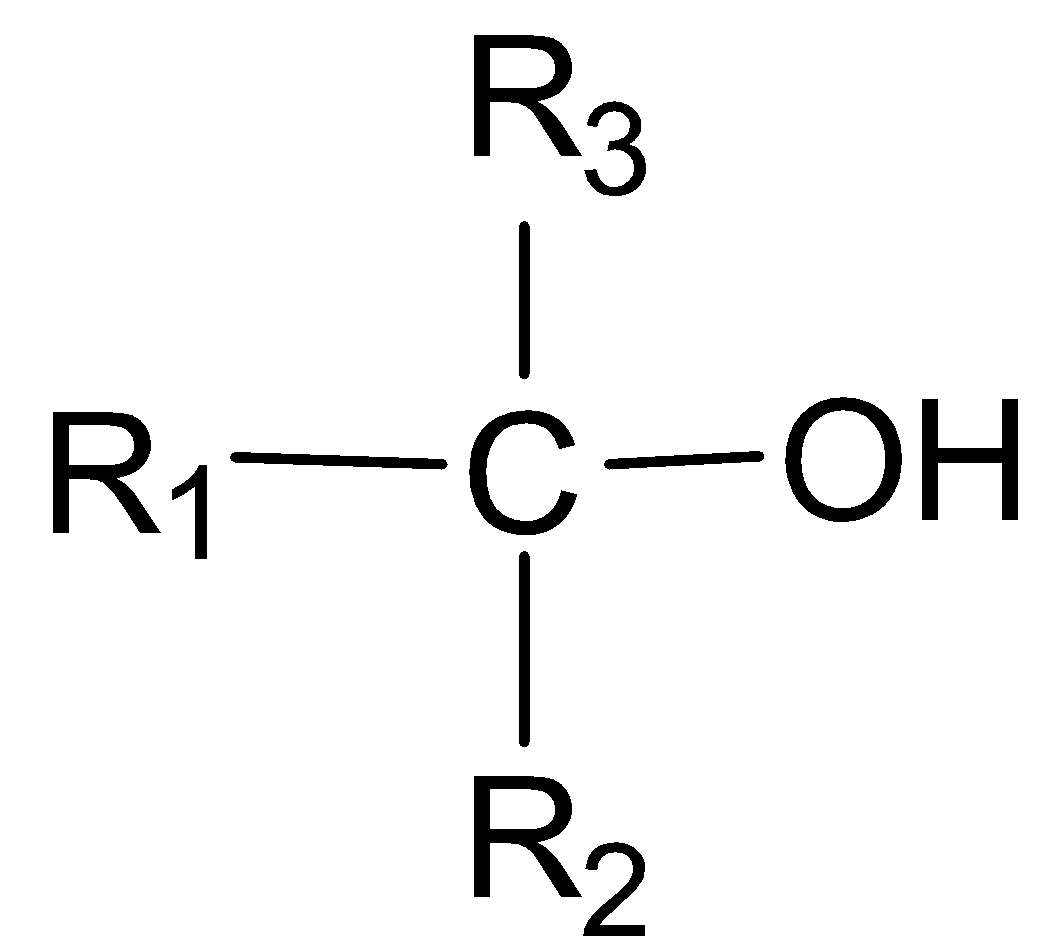 Tertiary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
The structure of 2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is :
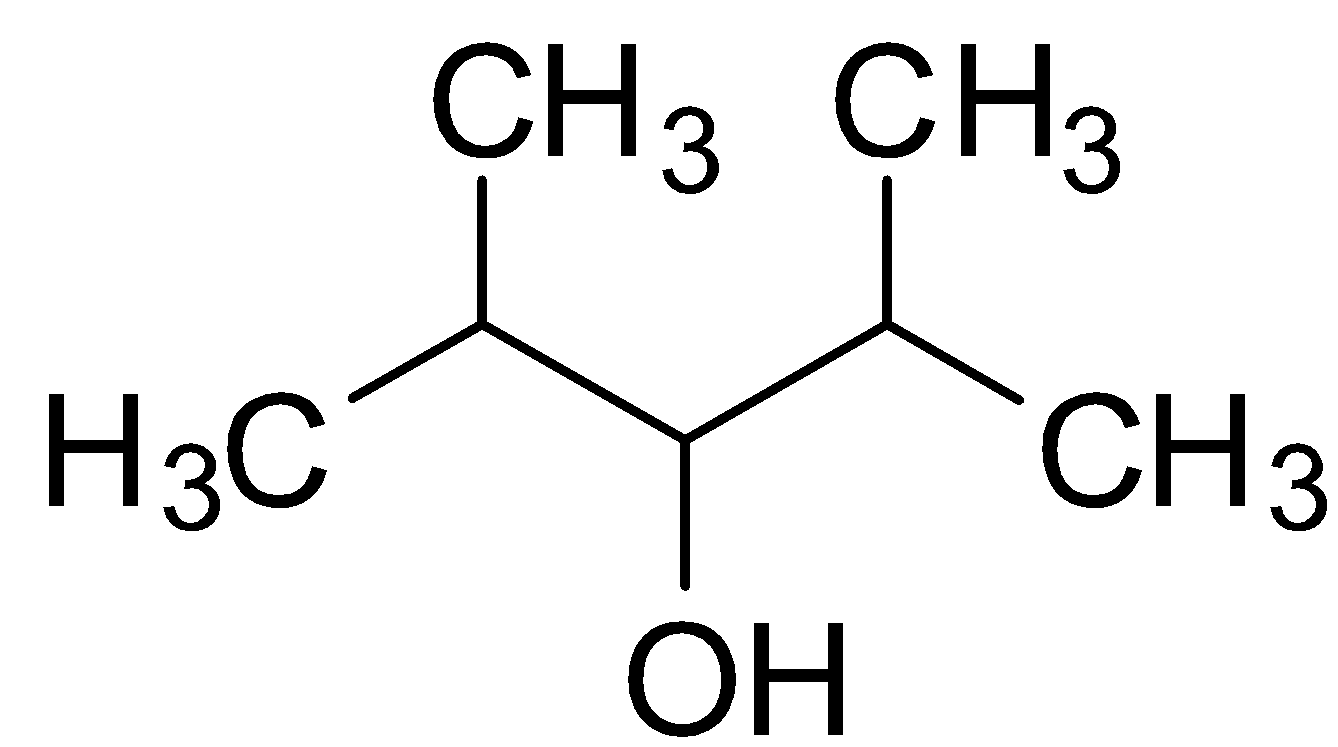
Dihydric alcohols are those classes of alcohols which have 2 hydroxyl (OH) groups in a single molecule. Since 2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol has only 1 OH group, it is clearly not a dihydric alcohol. It is rather a monohydric alcohol.
2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is therefore a secondary alcohol because the carbon having OH group is attached to two $-CH-{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$ Isopropyl group.
Hence the correct answer is option (B) secondary alcohol.
Note:
In general, primary carbons are carbons attached to one other carbon, secondary carbons attached to two other carbons, tertiary carbons to three other carbons, and quaternary carbons to four other carbons.

Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are classified on the basis of the number of other carbon atoms being attached to the carbon having the hydroxyl (OH) group.
Complete answer:
The classification of alcohols is done on the basis of the attachment of the carbon atom holding the hydroxyl group (OH) to other alkyl groups and is classified as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols.
In a primary alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group as shown below-
\[{{R}_{1}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\]
In a secondary alcohol, the carbon atom with which the -OH group is attached, is further joined directly to two alkyl groups, which may be the same or different.

In a tertiary alcohol, the carbon atom with which the -OH group is attached, is further joined directly to three alkyl groups and is not attached to any hydrogen atom.

The structure of 2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is :

Dihydric alcohols are those classes of alcohols which have 2 hydroxyl (OH) groups in a single molecule. Since 2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol has only 1 OH group, it is clearly not a dihydric alcohol. It is rather a monohydric alcohol.
2,4-Dimethyl-3-pentanol is therefore a secondary alcohol because the carbon having OH group is attached to two $-CH-{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$ Isopropyl group.
Hence the correct answer is option (B) secondary alcohol.
Note:
In general, primary carbons are carbons attached to one other carbon, secondary carbons attached to two other carbons, tertiary carbons to three other carbons, and quaternary carbons to four other carbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




