
1,3 butadiene on reaction with HBr/water gives primarily 1-bromo-2-butene at high temperatures. Give the reaction.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The answer for the question is a basic organic reaction which is based on the Markovnikov’s rule that is applicable to the addition reactions of asymmetric unsaturated compounds and the mechanism of addition will lead you to the answer.
Complete answer:
We are familiar with the several types of reactions that include elimination reactions, addition reactions, substitution reactions and also various other named reactions.
Now, let us see the basic mechanism that the above molecule undergoes to give the required product.
Now, here the compound given is 1,3 butadiene and when treated at higher temperature, we get 1-bromo-2-butene and therefore, this is an example of an additional reaction which basically follows Markovnikov's rule.
According to this rule, the nucleophile attaches to that carbon atom of alkene which has less number of hydrogen atoms present.
Here, butadiene has double bonds at the extreme ands and therefore attachment at ant of extreme end to get 1 – bromo derivative at higher temperature. Thus, only one double bond gets saturated and the other remains unsaturated itself.
Thus, the possibilities of the attack of nucleophile can be given in the form of reaction at higher temperature as shown below,
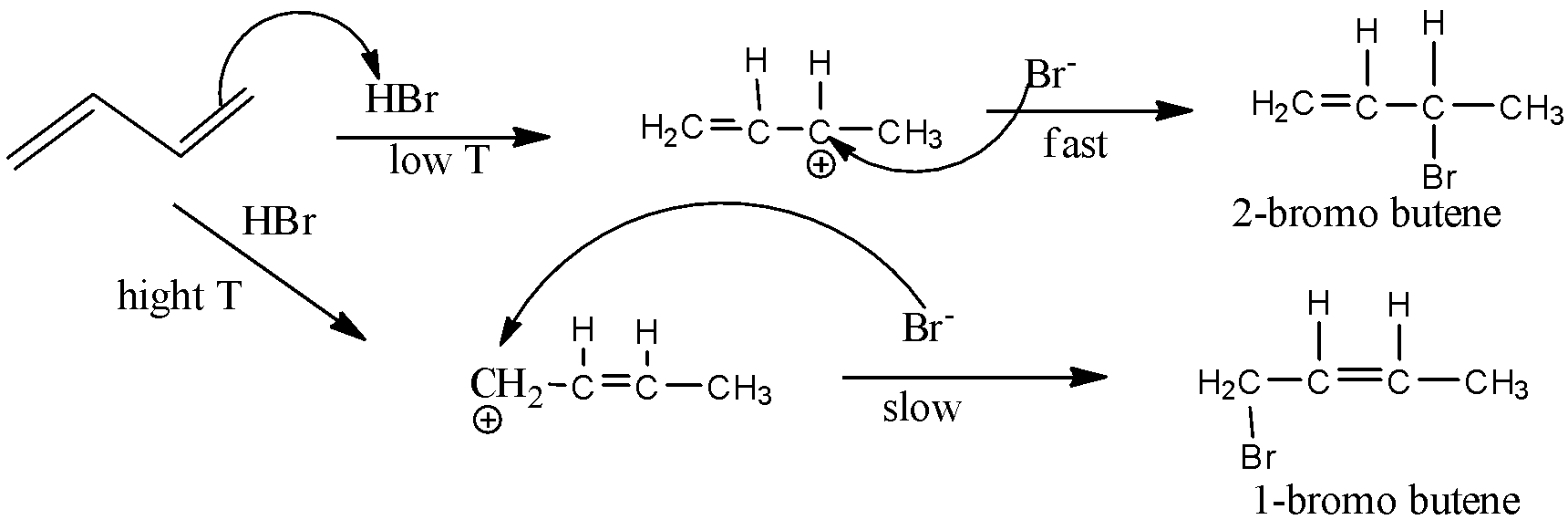
Thus, at high temperature, the reaction is slow and thermodynamically favourable which gives the required product whereas at low temperature it is kinetically favourable.
Note: Here 1,3 butadiene is an unsaturated alkene and if this is treated with hydrogen bromide at lower temperature then we get 2 – bromo derivative and to get 1 – bromo derivative, higher temperature is needed. This fact will help you to solve this type of question.
Complete answer:
We are familiar with the several types of reactions that include elimination reactions, addition reactions, substitution reactions and also various other named reactions.
Now, let us see the basic mechanism that the above molecule undergoes to give the required product.
Now, here the compound given is 1,3 butadiene and when treated at higher temperature, we get 1-bromo-2-butene and therefore, this is an example of an additional reaction which basically follows Markovnikov's rule.
According to this rule, the nucleophile attaches to that carbon atom of alkene which has less number of hydrogen atoms present.
Here, butadiene has double bonds at the extreme ands and therefore attachment at ant of extreme end to get 1 – bromo derivative at higher temperature. Thus, only one double bond gets saturated and the other remains unsaturated itself.
Thus, the possibilities of the attack of nucleophile can be given in the form of reaction at higher temperature as shown below,

Thus, at high temperature, the reaction is slow and thermodynamically favourable which gives the required product whereas at low temperature it is kinetically favourable.
Note: Here 1,3 butadiene is an unsaturated alkene and if this is treated with hydrogen bromide at lower temperature then we get 2 – bromo derivative and to get 1 – bromo derivative, higher temperature is needed. This fact will help you to solve this type of question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




