
(1) In the figure below, find the value of $ 'x' $
(i)
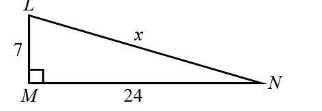
(ii)
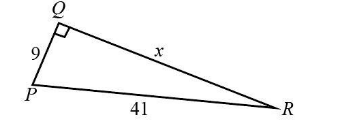
(iii)
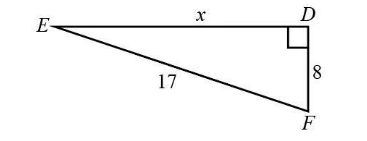
(2) In the right-angled $ \Delta PQR $ , $ \angle P = {90^ \circ } $ . If $ l\left( {PQ} \right) = 24\;{\rm{cm}} $ and $ l\left( {PR} \right) = 10\;{\rm{cm}} $ , find the length of seg $ QR $ .



Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: According to the data given in different figures, we will use Pythagoras theorem which states that,
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
Where, $ P $ is perpendicular, $ B $ is base and $ H $ is the hypotenuse of the triangle. We will substitute the values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse accordingly in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(i)
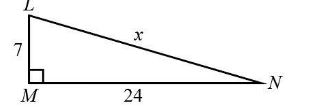
Given:
The perpendicular of the $ \Delta LMN $ is $ P = 7 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta LMN $ is $ B = 24 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 7 for $ P $ and 24 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ H $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{7^2} + {24^2} = {x^2}\\
49 + 576 = {x^2}
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 576 + 49\\
{x^2} = 625\\
x = 25
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 25.
(ii)
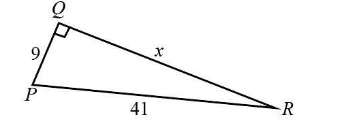
Given:
The hypotenuse of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ H = 41 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ B = 9 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 41 for $ H $ and 9 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ P $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{c}
{x^2} + {9^2} = {41^2}\\
{x^2} + 81 = 1681
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 1681 - 81\\
{x^2} = 1600\\
x = 40
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 40.
(iii)
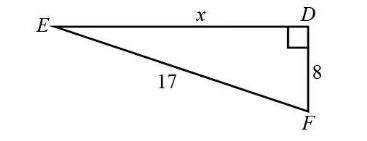
Given:
The hypotenuse of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ H = 17 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ B = 8 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 17 for $ H $ and 8 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ P $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} + {8^2} = {17^2}\\
{x^2} + 64 = 289
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 289 - 64\\
{x^2} = 225\\
x = 15
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 15.
Note: Make sure to substitute the correct values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse in the Pythagoras theorem. The common mistake that happen is in the misinterpretation of the data given in the question.
(2)
Hint:As base and perpendicular is already given in the question, we will use Pythagoras theorem to find the hypotenuse of the triangle which states that,
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
Where, $ P $ is perpendicular, $ B $ is base and $ H $ is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
We will substitute the values of perpendicular and base in the expression to find hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
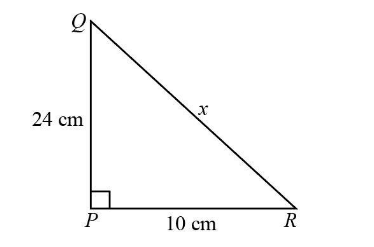
Given:
The perpendicular of the $ \Delta PQR $ that is segment $ PQ $ is $ P = 24\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ that is segment $ PR $ is $ B = 10\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
Assume hypotenuse of the triangle that is the segment $ QR $ as $ x $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that,
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute $ 24\;{\rm{cm}} $ 2 for $ P $ and $ 10\;{\rm{cm}} $ for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ H $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{c}
{\left( {{\rm{24}}\,{\rm{cm}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{10}}\;{\rm{cm}}} \right)^2} = {x^2}\\
576\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} + 100\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} = {x^2}
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression
$ \begin{array}{c}
{x^2} = 576\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} + 100\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\\
{x^2} = 676\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\\
x = 26\;{\rm{cm}}
\end{array} $
Therefore, the length of segment $ QR $ is $ 26\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
Note:Make sure to substitute the correct values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse in the Pythagoras theorem. The common mistake that happens is in the misinterpretation of the data given in the question.
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
Where, $ P $ is perpendicular, $ B $ is base and $ H $ is the hypotenuse of the triangle. We will substitute the values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse accordingly in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(i)

Given:
The perpendicular of the $ \Delta LMN $ is $ P = 7 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta LMN $ is $ B = 24 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 7 for $ P $ and 24 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ H $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{7^2} + {24^2} = {x^2}\\
49 + 576 = {x^2}
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 576 + 49\\
{x^2} = 625\\
x = 25
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 25.
(ii)

Given:
The hypotenuse of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ H = 41 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ B = 9 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 41 for $ H $ and 9 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ P $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{c}
{x^2} + {9^2} = {41^2}\\
{x^2} + 81 = 1681
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 1681 - 81\\
{x^2} = 1600\\
x = 40
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 40.
(iii)

Given:
The hypotenuse of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ H = 17 $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ is $ B = 8 $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute 17 for $ H $ and 8 for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ P $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} + {8^2} = {17^2}\\
{x^2} + 64 = 289
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = 289 - 64\\
{x^2} = 225\\
x = 15
\end{array} $
Therefore, the value of $ x $ is 15.
Note: Make sure to substitute the correct values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse in the Pythagoras theorem. The common mistake that happen is in the misinterpretation of the data given in the question.
(2)
Hint:As base and perpendicular is already given in the question, we will use Pythagoras theorem to find the hypotenuse of the triangle which states that,
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
Where, $ P $ is perpendicular, $ B $ is base and $ H $ is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
We will substitute the values of perpendicular and base in the expression to find hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given:
The perpendicular of the $ \Delta PQR $ that is segment $ PQ $ is $ P = 24\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
The base of the $ \Delta PQR $ that is segment $ PR $ is $ B = 10\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
Assume hypotenuse of the triangle that is the segment $ QR $ as $ x $ .
From the Pythagoras theorem we know that,
$ {P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2} $
We will substitute $ 24\;{\rm{cm}} $ 2 for $ P $ and $ 10\;{\rm{cm}} $ for $ B $ and $ x $ for $ H $ in the above expression.
$ \begin{array}{c}
{\left( {{\rm{24}}\,{\rm{cm}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{10}}\;{\rm{cm}}} \right)^2} = {x^2}\\
576\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} + 100\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} = {x^2}
\end{array} $
We will rewrite the above expression
$ \begin{array}{c}
{x^2} = 576\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}} + 100\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\\
{x^2} = 676\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{2}}}\\
x = 26\;{\rm{cm}}
\end{array} $
Therefore, the length of segment $ QR $ is $ 26\;{\rm{cm}} $ .
Note:Make sure to substitute the correct values of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse in the Pythagoras theorem. The common mistake that happens is in the misinterpretation of the data given in the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




