
(1) How would I use the kinetic equations to derive a general equation for the time it takes a ball dropped from rest at vertical height$h$to reach the ground?
(2) Using the result from the first part, write a general equation for the distance travelled by a projectile that is rolling off a table of height $h$with a horizontal velocity ${{v}_{0x}}$.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will be using the concepts of motion of a body in one dimension. We will also be using the equation of motions to derive our answers. For the second portion, we will be using the concept of a horizontal projectile.
Formula used:
First equation of motion: $v=u+at$
Second equation of motion: $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Third equation of motion: ${{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as$
Where $v$ is the final velocity, $u$is the initial velocity, $a$ is the acceleration and $t$ is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to find our answers, we will be considering two different cases
CASE 1:
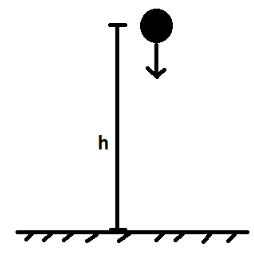
As we can see from the figure, the ball is dropped vertically downwards from a height $h$.Now, as the ball is dropped, the initial velocity $u$ of the ball will be zero. After being dropped, the ball will fall down to the ground under the effect of gravitational acceleration $g$. Therefore, using the second equation of motion, we get
\[h=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
\Rightarrow {{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{2h}{g} \\
\therefore t=\sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\\]
Therefore, the above equation shows the time taken by the ball to reach the ground.
CASE 2: Now, we will look upon an another diagram
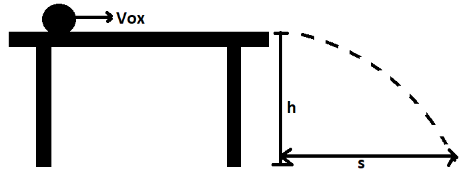
As it can be seen from the figure, it is a case of a horizontal projectile. The time of flight for such a case is also given by the equation which we derived above. Now, it is described that the ball moves with a horizontal velocity of ${{v}_{0x}}$ and is projected from the edge of the table having height $h$. Now, as we know that the horizontal velocity remains constant for such cases, we can find the horizontal distance covered by the projectile as
\[s={{v}_{0x}}\times t \\ \Rightarrow s={{v}_{0x}}\times \sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\ \Rightarrow {{s}^{2}}=v_{0x}^{2}\left( \dfrac{2h}{g} \right) \\ \therefore s={{v}_{0x}}\sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\ \]
Therefore, the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile is given by the above equation.
Note:It is very important to note that the motion in the first case is a one dimensional motion whereas, the motion in the second case is a motion in two dimensional. It is important to take both the components of velocity into consideration in the second part. We have only taken the horizontal component as it was only needed to solve our problem. Also the time period we calculated in the first case is equal to the time of flight in the second case because in both the cases, the vertical component of the initial velocity is zero.
Formula used:
First equation of motion: $v=u+at$
Second equation of motion: $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Third equation of motion: ${{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as$
Where $v$ is the final velocity, $u$is the initial velocity, $a$ is the acceleration and $t$ is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to find our answers, we will be considering two different cases
CASE 1:

As we can see from the figure, the ball is dropped vertically downwards from a height $h$.Now, as the ball is dropped, the initial velocity $u$ of the ball will be zero. After being dropped, the ball will fall down to the ground under the effect of gravitational acceleration $g$. Therefore, using the second equation of motion, we get
\[h=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
\Rightarrow {{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{2h}{g} \\
\therefore t=\sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\\]
Therefore, the above equation shows the time taken by the ball to reach the ground.
CASE 2: Now, we will look upon an another diagram

As it can be seen from the figure, it is a case of a horizontal projectile. The time of flight for such a case is also given by the equation which we derived above. Now, it is described that the ball moves with a horizontal velocity of ${{v}_{0x}}$ and is projected from the edge of the table having height $h$. Now, as we know that the horizontal velocity remains constant for such cases, we can find the horizontal distance covered by the projectile as
\[s={{v}_{0x}}\times t \\ \Rightarrow s={{v}_{0x}}\times \sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\ \Rightarrow {{s}^{2}}=v_{0x}^{2}\left( \dfrac{2h}{g} \right) \\ \therefore s={{v}_{0x}}\sqrt{\dfrac{2h}{g}} \\ \]
Therefore, the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile is given by the above equation.
Note:It is very important to note that the motion in the first case is a one dimensional motion whereas, the motion in the second case is a motion in two dimensional. It is important to take both the components of velocity into consideration in the second part. We have only taken the horizontal component as it was only needed to solve our problem. Also the time period we calculated in the first case is equal to the time of flight in the second case because in both the cases, the vertical component of the initial velocity is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




