
1) Explain the limitations of Octet rule.
2) How many electrons will be around \[I\](iodine) in the compound \[I{F_7}\].
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: Iodine heptafluoride (\[I{F_7}\] )is an interhalogen compound, a compound formed by one halogen reacting with another halogen. The halogen-halogen bond in interhalogen compounds is weaker than that of bonds in di-halogen molecules. By constructing the Lewis structure, we find the number of electrons will be around \[I\](iodine) in the compound \[I{F_7}\].
Complete answer:
1)
Limitations of Octet rule: 1. Hydrogen with one electron attains stability by sharing, gaining or losing one valence electron. It does not need to complete octet to attain stability. Also, \[He\] has only \[2\] electrons and is stable. 2. Incomplete octet: In certain molecules such as \[Be{H_2}\], \[BeC{l_2}\], \[B{H_3}\], \[B{F_3}\], the central atom has less than \[8\] electrons in its valence shell, yet the molecule is stable. 3. Expanded octet: In certain molecules such as \[P{F_5}\],\[S{F_6}\], \[I{F_7}\], \[{H_2}S{O_4}\], the central atom has more than \[8\] valence electrons, yet the molecule is stable.
Explanation:
One limitation of the octet rule is that it cannot be applied to the nonmetals after silicon in the periodic table.
These elements can “expand their octet” and have more than eight valence electrons around the central atom.
Examples are \[P{F_5}\],\[S{F_6}\], and \[{H_2}S{O_4}\].
The \[P\] atom in \[P{F_5}\] has \[10\] electrons in its valence shell:
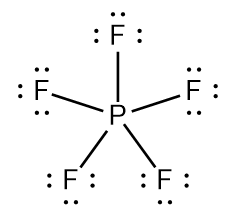
The \[S\] atom in \[S{F_6}\] has \[12\] electrons in its valence shell:
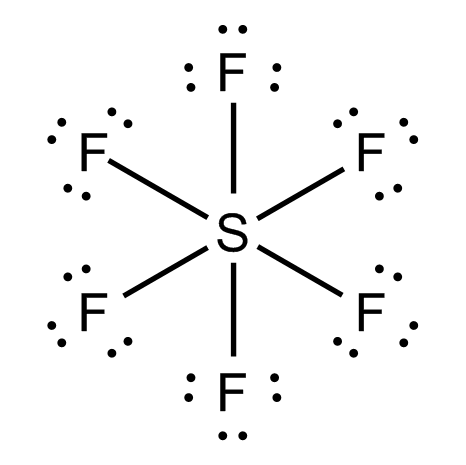
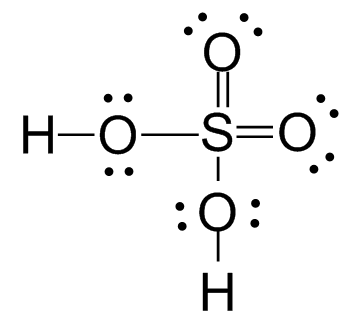
And so does the \[S\] atom in \[{H_2}S{O_4}\].
Molecules with an odd number of electrons such as \[NO\] and \[N{O_2}\] cannot satisfy the octet rule. One atom must have an odd number of electrons. The \[N\] atom in \[NO\] has only \[7\] electrons in its valence shell. In \[N{O_2}\], one of the \[O\] atoms has only \[7\] electrons in its valence shell.
In some molecules the central atom cannot possibly have eight valence electrons. For example, \[BeC{l_2}\] and \[BC{l_3}\] do not obey the octet rule. \[Be\] has only \[4\] electrons in its valence shell and \[B\] has only \[6\] electrons in its valence shell.
2)
The Lewis structure of \[I{F_7}\]:
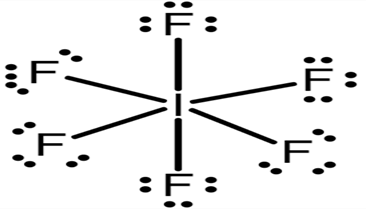
The \[I\](iodine) atom in the compound \[I{F_7}\] is surrounded by \[12\] electrons (six pairs of electrons) yet it is stable.
Note:
Note that in octet rule, atoms can combine either by transferring or by sharing their valence electrons to attain an octet of electrons in their valence shell. \[I{F_7}\] is a colourless gas. It is prepared by reaction iodine pentafluoride with fluorine gas. Halogens are extremely reactive in nature as they require only electrons in their valence shell to complete their octet.
Complete answer:
1)
Limitations of Octet rule: 1. Hydrogen with one electron attains stability by sharing, gaining or losing one valence electron. It does not need to complete octet to attain stability. Also, \[He\] has only \[2\] electrons and is stable. 2. Incomplete octet: In certain molecules such as \[Be{H_2}\], \[BeC{l_2}\], \[B{H_3}\], \[B{F_3}\], the central atom has less than \[8\] electrons in its valence shell, yet the molecule is stable. 3. Expanded octet: In certain molecules such as \[P{F_5}\],\[S{F_6}\], \[I{F_7}\], \[{H_2}S{O_4}\], the central atom has more than \[8\] valence electrons, yet the molecule is stable.
Explanation:
One limitation of the octet rule is that it cannot be applied to the nonmetals after silicon in the periodic table.
These elements can “expand their octet” and have more than eight valence electrons around the central atom.
Examples are \[P{F_5}\],\[S{F_6}\], and \[{H_2}S{O_4}\].
The \[P\] atom in \[P{F_5}\] has \[10\] electrons in its valence shell:

The \[S\] atom in \[S{F_6}\] has \[12\] electrons in its valence shell:

And so does the \[S\] atom in \[{H_2}S{O_4}\].

Molecules with an odd number of electrons such as \[NO\] and \[N{O_2}\] cannot satisfy the octet rule. One atom must have an odd number of electrons. The \[N\] atom in \[NO\] has only \[7\] electrons in its valence shell. In \[N{O_2}\], one of the \[O\] atoms has only \[7\] electrons in its valence shell.
In some molecules the central atom cannot possibly have eight valence electrons. For example, \[BeC{l_2}\] and \[BC{l_3}\] do not obey the octet rule. \[Be\] has only \[4\] electrons in its valence shell and \[B\] has only \[6\] electrons in its valence shell.
2)
The Lewis structure of \[I{F_7}\]:

The \[I\](iodine) atom in the compound \[I{F_7}\] is surrounded by \[12\] electrons (six pairs of electrons) yet it is stable.
Note:
Note that in octet rule, atoms can combine either by transferring or by sharing their valence electrons to attain an octet of electrons in their valence shell. \[I{F_7}\] is a colourless gas. It is prepared by reaction iodine pentafluoride with fluorine gas. Halogens are extremely reactive in nature as they require only electrons in their valence shell to complete their octet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




