
0.44g of a monohydric alcohol when added to methylmagnesium iodide in ether liberates 112 \[\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\] of methane at STP. With PCC, the same alcohol forms a carbonyl compound that undergoes a silver mirror test. The monohydric alcohol is:
(A) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$
(B) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH$
(C)
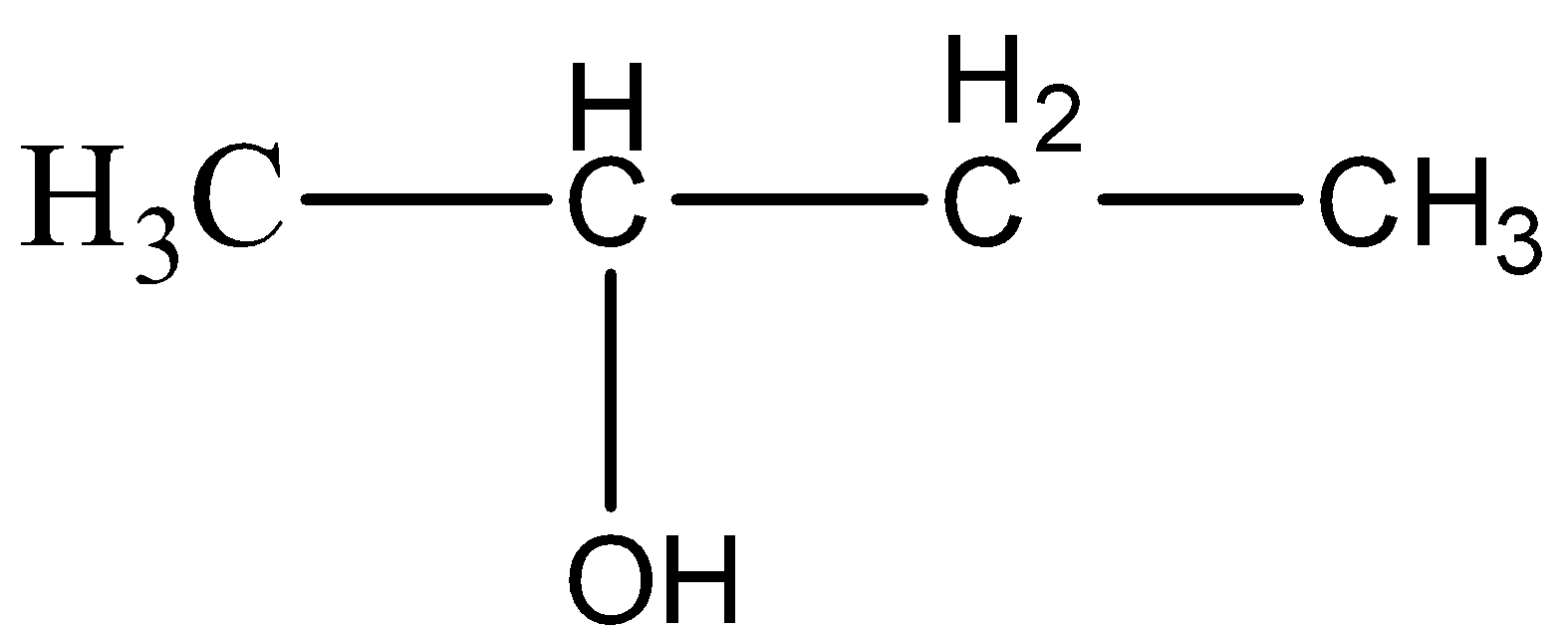
(D)
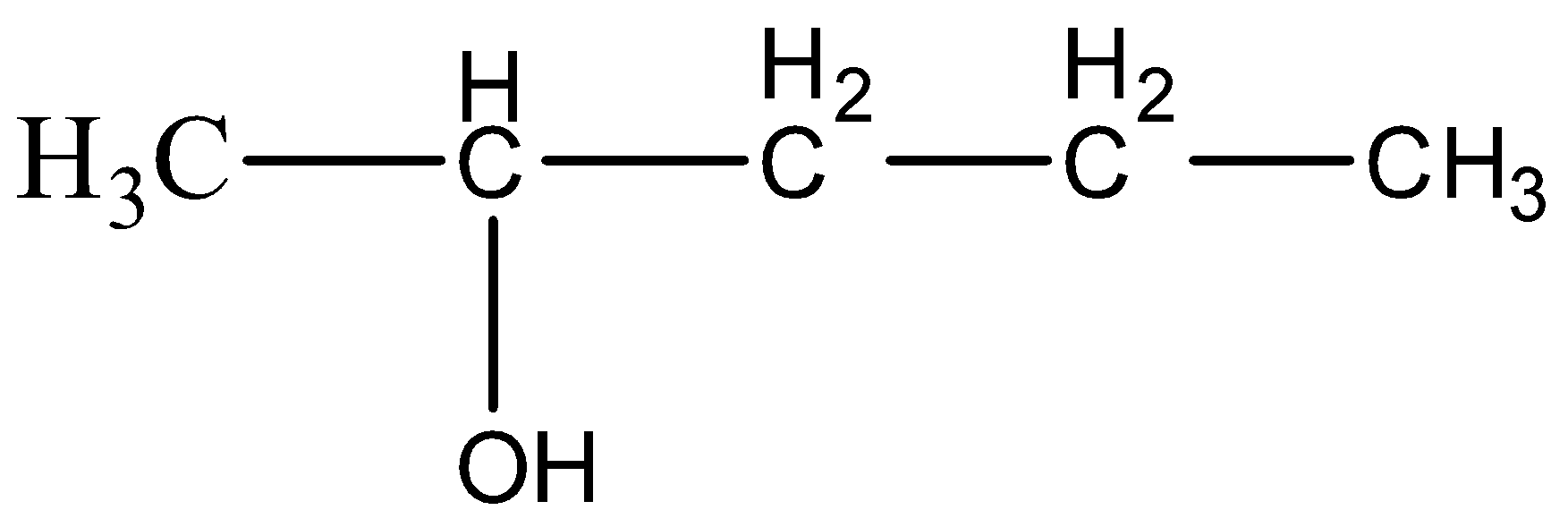


Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: PCC converts primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary aldehydes to ketones. Only aldehydes will give a positive silver mirror test. All alcohols will liberate methane when allowed to react with methyl magnesium iodide.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all we will see which of the given compounds will give a product that gives a positive silver mirror test.
- Now, we are given that the monohydric alcohol given to us gives a positive silver mirror test.
- Note that aldehydes give positive silver mirror tests. The reaction of aldehyde in a silver mirror test is shown below.
\[R-CHO+2{{[Ag{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}]}^{+}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2Ag+RCOOH+2{{H}^{+}}\]
- Here the complex of silver is formed by reaction of Ammonium hydroxide with sodium hydroxide and Silver nitrate. Thus, due to the formation of metallic silver, we get confirmation of a positive test.
- PCC stands for Pyridinium Chlorochromate. It is a reagent that specifically converts secondary alcohols to corresponding ketones and primary alcohols to corresponding aldehydes. Let’s see which products it will give when it will react with the given compounds.
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CCHO$
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHCHO$
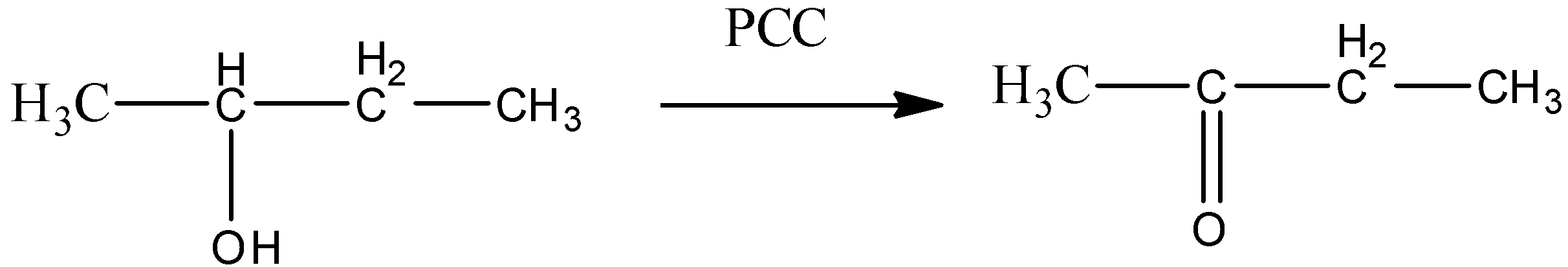
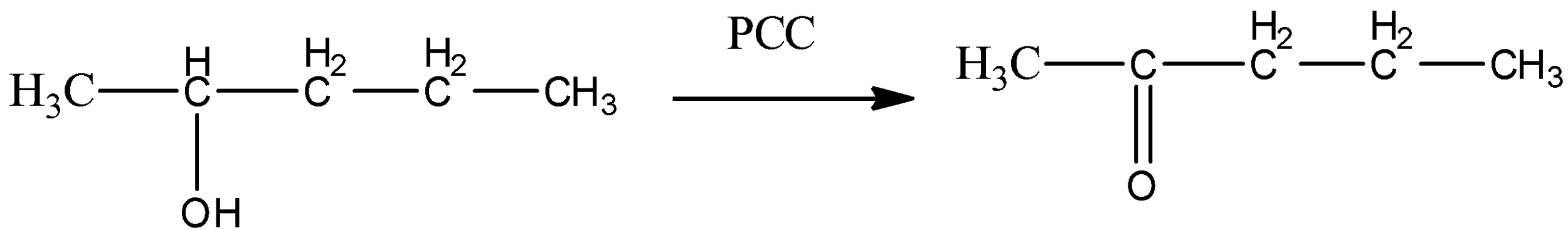
So, from the above discussion, we can say that alcohols given in option (A) and (B) will only give aldehyde as a final product. Ketones cannot give positive silver mirror tests. So, option (C) and (D) cannot be true.
Let’s calculate how much methane will the compounds given in option (A) and (B) will generate in order to get the correct answer.
${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}MgI\to {{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OMgI+C{{H}_{4}}$
Now, molecular weight of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ is 88$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$ and molecular weight of methane is 16$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$.
- As both compounds are one mole each in the reaction, we can say that 88gm of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ will generate 16 gm of methane. So, for 0.44gm of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$, we can write that it will generate $\dfrac{0.44\times 16}{88}$= 0.08 gm of methane.
Now, we will need to find the volume of 0.08gm of methane.
- We can write that one mole of every gas has a volume of 22.4L at STP.
Now, Moles of Methane$=\dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Molecular weight}}=\dfrac{0.08}{16}=0.005moles$
So, we can write that as one mole of gas has a volume of 22.4L, 0.005moles of a gas will have volume of 0.005$\times $ 22.4 = 0.112L
Now, we are given volume of the gas in $c{{m}^{3}}$ unit. So, we will have to convert it.
So, we know that $1000c{{m}^{3}}=1L$
So, 0.112L = 0.112$\times $1000 = 112$c{{m}^{3}}$
Thus, we can say that when ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ will react with Methyl magnesium iodide, it will give 112$c{{m}^{3}}$ of methane gas at STP.
Now, let’s see the case of ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH$ . It will react with Grignard reagent as follows.
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}MgI\to C{{H}_{4}}+{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OMgI$
We can say that here as molecular weight of the alcohol is 74$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$ , the amount of methane generated by 0.44gm of the alcohol will be $\dfrac{0.44\times 16}{74}$ = 0.095gm
As we convert into moles, we will get moles = $\dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Number of moles}}=\dfrac{0.095}{16}$ = 0.0059moles
So, its volume will be 0.0059 $\times $22.4 = 0.1321L (as every gas has a volume of 22.4L for concentration of one mole)
Now, we know that $1000c{{m}^{3}}=1L$
So ,0.1321L = 0.1321$\times $1000 = 132.21$c{{m}^{3}}$
Thus, we can say that this alcohol will generate 132.21$c{{m}^{3}}$ of methane gas when it will react with the Grignard reagent given in the question.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that here, you need not to calculate the methane gas produced by each of the alcohol because the other two alcohols get rejected by some other criteria given in the question. So, make sure that you keep that in mind.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all we will see which of the given compounds will give a product that gives a positive silver mirror test.
- Now, we are given that the monohydric alcohol given to us gives a positive silver mirror test.
- Note that aldehydes give positive silver mirror tests. The reaction of aldehyde in a silver mirror test is shown below.
\[R-CHO+2{{[Ag{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}]}^{+}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2Ag+RCOOH+2{{H}^{+}}\]
- Here the complex of silver is formed by reaction of Ammonium hydroxide with sodium hydroxide and Silver nitrate. Thus, due to the formation of metallic silver, we get confirmation of a positive test.
- PCC stands for Pyridinium Chlorochromate. It is a reagent that specifically converts secondary alcohols to corresponding ketones and primary alcohols to corresponding aldehydes. Let’s see which products it will give when it will react with the given compounds.
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CCHO$
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHCHO$


So, from the above discussion, we can say that alcohols given in option (A) and (B) will only give aldehyde as a final product. Ketones cannot give positive silver mirror tests. So, option (C) and (D) cannot be true.
Let’s calculate how much methane will the compounds given in option (A) and (B) will generate in order to get the correct answer.
${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}MgI\to {{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OMgI+C{{H}_{4}}$
Now, molecular weight of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ is 88$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$ and molecular weight of methane is 16$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$.
- As both compounds are one mole each in the reaction, we can say that 88gm of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ will generate 16 gm of methane. So, for 0.44gm of ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$, we can write that it will generate $\dfrac{0.44\times 16}{88}$= 0.08 gm of methane.
Now, we will need to find the volume of 0.08gm of methane.
- We can write that one mole of every gas has a volume of 22.4L at STP.
Now, Moles of Methane$=\dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Molecular weight}}=\dfrac{0.08}{16}=0.005moles$
So, we can write that as one mole of gas has a volume of 22.4L, 0.005moles of a gas will have volume of 0.005$\times $ 22.4 = 0.112L
Now, we are given volume of the gas in $c{{m}^{3}}$ unit. So, we will have to convert it.
So, we know that $1000c{{m}^{3}}=1L$
So, 0.112L = 0.112$\times $1000 = 112$c{{m}^{3}}$
Thus, we can say that when ${{(CH)}_{3}}CC{{H}_{2}}OH$ will react with Methyl magnesium iodide, it will give 112$c{{m}^{3}}$ of methane gas at STP.
Now, let’s see the case of ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH$ . It will react with Grignard reagent as follows.
${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}MgI\to C{{H}_{4}}+{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CHC{{H}_{2}}OMgI$
We can say that here as molecular weight of the alcohol is 74$gmmo{{l}^{-}}$ , the amount of methane generated by 0.44gm of the alcohol will be $\dfrac{0.44\times 16}{74}$ = 0.095gm
As we convert into moles, we will get moles = $\dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Number of moles}}=\dfrac{0.095}{16}$ = 0.0059moles
So, its volume will be 0.0059 $\times $22.4 = 0.1321L (as every gas has a volume of 22.4L for concentration of one mole)
Now, we know that $1000c{{m}^{3}}=1L$
So ,0.1321L = 0.1321$\times $1000 = 132.21$c{{m}^{3}}$
Thus, we can say that this alcohol will generate 132.21$c{{m}^{3}}$ of methane gas when it will react with the Grignard reagent given in the question.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that here, you need not to calculate the methane gas produced by each of the alcohol because the other two alcohols get rejected by some other criteria given in the question. So, make sure that you keep that in mind.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




