




Key Tips for Accurate Protractor Reading and Exam Success
Protractors are useful, clear plastic tools for everyday life; we all have seen the protractor in the geometry box. They can be used for measuring different types of angles. It is a device used to measure and plot angles from 0 to 180 degrees, clockwise and anticlockwise. It has a straight edge with one or more semicircles on the edges.
The protractor has a scale usually marked with degrees or radians (any angle in minutes). It can be used for measuring angles in a plane and three-dimensional space. The protractor scale can measure angles to find the area of a triangle, the volume of a cylinder, and so on. We will be looking at a protractor scale, a scale in maths, how to read a protractor and how to use a protractor with examples in this article.
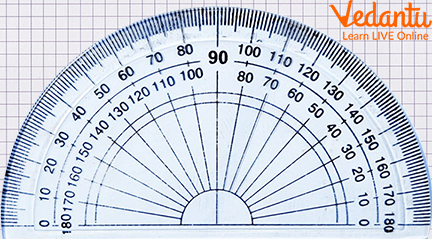
A Common Protractor
What Is a Protractor?
A protractor is a type of measuring tool that helps us find angles. It has two parts, a straightedge and a curved ruler. A line on the protractor represents the angle we are trying to find. Protractors are used in many different maths problems.
A general protractor consists of an inner and outer scale, graduated from 0 degrees to 180 degrees. It is a tool that helps us draw a line or shape using two different angles. It’s beneficial in teaching kids how to use angles and draw shapes. The tool is also helpful for artists, engineers, architects, and many more who need to measure angles. They use different kinds of protractors for accurate measurement of angles.
360-degree Protractor
A 360-degree protractor is a tool used to measure angles in a circle. It has a flat and circular surface and can be used for drawing circles. It is also used in geometry.
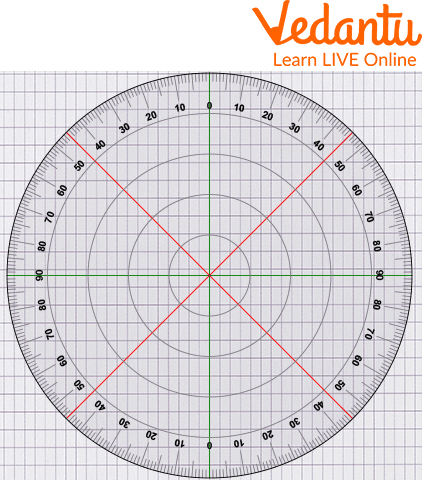
A 360-degree Protractor
What is Scale in Maths?
Scale in Mathematics is a range of levels or numbers used to measure numbers. Here, it is simply the angle marking from 0 degrees to 180 degrees in a general protractor.
How to Read and Use a Protractor
While measuring through a protractor, the measure is usually in degrees. If the angle is on the left side of the protractor, we use the outer edge measurement, and if the angle is on the right side of the protractor, we use the inner edge measurements.
The steps to measure and read the angle are as follows:
Step 1: Place the protractor's centre on the angle's vertex.
Step 2: Superimpose one side of the angle with the zero line of the protractor.
Step 3: The angle equals the number of degrees crossed on the protractor.
Let us look at an example to read and measure the angle of 60 degrees.
Step 1: Align the protractor with the ray OB as shown below. Start reading from the $0^{\circ}$ mark on the bottom-right of the protractor.
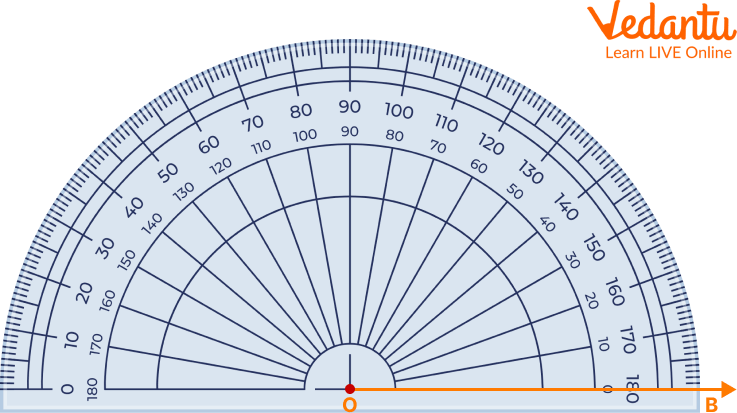
Reading the Protractor
Step 2: The angle measure is the number on the protractor that coincides with the second ray. Measure the angle using the number on the lower arc of the protractor.
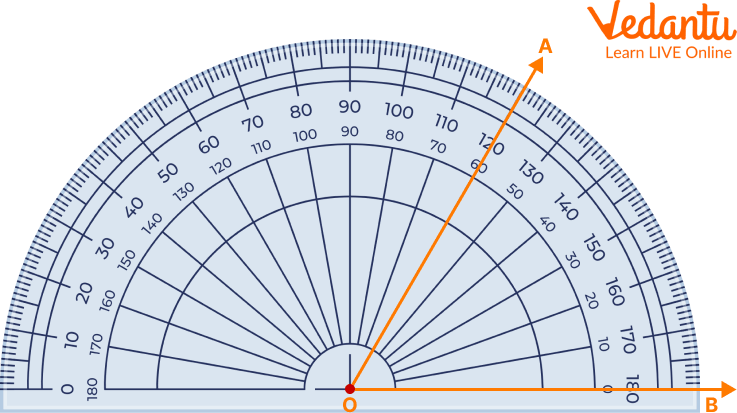
Protractor Showing an Angle 60 Degree
Therefore, $\angle A O B=60^{\circ}$. Since the measure is greater than $0^{\circ}$ and lesser than $90^{\circ}$, we can say that $\angle A O B$ is an acute angle.
This way, we can read and use the protractor to measure the angle.
Solved Example
Q1. Find the measure of the angle given in the picture below.
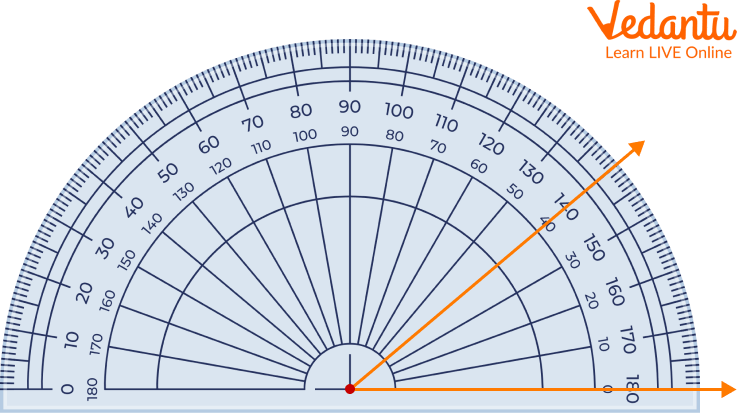
Solved Example
Ans: First, place the protractor's centre perfectly on the line.
Now, look at the inner scale of the right side.
Then, check the angle passing through the line.
We get 40 degrees as the answer.
Practice Questions
Identify the angle measures.
1. The measure of the angle is _____ degrees.
Ans:
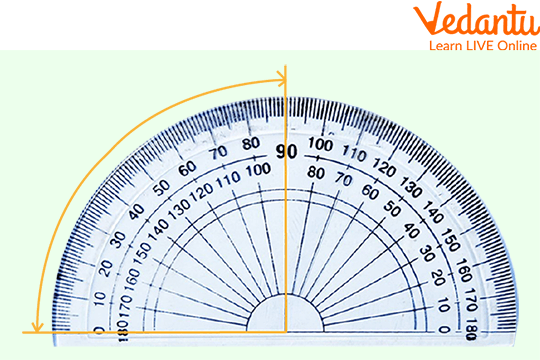
Practice Questions
Ans: 90 degrees
2. The measure of the angle is _____ degrees.
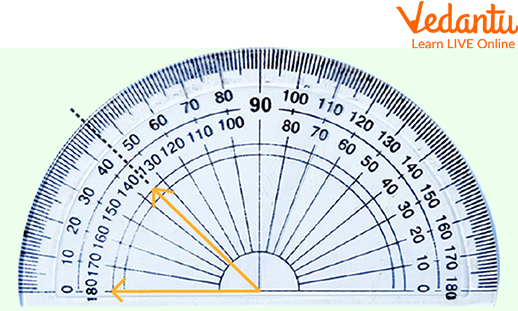
Practice Question
Ans: 135 degrees
Summary
A protractor is a measuring instrument for measuring angles, typically made of transparent plastic or glass. Some protractors are simple half-discs or full circles. More advanced protractors, such as the bevel protractor, have one or two swinging arms, which can be used to help measure the angle. A protractor is a great tool for measuring angles in various mathematical problems.
They are also excellent for use in geometry, measuring the slope of a line, and calculating different volumes and areas. There are two types of protractors: semi-circular (0 degrees to 180 degrees) and circular (0 degrees to 360 degrees). Engineers use these to create technical designs for different construction sites.
FAQs on How to Use a Protractor Scale: Step-by-Step Guide
1. What is a protractor scale?
A protractor scale is the set of degree markings on a protractor, which is a semicircular or circular tool used in geometry. These scales help users accurately measure or construct angles, usually marked from $0^{\circ}$ to $180^{\circ}$, or all around up to $360^{\circ}$.
2. How do you read a protractor scale?
To read a protractor scale, align the protractor's base line with one side of the angle and position its center at the angle's vertex. Then, read the degree measurement where the other angle side intersects the scale, using either the inner or outer set of numbers as needed.
3. What are the types of protractor scales?
The main types of protractor scales are:
- Semi-circular (0°–180°)
- Full circular (0°–360°)
- Double-row scales (inner and outer for different directions)
4. Why do some protractors have two scales?
Some protractors have both inner and outer degree scales to make measurement easier in both directions. This allows users to measure angles from either side of the vertex, improving flexibility and accuracy during geometric drawing or engineering work.
5. How accurate is a protractor scale?
A standard protractor scale typically measures angles to the nearest one degree. While this is sufficiently accurate for most classroom and drafting tasks, more precise measurements may require specialized instruments like a vernier protractor for higher accuracy.
6. What materials are used to make protractors and their scales?
Protractors and their scales are commonly made from:
- Plastic (transparent)
- Metal (aluminum or steel)
- Wood
7. How do you use a protractor scale to draw an angle?
To use a protractor scale to draw an angle, place the protractor's baseline along one line, mark the vertex, then count to the desired degree marking on the scale. Make a dot there, then use a ruler to connect the dot to the vertex to form the angle.
8. What is the smallest unit on a protractor scale?
On most standard protractors, the smallest unit on the scale is one degree ($1^{\circ}$). This means angles can be measured or drawn with an accuracy up to $1^{\circ}$, which is suitable for general mathematics and geometric drawing purposes.
9. Can a protractor scale measure obtuse and acute angles?
Yes, a protractor scale can measure both
- Acute angles (less than $90^{\circ}$)
- Obtuse angles (greater than $90^{\circ}$ and less than $180^{\circ}$)
10. What is the purpose of the center hole in a protractor’s scale?
The center hole in a protractor's scale marks the vertex point where two lines meet to form the angle. Placing this hole exactly on the angle's vertex ensures you measure the angle correctly using the scale markings.
11. Why are protractor scale numbers sometimes reversed?
Protractor scale numbers are sometimes reversed to allow measurement from either direction for convenience. The dual numbering helps users read angles on both the inner and outer arcs, whether measuring clockwise or counterclockwise from the base line.
12. How is a protractor scale used in mathematics?
Protractor scales are used in mathematics for measuring and drawing precise angles during geometric constructions, proofs, and problem-solving. They assist in identifying angle measures such as right angles ($90^{\circ}$), straight angles ($180^{\circ}$), and other specific degrees required for accurate geometry work.

















